Abstract
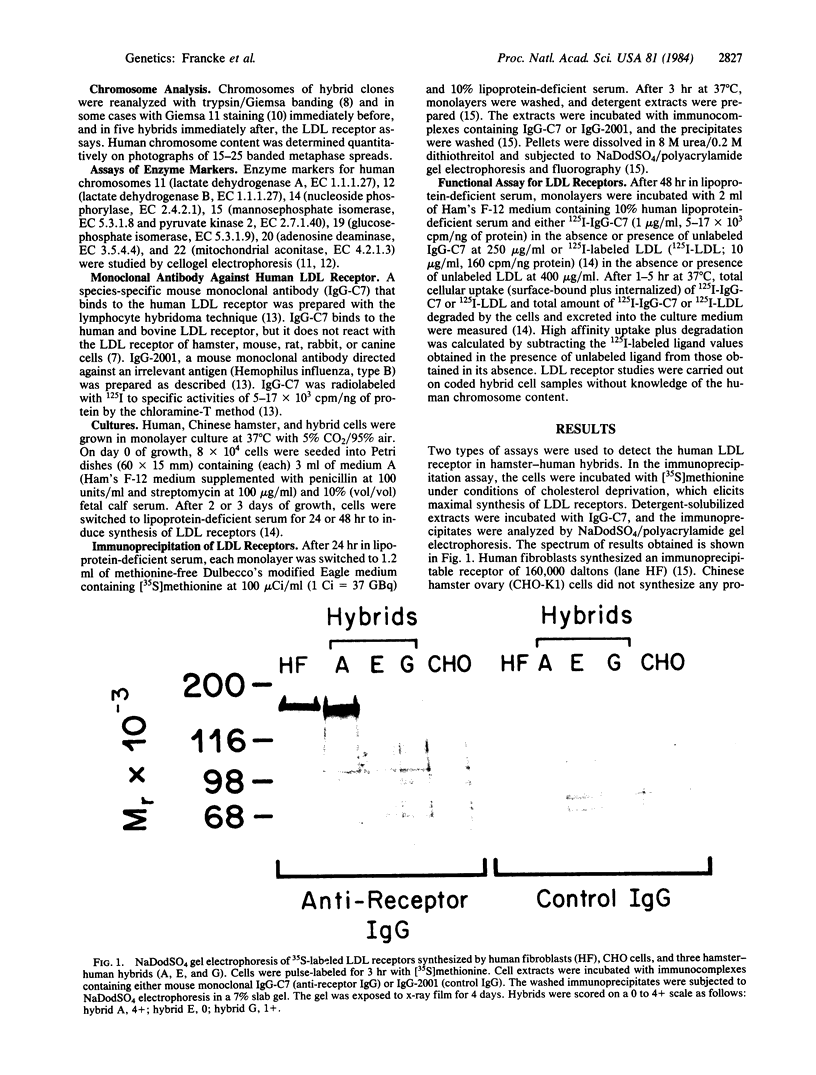
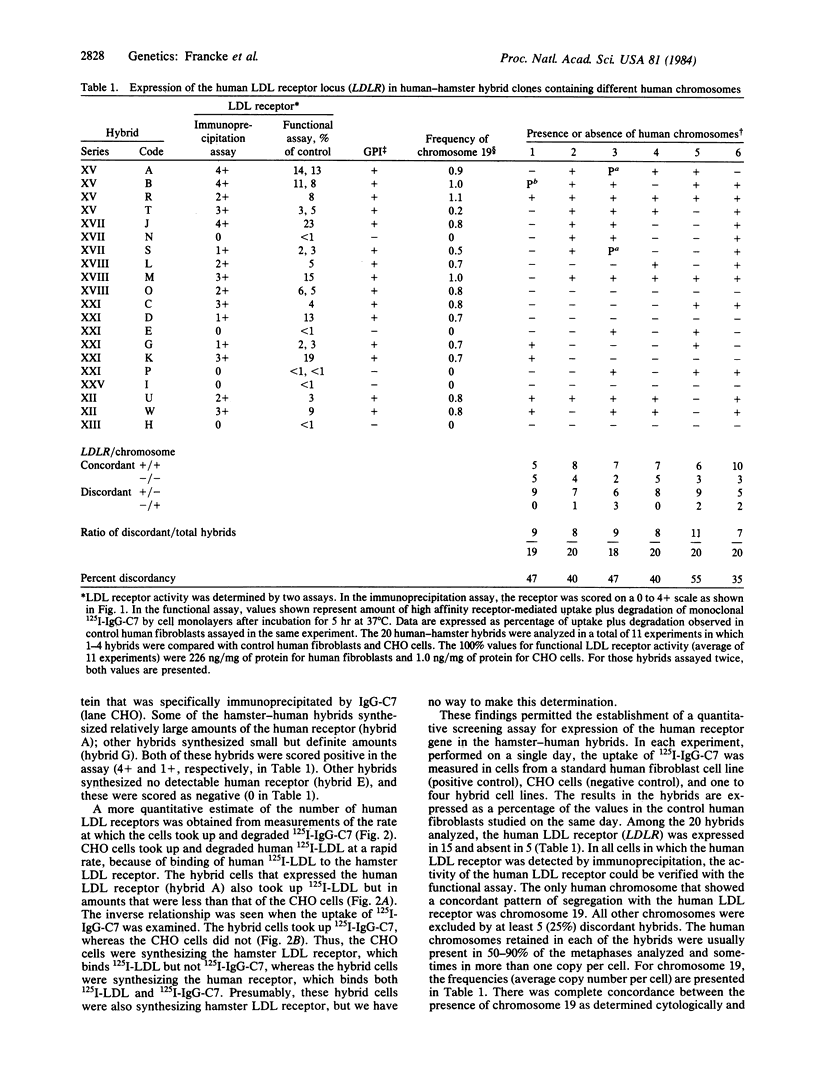
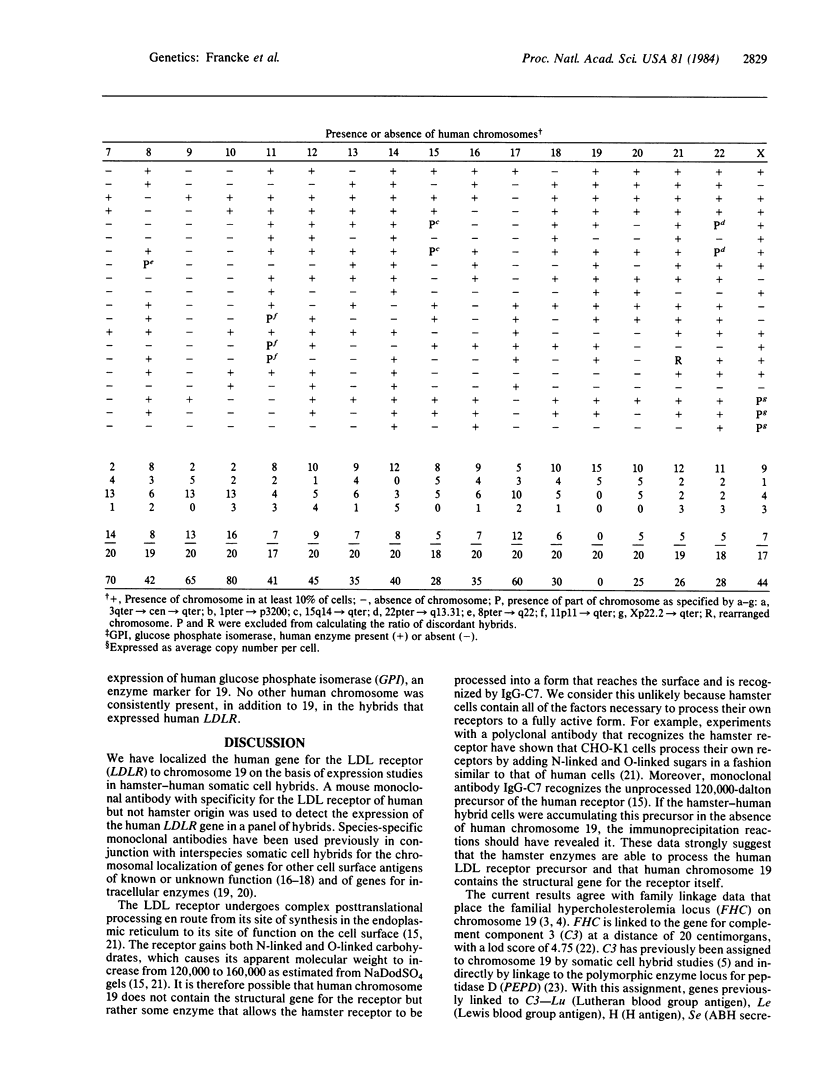
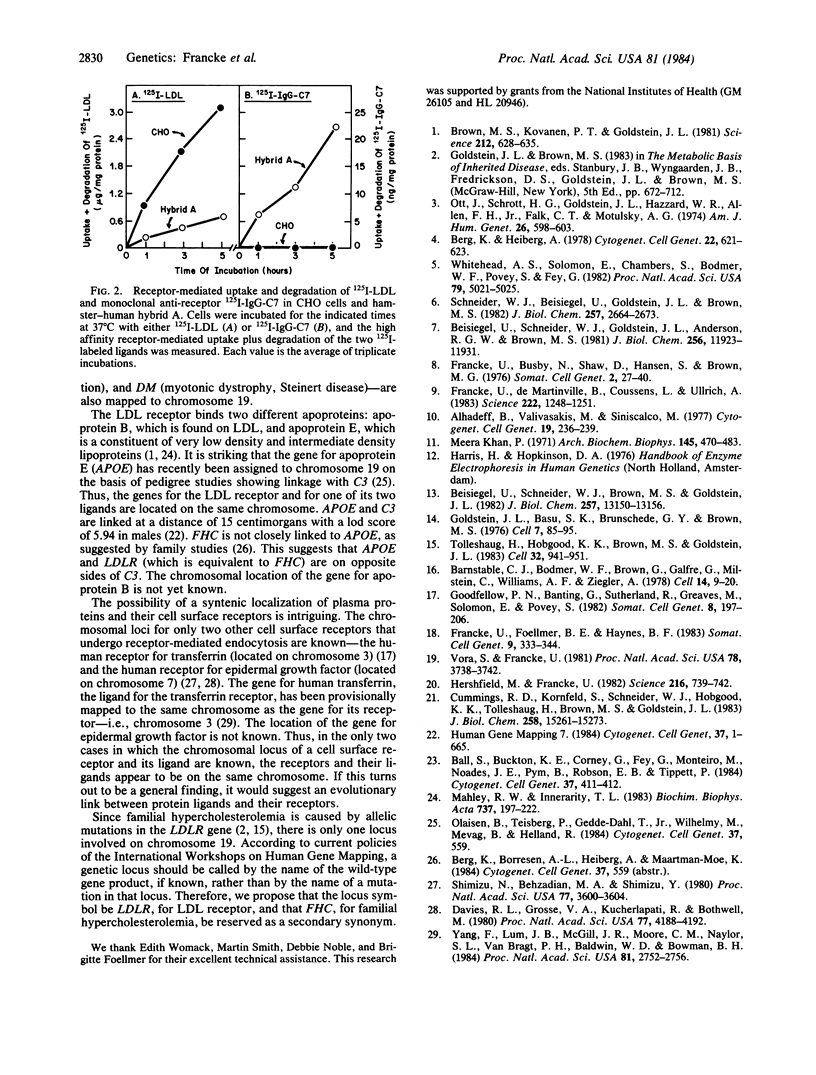
The availability of a species-specific monoclonal antibody that recognizes the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor of human but not hamster origin permitted assignment of the structural gene for the human receptor to chromosome 19. The antibody was used to detect the human LDL receptor in a series of hamster-human somatic cell hybrids by two assays: (i) a structural assay that measured cellular incorporation of [35S]methionine into immunoprecipitable receptor and (ii) a functional assay that measured the rate of receptor-dependent uptake and degradation of the 125I-labeled anti-receptor monoclonal antibody. Both assays showed that the human LDL receptor was expressed in 15 out of 20 hybrid cell lines. Expression of the human LDL receptor was 100% concordant with the presence of human chromosome 19; all other human chromosomes showed at least 25% discordance. As expected, the gene for the LDL receptor (LDLR) is located on the same chromosome as the gene for the disease familial hypercholesterolemia, which has been previously mapped to chromosome 19 by pedigree studies and is caused by allelic mutations at the LDL receptor locus. The gene for apolipoprotein E, a ligand for the LDL receptor, is also known to be located on chromosome 19, raising the possibility of an evolutionary link between a protein ligand and its receptor.