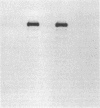
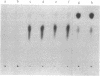
Abstract
An ADP-ribosyltransferase was found in elongation factor 2 (EF-2) preparations from polyoma virus-transformed baby hamster kidney (pyBHK) cells. Like fragment A of diphtheria toxin and Pseudomonas toxin A, this eukaryotic cellular enzyme transfers [14C]adenosine from NAD+ to EF-2. However, the cellular transferase is immunologically distinct from fragment A. The transferase also can be distinguished from fragment A and Pseudomonas toxin A by the inhibition of the activity of the former by cytoplasmic extracts and by histamine. Snake venom phosphodiesterase digestion of the [14C]adenosine-labeled EF-2 product of the cellular transferase reaction yielded [14C]AMP, indicating that the cellular enzyme is a mono(ADP-ribosyl)transferase. The forward ADP-ribosylation reaction catalyzed by the cellular enzyme is reversed by fragment A, yielding [14C]NAD+. The results strongly suggest that the cellular transferase is a mono(ADP-ribosyl)transferase, which ADP-ribosylates the same diphthamide residue of EF-2 as does fragment A and Pseudomonas toxin A.
Full text
PDF
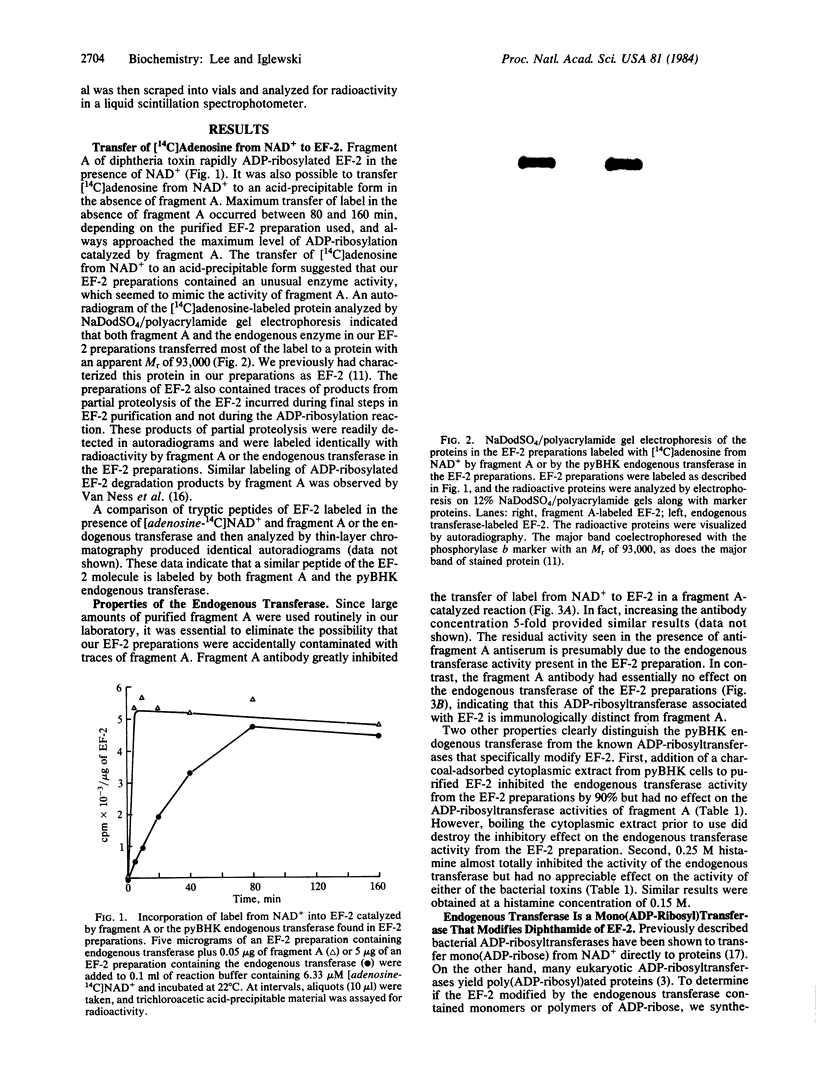
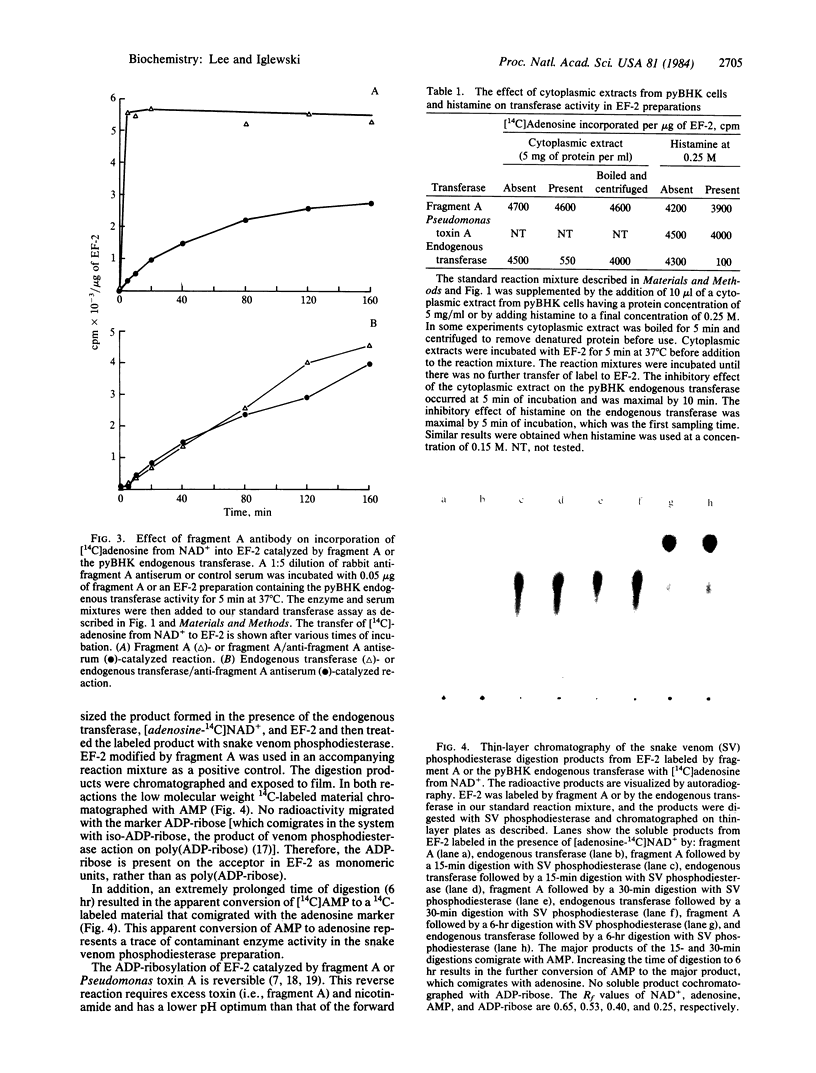

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamietz P., Wielckens K., Bredehorst R., Lengyel H., Hilz H. Subcellular distribution of mono(ADP-ribose) protein conjugates in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jul 16;101(1):96–103. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredehorst R., Wielckens K., Adamietz P., Steinhagen-Thiessen E., Hilz H. Mono(ADP-ribosyl)ation and poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of proteins in developing liver and in hepatomas: relation of conjugate subfractions to metabolic competence and proliferation rates. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):267–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredehorst R., Wielckens K., Gartemann A., Lengyel H., Klapproth K., Hilz H. Two different types of bonds linking single ADP-ribose residues covalently to proteins. Quantification in eukaryotic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec 1;92(1):129–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Bodley J. W. Primary structure at the site in beef and wheat elongation factor 2 of ADP-ribosylation by diphtheria toxin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jul 15;103(2):253–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Dinius L. L. The elongation factor 2 content of mammalian cells. Assay method and relation to ribosome number. