Abstract
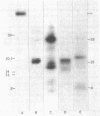
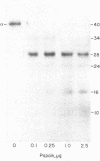
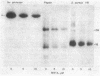
Proteolytic fragments of the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor retain the ability to bind alpha-bungarotoxin following resolution by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immobilization on protein transfers. The alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor of Torpedo electric organ was digested with four proteases: Staphylococcus aureus V-8 protease, papain, bromelain, and proteinase K. The proteolytic fragments resolved on 15% polyacrylamide gels were electrophoretically transferred onto positively charged nylon membrane filters. When incubated with 0.3 nM 125I-labeled alpha-bungarotoxin and autoradiographed, the transfers yielded patterns of labeled bands characteristic for each protease. The molecular masses of the fragments binding toxin ranged from 7 to 34 kDa, with major groupings in the 8-, 18-, and 28-kDa ranges. The apparent affinity of the fragments for alpha-bungarotoxin as determined from the IC50 value was 6.7 X 10(-8) M. The labeling of fragments with alpha-bungarotoxin could be inhibited by prior affinity alkylation of receptor-containing membranes with 4-(N-maleimido)-alpha-benzyltrimethylammonium iodide. These findings demonstrate that immobilized proteolytic fragments as small as 1/5 the size of the alpha subunit retain the structural characteristics necessary for binding alpha-bungarotoxin, although the toxin is bound to the fragments with lower affinity than to the native receptor. The effect of affinity ligand alkylation demonstrates that the alpha-bungarotoxin binding site detected on the proteolytic fragments is the same as the affinity-labeled acetylcholine binding site on the intact acetylcholine receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G., Tzartos S., Gullick W., Lindstrom J. Transmembrane orientation of an early biosynthetic form of acetylcholine receptor delta subunit determined by proteolytic dissection in conjunction with monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci. 1983 Sep;3(9):1773–1784. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-09-01773.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio T., Ballivet M., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor gamma subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor: correlation of molecular structure with functional properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:491–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delepelaire P., Chua N. H. Lithium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of thylakoid membranes at 4 degrees C: Characterizations of two additional chlorophyll a-protein complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):111–115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillers-Thiery A., Giraudat J., Bentaboulet M., Changeux J. P. Complete mRNA coding sequence of the acetylcholine binding alpha-subunit of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor: a model for the transmembrane organization of the polypeptide chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2067–2071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn S. M., Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. Separate sites of low and high affinity for agonists on Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2512–2518. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Rafto S. Comparison of the subunits of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor by peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 23;18(2):301–307. doi: 10.1021/bi00569a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Hawrot E., Lentz T. L. Binding of alpha-bungarotoxin to isolated alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor of Torpedo californica: quantitative analysis with protein blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4973–4977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to a positively charged membrane filter. Anal Biochem. 1982 Aug;124(2):396–405. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Lindstrom J. M. Comparison of the subunit structure of acetylcholine receptors from muscle and electric organ of Electrophorus electricus. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3801–3807. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. Monoclonal antibodies as probes of acetylcholine receptor structure. 1. Peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2173–2180. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty J. G., Froehner S. C. Restoration of 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin binding activity to the alpha subunit of Torpedo acetylcholine receptor isolated by gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8294–8297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R. C., Dahmus M. E. Rapid visualization of protein bands in preparative SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:582–590. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Weill C. L., McNamee M. G., Valderrama R. Facets of the structures of acetylcholine receptors from Electrophorus and Torpedo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:203–210. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y. Chemistry and pharmacology of polypeptide toxins in snake venoms. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1972;12:265–286. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.12.040172.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Merlie J., Yogeeswaran G. Biochemical properties of acteylcholine receptor subunits from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4465–4470. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson N. M., Hall Z. W. Subunit structure and peptide mapping of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors from rat muscle. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3392–3401. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Furutani Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Miyata T., Numa S. Primary structure of alpha-subunit precursor of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):793–797. doi: 10.1038/299793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oblas B., Boyd N. D., Singer R. H. Analysis of receptor-ligand interactions using nitrocellulose gel transfer: application to Torpedo acetylcholine receptor and alpha-bungarotoxin. Anal Biochem. 1983 Apr 1;130(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90641-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L. E. Acetylcholine receptor: complex of homologous subunits. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7384786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Karlin A. Molecular weight in detergent solution of acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2035–2038. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumikawa K., Houghton M., Smith J. C., Bell L., Richards B. M., Barnard E. A. The molecular cloning and characterisation of cDNA coding for the alpha subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5809–5822. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Changeux J. P. High affinity binding of alpha-bungarotoxin to the purified alpha-subunit and to its 27,000-dalton proteolytic peptide from Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor. Requirement for sodium dodecyl sulfate. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):381–387. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosin J. M., Lyddiatt A., Dolly J. O., Barnard E. A. Stoichiometry of the ligand-binding sites in the acetylcholine-receptor oligomer from muscle and from electric organ. Measurement by affinity alkylation with bromoacetylcholine. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):495–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04821.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]