Abstract
Immunoneutralization studies with a monoclonal antibody to somatomedin C (Sm-C) were undertaken to further determine the role of this peptide in cellular proliferation. For our model we used density-arrested cultures of BALB/c 3T3 cells. Transient exposure of these cells to platelet-derived growth factor enables them to respond to platelet-poor plasma by progressing through the G1 stage and undergoing renewed DNA synthesis. In this system, the combination of nanogram concentrations of Sm-C and epidermal growth factor can fully substitute for plasma, and microgram concentrations of insulin can substitute for Sm-C by crossreacting with the Sm-C receptor. We now show that a monoclonal antibody to Sm-C, which in defined medium blocks the mitogenic effect of Sm-C but not insulin, also blocks the stimulation of DNA synthesis by human plasma or calf serum. Furthermore, by adding the antibody at progressively later times during G1, we show that these cells escape from their dependence on Sm-C for DNA synthesis after traversing G1 to a point at or near the G1/S boundary.
Full text
PDF
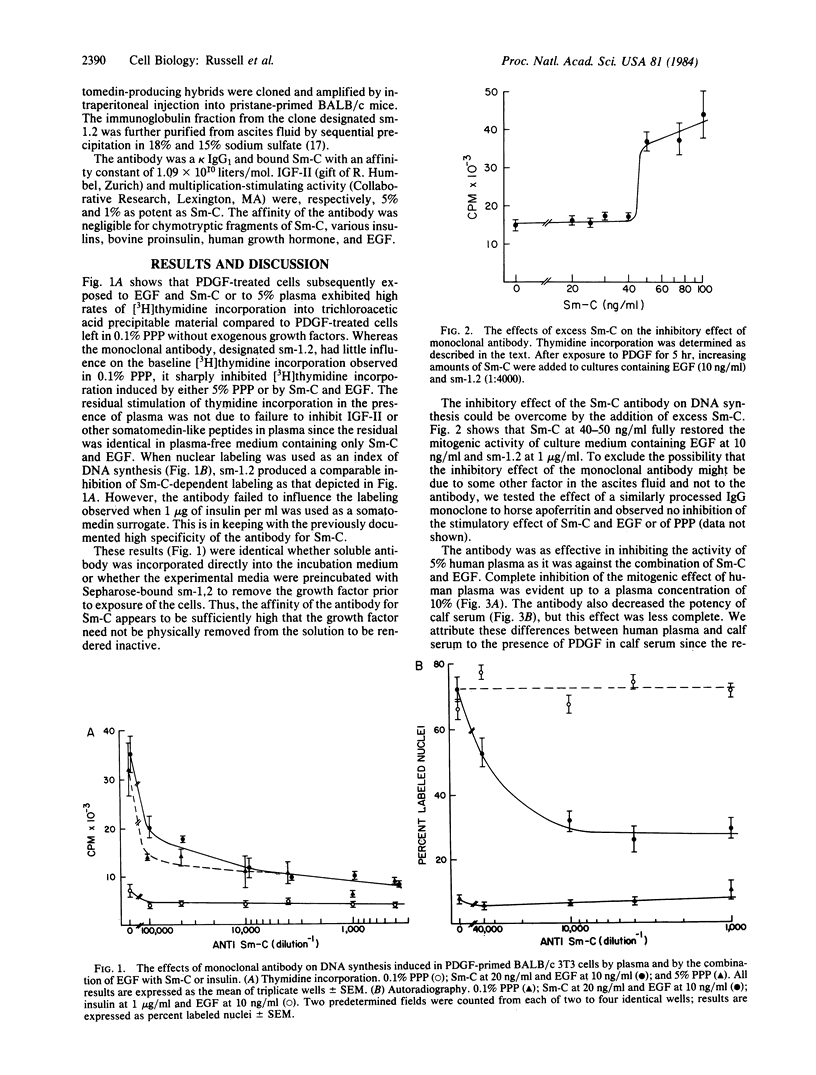
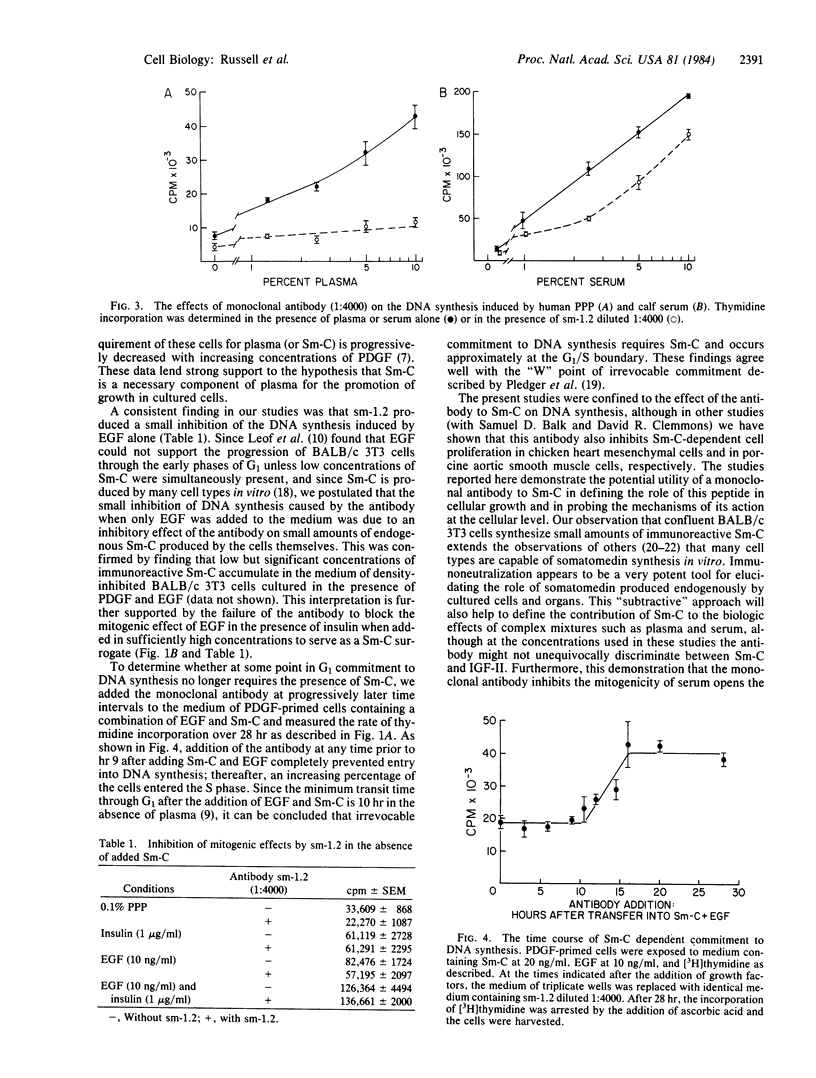

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. O., Nissley S. P., Handwerger S., Rechler M. M. Developmental patterns of insulin-like growth factor-I and -II synthesis and regulation in rat fibroblasts. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):150–153. doi: 10.1038/302150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D., Stiles C. D. Purification of human platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1809–1813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N., Stathakos D., Scher C. D. Isolation of a cationic polypeptide from human serum that stimulates proliferation of 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2635–2639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J. Hormonal control of immunoreactive somatomedin production by cultured human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):10–19. doi: 10.1172/JCI110001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Applewhite G. T., Underwood L. E. Evidence that somatomedin is synthesized by multiple tissues in the fetus. Dev Biol. 1980 Mar 15;75(2):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Hall K., Raben M. S., Salmon W. D., Jr, van den Brande J. L., van Wyk J. J. Somatomedin: proposed designation for sulphation factor. Nature. 1972 Jan 14;235(5333):107–107. doi: 10.1038/235107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Wasteson A. Platelet-derived growth factor: purification and partial characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3722–3726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekwick R. A. The serum proteins in multiple myelomatosis. