Abstract
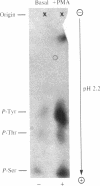
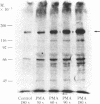
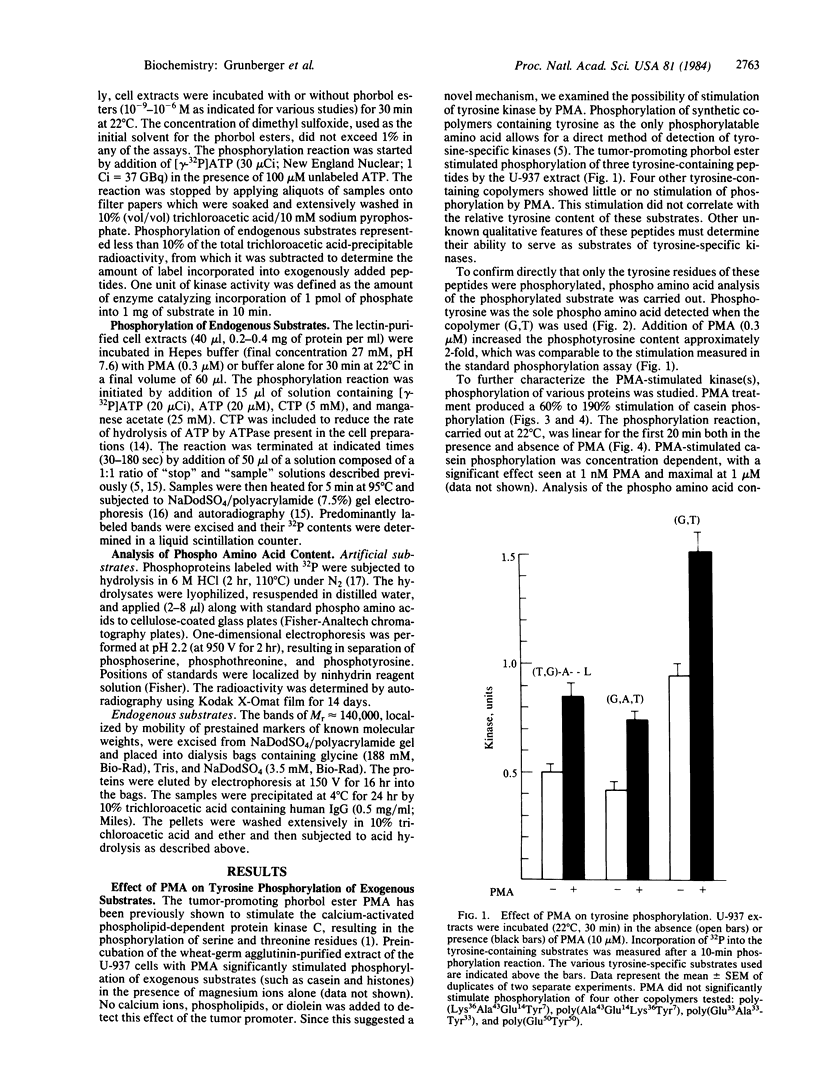
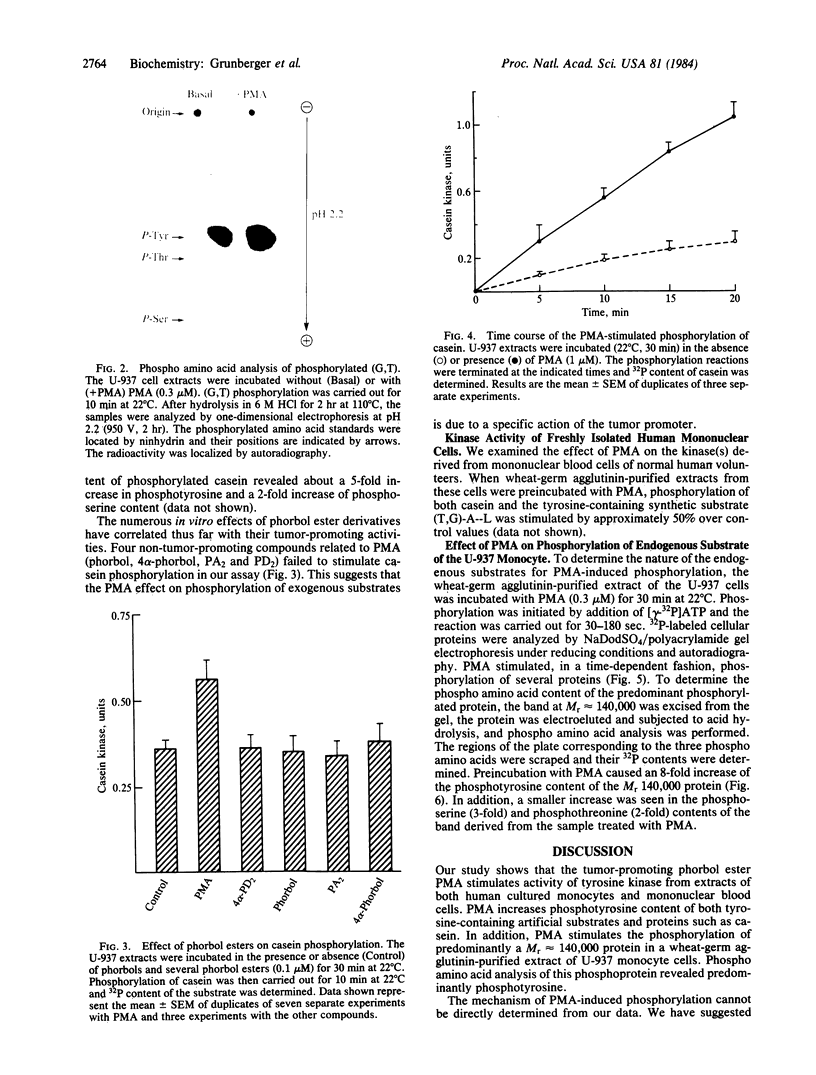
Solubilized lectin-purified extracts from human monocyte-like cells (U-937) and freshly isolated human mononuclear cells preincubated in the presence of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) stimulated phosphorylation of synthetic tyrosine-containing polymers and of casein. Tyrosine phosphorylation was confirmed by phospho amino acid analysis. PMA stimulated phosphorylation of exogenous substrates in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. This phosphorylation reaction did not require addition of phospholipid, diolein, or calcium. Biologically inactive phorbol compounds did not stimulate phosphorylation in this system. In addition, PMA enhanced phosphorylation of a Mr approximately equal to 140,000 protein as well as several other endogenous proteins in the U-937 extracts. PMA treatment stimulated predominantly phosphorylation on tyrosine residues of the Mr 140,000 protein. Tyrosine phosphorylation, typical of growth-promoting peptides such as insulin or epidermal growth factor, is believed to play a role in regulating normal and disordered cellular growth and proliferation. The demonstration of PMA-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation might provide a clue to the mechanism of cellular differentiation and proliferation induced by the tumor promoter.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop R., Martinez R., Nakamura K. D., Weber M. J. A tumor promoter stimulates phosphorylation on tyrosine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Sep 15;115(2):536–543. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Westermark B., Wasteson A., Heldin C. H. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific phosphorylation by platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):419–420. doi: 10.1038/295419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Phorbol ester and diacylglycerol induce protein phosphorylation at tyrosine. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):487–490. doi: 10.1038/306487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberger G., Gorden P. Affinity alteration of insulin receptor induced by a phorbol ester. Am J Physiol. 1982 Oct;243(4):E319–E324. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.4.E319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberger G., Zick Y., Roth J., Gorden P. Protein kinase activity of the insulin receptor in human circulating and cultured mononuclear cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Sep 15;115(2):560–566. