Abstract
A chemically synthesized gene for human interferon-gamma has been cloned into a prokaryotic expression vector under the regulation of a synthetic constitutive transcriptional-translational control unit that contains a strong bacteriophage T5 early promoter and a strong ribosome-binding site. Cells harboring the recombinant plasmid express high levels (4 X 10(9) units per liter of culture) of antiviral activity specific for interferon-gamma. Analysis of total cell lysates on NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels revealed a 17,200-dalton protein, expected for the nonglycosylated form of human interferon-gamma, that constitutes greater than 15% of total cell protein.
Full text
PDF

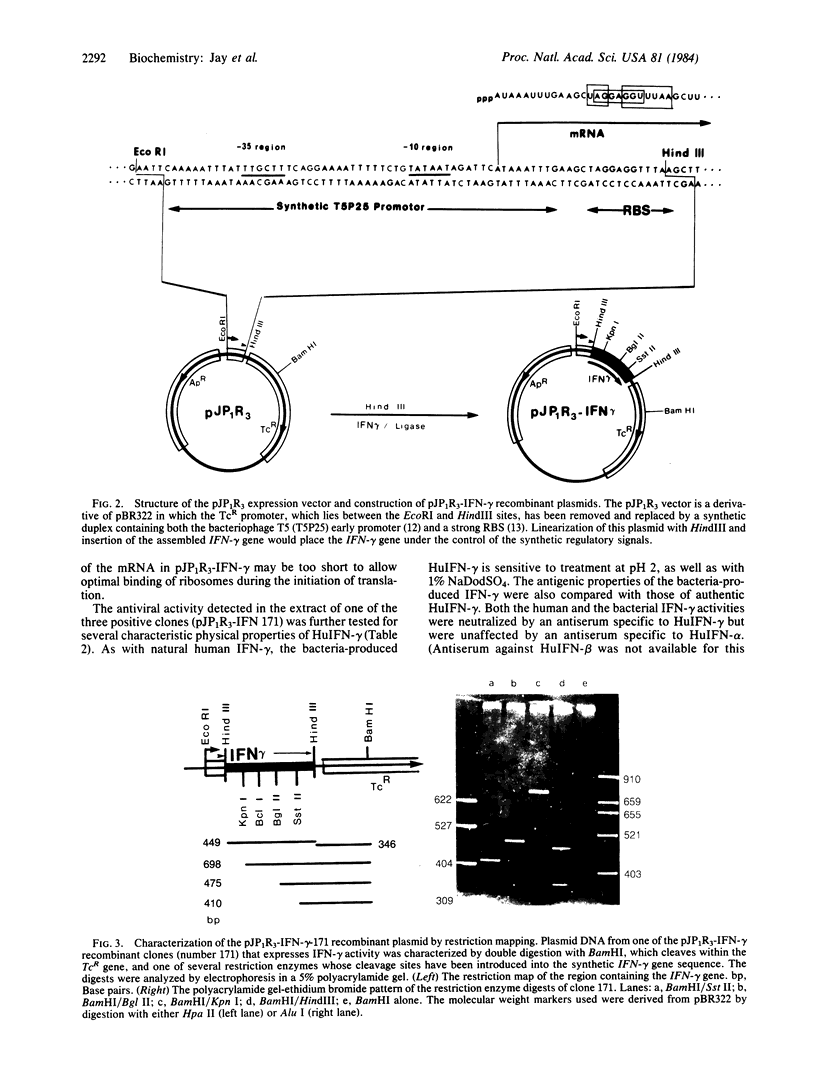


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaconas G., van de Sande J. H. 5'-32P labeling of RNA and DNA restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer E., Skup D., Prasad K. S., De Maeyer-Guignard J., Williams B., Meacock P., Sharpe G., Pioli D., Hennam J., Schuch W. Expression of a chemically synthesized human alpha 1 interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4256–4259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Cheroutre H., Taya Y., Degrave W., Van Heuverswyn H., Fiers W. Molecular cloning of human immune interferon cDNA and its expression in eukaryotic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2487–2501. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Langner A., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Bujard H. Cloning and analysis of strong promoters is made possible by the downstream placement of a RNA termination signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4936–4940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Shepard H. M., Yelverton E., Leung D., Crea R., Sloma A., Pestka S. Synthesis of human fibroblast interferon by E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4057–4074. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Yelverton E., Ullrich A., Heyneker H. L., Miozzari G., Holmes W., Seeburg P. H., Dull T., May L., Stebbing N. Human leukocyte interferon produced by E. coli is biologically active. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):411–416. doi: 10.1038/287411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Pennica D., Yelverton E., Najarian R., Simonsen C. C., Derynck R., Sherwood P. J., Wallace D. M., Berger S. L. Expression of human immune interferon cDNA in E. coli and monkey cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):503–508. doi: 10.1038/295503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lauer G., Roberts T. M., Ptashne M. Improved methods for maximizing expression of a cloned gene: a bacterium that synthesizes rabbit beta-globin. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90640-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzeman R. A., Hagie F. E., Levine H. L., Goeddel D. V., Ammerer G., Hall B. D. Expression of a human gene for interferon in yeast. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):717–722. doi: 10.1038/293717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay E., Seth A. K., Rommens J., Sood A., Jay G. Gene expression: chemical synthesis of E. coli ribosome binding sites and their use in directing the expression of mammalian proteins in bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6319–6329. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Khoury G., Seth A. K., Jay E. Construction of a general vector for efficient expression of mammalian proteins in bacteria: use of a synthetic ribosome binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5543–5548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommens J., MacKnight D., Pomeroy-Cloney L., Jay E. Gene expression: chemical synthesis and molecular cloning of a bacteriophage T5 (T5P25) early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5921–5940. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simatake H., Rosenberg M. Purified lambda regulatory protein cII positively activates promoters for lysogenic development. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):128–132. doi: 10.1038/292128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Oshima T., Ohsuye K., Ono T., Mizono A., Ueno A., Nakazato H., Tsujimoto M., Higashi N., Noguchi T. Expression in Escherichia coli of chemically synthesized gene for the human immune interferon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1707–1723. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Guarente L., Roberts T. M., Kimelman D., Douhan J., 3rd, Ptashne M. Expression of the human fibroblast interferon gene in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5230–5233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelverton E., Leung D., Weck P., Gray P. W., Goeddel D. V. Bacterial synthesis of a novel human leukocyte interferon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):731–741. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Bujard H. Interaction of E. coli RNA polymerase with promotors of coliphage T5: the rates of complex formation and decay and their correlation with in vitro and in vivo transcriptional activity. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Dec 9;157(3):301–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00268667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gabain A., Bujard H. Interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with promoters of several coliphage and plasmid DNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):189–193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]