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1248–1257. doi: 10.1042/bj0341248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Sequence analysis of somatomedin-C: confirmation of identity with insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2215–2217. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Van Wyk J. J., O'Keefe E. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is required only during the traverse of early G1 in PDGF stimulated density-arrested BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Aug;147(1):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Wharton W., van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and somatomedin C regulate G1 progression in competent BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Sep;141(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe E. J., Pledger W. J. A model of cell cycle control: sequential events regulated by growth factors. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1983 Aug;31(2-3):167–186. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(83)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. An ordered sequence of events is required before BALB/c-3T3 cells become committed to DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. Induction of DNA synthesis in BALB/c 3T3 cells by serum components: reevaluation of the commitment process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4481–4485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates growth in hypophysectomized rats. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):252–253. doi: 10.1038/296252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles C. D., Capone G. T., Scher C. D., Antoniades H. N., Van Wyk J. J., Pledger W. J. Dual control of cell growth by somatomedins and platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1279–1283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Klapper D. G., Fellows R. E., Grissom F. E., Schlueter R. J. Purification of somatomedin-C from human plasma: chemical and biological properties, partial sequence analysis, and relationship to other somatomedins. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):790–797. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Brande J. L., van Buul-Offers S. Effect of growth hormone and peptide fractions containing somatomedin activity on growth and cartilage metabolism of Snell dwarfmice. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1979 Oct;92(2):242–257. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0920242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wyk J. J., Underwood L. E., Baseman J. B., Hintz R. L., Clemmons D. R., Marshall R. N. Explorations of the insulinlike and growth-promoting properties of somatomedin by membrane receptor assays. Adv Metab Disord. 1975;8:127–150. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-027308-9.50015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