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):654–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayaishi O., Ueda K. Poly(ADP-ribose) and ADP-ribosylation of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:95–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Hayaishi O. Diphtheria toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3553–3555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Kato I., Hayaishi O. Adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis by diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4251–4260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Liu P. V., Kabat D. Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin Aiadenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of mammalian elongation factor 2 in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.138-144.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J., Bjorn M. J., Maxwell E. S. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S: an adenosine diphosphate ribosyltransferase distinct from toxin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3211–3215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski W. J., Lee H. Purification and properties of an altered form of elongation factor 2 from mutant cells resistant to intoxication by diphtheria toxin. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 1;134(2):237–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Isolation of an avian erythrocyte protein possessing ADP-ribosyltransferase activity and capable of activating adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3621–3624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer N. J., Bodley J. W. Diphtheria toxin. Site and configuration of ADP-ribosylation of diphthamide in elongation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8579–8581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Gill D. M. Diphtheria. Science. 1973 Oct 26;182(4110):353–358. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4110.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Uchida T., Harper A. A. An immunological study of the diphtheria toxin molecule. Immunochemistry. 1972 Sep;9(9):891–906. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. H., Stard P., Giri C. P., Smulson M. Cytoplasmic poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase during the HeLa cell cycle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Nov;171(1):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Barrowclough B., Bodley J. W. Recognition of elongation factor 2 by diphtheria toxin is not solely defined by the presence of diphthamide. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 20;120(1):4–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Howard J. B., Bodley J. W. ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 by diphtheria toxin. NMR spectra and proposed structures of ribosyl-diphthamide and its hydrolysis products. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10710–10716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]