Abstract
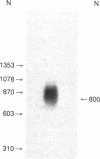
Molecular cloning of a cDNA has established the sequence of the translated portion of the mRNA for rat spleen thymosin beta 4. The presence of a methionyl initiator codon immediately preceding the codon for the first seryl residue of mature thymosin beta 4 is consistent with previous results indicating the absence of a signal peptide in the product translated in vitro from rat spleen mRNA. The cDNA sequence analysis also established the presence of two terminator codons immediately following the codon for the COOH-terminal seryl residue. Thymosin beta 4 is thus synthesized as a 5100-dalton peptide containing 44 amino acid residues. Removal of the initiator methionyl residue and acetylation of the NH2-terminal serine residue would yield mature thymosin beta 4 containing 43 amino acids. The absence of a signal peptide makes it unlikely that thymosin beta 4 is a secreted peptide.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson-Viitanen S., Ruggieri S., Natalini P., Horecker B. L. Distribution of thymosin beta 4 in vertebrate classes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):570–576. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90177-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson-Viitanen S., Ruggieri S., Natalini P., Horecker B. L. Thymosin beta 10, a new analog of thymosin beta 4 in mammalian tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Sep;225(2):407–413. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipowicz A. W., Horecker B. L. In vitro synthesis of thymosin beta 4 encoded by rat spleen mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1811–1815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedamu L., Dixon G. H. Assay of protamine messenger RNA from rainbow trout testis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1446–1454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedamu L., Dixon G. H. Purification and properties of biologically active rainbow trout testis protamine mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1455–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Hempstead J. L., Morgan J. I. Production and characterization of antibodies to thymosin beta 4. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):821–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
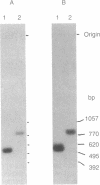
- Goodall G. J., Morgan J. I., Horecker B. L. Thymosin beta 4 in cultured mammalian cell lines. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):598–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90182-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Monahan J. J., Lomedico P. T., Bhatt R. S., Collier K. J., Hoffman B. J., Böhlen P., Esch F., Ling N., Zeytin F. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for the precursor of human growth hormone-releasing factor, somatocrinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4311–4314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannappel E., Xu G. J., Morgan J., Hempstead J., Horecker B. L. Thymosin beta 4: a ubiquitous peptide in rat and mouse tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2172–2175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low T. L., Hu S. K., Goldstein A. L. Complete amino acid sequence of bovine thymosin beta 4: a thymic hormone that induces terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase activity in thymocyte populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1162–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. J., Hannappel E., Morgan J., Hempstead J., Horecker B. L. Synthesis of thymosin beta 4 by peritoneal macrophages and adherent spleen cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4006–4009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]