Abstract
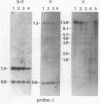
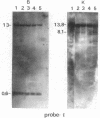
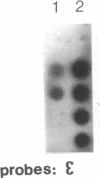
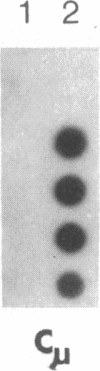
We have mapped the DNase I-hypersensitive sites around the epsilon-globin and c-myc genes in two human leukemia cell lines K562 and HL60. In K562 cells in which the epsilon-globin gene is transcribed, six DNase I-hypersensitive sites are found in 6 kilobases (kb) of upstream flanking DNA; in HL60 cells in which the c-myc gene is expressed, two DNase I-hypersensitive sites are observed in 2 kb of upstream DNA. Neither the inactive epsilon-globin gene in HL60 cells nor the inactive c-myc gene in K562 cells displays such upstream DNase I-hypersensitive sites. Our results are consistent with previous studies that have shown DNase I-hypersensitive sites within 1 kb of the 5' end of other expressed genes. In addition, we have found sites displaying even more DNase I sensitivity further upstream of expressed epsilon-globin and c-myc genes. Among the six DNase I-hypersensitive sites of the expressed epsilon-globin gene in K562 cells, the most sensitive site is located about 6 kb upstream of the epsilon-globin gene. When correlated with the DNA sequence upstream of the epsilon-globin gene, this site was found to correspond to a region that contains a stretch of 28 consecutive Ts, three enhancer core-like sequences, and a stretch of consecutive (C-A)15(T-A)6 alternating purine and pyrimidine bases. These findings suggest the possibility that an enhancer element for epsilon-globin gene expression resides within this DNase I-hypersensitive site.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan M., Lanyon W. G., Paul J. Multiple origins of transcription in the 4.5 Kb upstream of the epsilon-globin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcarek J. M., McMorris F. A. DNase I hypersensitive sites of globin genes of uninduced Friend erythroleukemia cells and changes during induction with dimethyl sulfoxide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10622–10628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baralle F. E., Shoulders C. C., Goodbourn S., Jeffreys A., Proudfoot N. J. The 5' flanking region of human epsilon-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4393–4404. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baralle F. E., Shoulders C. C., Proudfoot N. J. The primary structure of the human epsilon-globin gene. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):621–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J., Moulding C., Taub R., Murphy W., Stewart T., Potter H., Lenoir G., Leder P. The human c-myc oncogene: structural consequences of translocation into the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz E. J., Jr, Murnane M. J., Tonkonow B. L., Berman B. W., Mazur E. M., Cavallesco C., Jenko T., Snyder E. L., Forget B. G., Hoffman R. Embryonic-fetal erythroid characteristics of a human leukemic cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3509–3513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. Y., Folsom V., Wooley J. DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the chromatin of immunoglobulin kappa light chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2427–2431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Groudine M. Amplification of endogenous myc-related DNA sequences in a human myeloid leukaemia cell line. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):679–681. doi: 10.1038/298679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. G., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. DNA sequence preference of the progesterone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Onc gene amplification in promyelocytic leukaemia cell line HL-60 and primary leukaemic cells of the same patient. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):61–63. doi: 10.1038/299061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A., Erard F., Schneider A. P., Schechter A. N. Induction of hemoglobin accumulation in human K562 cells by hemin is reversible. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):459–461. doi: 10.1126/science.6163216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher R., Collins S., Trujillo J., McCredie K., Ahearn M., Tsai S., Metzgar R., Aulakh G., Ting R., Ruscetti F. Characterization of the continuous, differentiating myeloid cell line (HL-60) from a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1979 Sep;54(3):713–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Mason T. Heme regulates transcription of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae via an upstream activation site. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer E., Hofer-Warbinek R., Darnell J. E., Jr Globin RNA transcription: a possible termination site and demonstration of transcriptional control correlated with altered chromatin structure. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):887–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Pardue M. L., Lafer E. M., Möller A., Stollar B. D., Rich A. Antibodies to left-handed Z-DNA bind to interband regions of Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):417–422. doi: 10.1038/294417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S. RNA metabolism in the HeLa cell nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Siebenlist U., Korsmeyer S., Waldmann T., Leder P. Structure of the human immunoglobulin mu locus: characterization of embryonic and rearranged J and D genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):583–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90400-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins D. M., Paek I., Seeburg P. H., Axel R. Regulated expression of human growth hormone genes in mouse cells. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):623–631. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford T., Clegg J. B., Higgs D. R., Jones R. W., Thompson J., Weatherall D. J. Embryonic erythroid differentiation in the human leukemic cell line K562. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):348–352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Hayday A. C., Wiman K., Hayward W. S., Tonegawa S. Activation of the c-myc gene by translocation: a model for translational control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Fine structure of the regulatory region of simian virus 40 minichromosomes revealed by DNAase I digestion. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):133–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffery M., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation: DNase I hypersensitivity and DNA methylation near the globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1180–1184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. H., Smithies O. Human globin psi B2 is not a globin-related sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7809–7818. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Biro P. A., deRiel J. K., Lazarus H., Forget B. G. Restriction endonuclease mapping of the human gamma globin gene loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2519–2544. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O., Bohn M. A stretch of "late" SV40 viral DNA about 400 bp long which includes the origin of replication is specifically exposed in SV40 minichromosomes. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S. Active chromatin. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):289–295. doi: 10.1038/297289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin E. H., Wong-Staal F., Gelmann E. P., Dalla-Favera R., Papas T. S., Lautenberger J. A., Eva A., Reddy E. P., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Expression of cellular homologues of retroviral onc genes in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2490–2494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]