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80181-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Sahyoun N. E., Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. Phorbol esters stimulate the phosphorylation of receptors for insulin and somatomedin C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6211–6213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters inhibit binding of epidermal growth factor to cellular receptors. Science. 1978 Oct 20;202(4365):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.308698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Electrophoretic resolution of three major insulin receptor structures with unique subunit stoichiometries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7137–7141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Three multifunctional protein kinase systems in transmembrane control. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1980;32:113–135. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-81503-4_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert A., Grunberger G., Carpenter J. L., Dayer J. M., Orci L., Gorden P. The insulin receptor of a human monocyte-like cell line: characterization and function. Endocrinology. 1984 Jan;114(1):247–253. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-1-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomopoulos P., Testa U., Gourdin M. F., Hervy C., Titeux M., Vainchenker W. Inhibition of insulin receptor binding by phorbol esters. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):389–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werth D. K., Niedel J. E., Pastan I. Vinculin, a cytoskeletal substrate of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11423–11426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Kasuga M., Kahn C. R., Roth J. Characterization of insulin-mediated phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):75–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Rees-Jones R. W., Grunberger G., Taylor S. I., Moncada V., Gorden P., Roth J. The insulin-stimulated receptor kinase is a tyrosine-specific casein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 15;137(3):631–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Whittaker J., Roth J. Insulin stimulated phosphorylation of its own receptor. Activation of a tyrosine-specific protein kinase that is tightly associated with the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3431–3434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]