Abstract
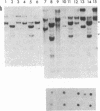
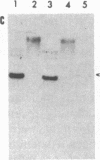
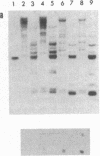
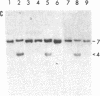
Mouse teratocarcinoma cells induced to differentiate in vitro undergo a massive (30%) demethylation of DNA. A similar undermethylation is also observed in the mouse extraembryonic membranes, the yolk sac and placenta. In both cases, the decrease in methyl moieties occurs at a large number of CpG sites spread out over the entire genome, as indicated by a restriction enzyme analysis of several mouse genes including dhfr, beta-major globin, and the H-2K gene family. In contrast to this, the embryo itself appears to undergo methylation de novo during early stages of embryogenesis. Thus, as opposed to somatic cells, events during early mouse development are associated with wide variations in the level of DNA methylation. Although these changes in DNA methylation seem to be an integral part of the differentiation process, its relation to specific gene expression is still unclear.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews G. K., Dziadek M., Tamaoki T. Expression and methylation of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene in embryonic, adult, and neoplastic tissues. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5148–5153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A., Taggart M., Macleod D. Loss of rDNA methylation accompanies the onset of ribosomal gene activity in early development of X. laevis. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Stein R., Gruenbaum Y., Naveh-Many T., Sciaky-Gallili N., Razin A. Effect of DNA methylation on gene expression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):605–609. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman V., Forrester L., Sanford J., Hastie N., Rossant J. Cell lineage-specific undermethylation of mouse repetitive DNA. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):284–286. doi: 10.1038/307284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Linnenbach A., Huebner K., Parnes J. R., Margulies D. H., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Control of expression of histocompatibility antigens (H-2) and beta 2-microglobulin in F9 teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5754–5758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Simonsen C. C., McEwan R. N., Schimke R. T. Structure of amplified normal and variant dihydrofolate reductase genes in mouse sarcoma S180 cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7887–7897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. Hypomethylation distinguishes genes of some human cancers from their normal counterparts. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):89–92. doi: 10.1038/301089a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Taggart R. T. Comparative gene mapping: order of loci on the X chromosome is different in mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3595–3599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. L. Investigation of cell lineage and differentiation in the extraembryonic endoderm of the mouse embryo. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1982 Apr;68:175–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautsch J. W., Wilson M. C. Delayed de novo methylation in teratocarcinoma suggests additional tissue-specific mechanisms for controlling gene expression. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):32–37. doi: 10.1038/301032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Eisenman R., Weintraub H. Chromatin structure of endogenous retroviral genes and activation by an inhibitor of DNA methylation. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):311–317. doi: 10.1038/292311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenbaum Y., Stein R., Cedar H., Razin A. Methylation of CpG sequences in eukaryotic DNA. FEBS Lett. 1981 Feb 9;124(1):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigh L. S., Owens B. B., Hellewell O. S., Ingram V. M. DNA methylation in chicken alpha-globin gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5332–5336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Harbers B., Spencer J. H. Nucleotide clusters in deoxyribonucleic acids. XII. The distribution of 5-methylcytosine in pyrimidine oligonucleotides of mouse L-cell satellite DNA and main band DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):738–746. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90572-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R., Pugh J. E. DNA modification mechanisms and gene activity during development. Science. 1975 Jan 24;187(4173):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Steinmetz M., Goodenow R. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):685–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakob H., Dubois P., Eisen H., Jacob F. Effets de l'hexaméthylènebisacétamide sur la différenciation de cellules de carcinome embryonnaire. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1978 Jan;286(1):109–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho R., Weissman I. L., Early P., Cole J., Hood L. Organization of kappa light chain genes in germ-line and somatic tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. E., DeFeo D., Piatigorsky J. Transcription and site-specific hypomethylation of the delta-crystallin genes in the embryonic chicken lens. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8172–8176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähner D., Stuhlmann H., Stewart C. L., Harbers K., Löhler J., Simon I., Jaenisch R. De novo methylation and expression of retroviral genomes during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):623–628. doi: 10.1038/298623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Pan S., Solter D., Linnenbach A., Croce C., Huebner K. Expression of H-2, laminin and SV40 T and TASA on differentiation of transformed murine teratocarcinoma cells. Nature. 1980 Dec 11;288(5791):615–618. doi: 10.1038/288615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman J. M., Speers W. C., Swartzendruber D. E., Pierce G. B. Neoplastic differentiation: characteristics of cell lines derived from a murine teratocarcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Aug;84(1):13–27. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040840103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R. Effects of vitamin A and its analogs (retinoids) on normal and neoplastic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 12;605(1):33–91. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Chambon P. DNA methylation: organ specific variations in the methylation pattern within and around ovalbumin and other chicken genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2081–2103. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manes C., Menzel P. Demethylation of CpG sites in DNA of early rabbit trophoblast. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):589–590. doi: 10.1038/293589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor A. L., Golden L., Weiss E., Bullman H., Hurst J., Simpson E., James R. F., Townsend A. R., Taylor P. M., Schmidt W. Expression of murine H-2Kb histocompatibility antigen in cells transformed with cloned H-2 genes. Nature. 1982 Aug 5;298(5874):529–534. doi: 10.1038/298529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Shapiro L. J. Reactivation of an inactive human X chromosome: evidence for X inactivation by DNA methylation. Science. 1981 Jan 23;211(4480):393–396. doi: 10.1126/science.6164095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morello D., Daniel F., Baldacci P., Cayre Y., Gachelin G., Kourilsky P. Absence of significant H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin mRNA expression by mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):260–262. doi: 10.1038/296260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Schimke R. T. Structure and genomic organization of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L. Differential regulation of metallothionein-thymidine kinase fusion genes in transgenic mice and their offspring. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):701–710. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Riggs A. D. DNA methylation and gene function. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):604–610. doi: 10.1126/science.6254144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Jones P. A. 5-methylcytosine, gene regulation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1983;40:1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60678-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D. X inactivation, differentiation, and DNA methylation. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;14(1):9–25. doi: 10.1159/000130315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Sager R. Tissue specificity and clustering of methylated cystosines in bovine satellite I DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3584–3588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solage A., Cedar H. Organization of 5-methylcytosine in chromosomal DNA. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2934–2938. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Razin A., Cedar H. In vitro methylation of the hamster adenine phosphoribosyltransferase gene inhibits its expression in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3418–3422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Sciaky-Gallili N., Razin A., Cedar H. Pattern of methylation of two genes coding for housekeeping functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2422–2426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. L., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. De novo methylation, expression, and infectivity of retroviral genomes introduced into embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4098–4102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S. Mouse teratocarcinoma cells: prospects for the study of embryogenesis and neoplasia. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):277–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90313-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm K. S., Taylor J. H. Distribution of 5-methylcytosine in the DNA of somatic and germline cells from bovine tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4537–4546. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Appella E., Jay G. Developmental activation of the H-2K gene is correlated with an increase in DNA methylation. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):457–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Tiemeier D. C., Seidman J. G., Peterlin B. M., Sullivan M., Maizel J. V., Leder P. Intervening sequence of DNA identified in the structural portion of a mouse beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):725–729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation at a CCGG sequence in the large intron of the rabbit beta-globin gene: tissue-specific variations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4631–4634. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.12.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. L., Jones P. A. Inhibition of DNA methylation by chemical carcinogens in vitro. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90514-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ploeg L. H., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation in the human gamma delta beta-globin locus in erythroid and nonerythroid tissues. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):947–958. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]