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alhadeff B., Velivasakis M., Siniscalco M. Simultaneous identification of chromatid replication and of human chromosomes in metaphases of man-mouse somatic cell hybrids. (With 1 color plate). Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1977;19(4):236–239. doi: 10.1159/000130814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Schneider W. J., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Immunoblot analysis of low density lipoprotein receptors in fibroblasts from subjects with familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13150–13156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Schneider W. J., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Monoclonal antibodies to the low density lipoprotein receptor as probes for study of receptor-mediated endocytosis and the genetics of familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11923–11931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg K., Heiberg A. Linkage between familial hypercholesterolemia with xanthomatosis and the C3 polymorphism confirmed. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):621–623. doi: 10.1159/000131037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Kovanen P. T., Goldstein J. L. Regulation of plasma cholesterol by lipoprotein receptors. Science. 1981 May 8;212(4495):628–635. doi: 10.1126/science.6261329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings R. D., Kornfeld S., Schneider W. J., Hobgood K. K., Tolleshaug H., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Biosynthesis of N- and O-linked oligosaccharides of the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15261–15273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. L., Grosse V. A., Kucherlapati R., Bothwell M. Genetic analysis of epidermal growth factor action: assignment of human epidermal growth factor receptor gene to chromosome 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4188–4192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Busby N., Shaw D., Hansen S., Brown M. G. Intrachromosomal gene mapping in man: assignment of nucleoside phosphorylase to region 14cen leads to 14q21 by interspecific hybridization of cells with a t(X;14) (p22;q21) translocation. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Jan;2(1):27–40. doi: 10.1007/BF01539240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Foellmer B. E., Haynes B. F. Chromosome mapping of human cell surface molecules: monoclonal anti-human lymphocyte antibodies 4F2, A3D8, and A1G3 define antigens controlled by different regions of chromosome 11. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 May;9(3):333–344. doi: 10.1007/BF01539142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., de Martinville B., Coussens L., Ullrich A. The human gene for the beta subunit of nerve growth factor is located on the proximal short arm of chromosome 1. Science. 1983 Dec 16;222(4629):1248–1251. doi: 10.1126/science.6648531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Release of low density lipoprotein from its cell surface receptor by sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Banting G., Sutherland R., Greaves M., Solomon E., Povey S. Expression of human transferrin receptor is controlled by a gene on chromosome 3: assignment using species specificity of a monoclonal antibody. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Mar;8(2):197–206. doi: 10.1007/BF01538677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield M. S., Francke U. The human genes for S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase and adenosine deaminase are syntenic on chromosome 20. Science. 1982 May 14;216(4547):739–742. doi: 10.1126/science.7079734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L. Lipoprotein receptors and cholesterol homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):197–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P. Enzyme electrophoresis on cellulose acetate gel: zymogram patterns in mgh-mouse and man--Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Aug;145(2):470–483. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(71)80007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J., Schrott H. G., Goldstein J. L., Hazzard W. R., Allen F. H., Jr, Falk C. T., Motulsky A. G. Linkage studies in a large kindred with familial hypercholesterolemia. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):598–603. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. J., Beisiegel U., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Purification of the low density lipoprotein receptor, an acidic glycoprotein of 164,000 molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2664–2673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu N., Behzadian M. A., Shimizu Y. Genetics of cell surface receptors for bioactive polypeptides: binding of epidermal growth factor is associated with the presence of human chromosome 7 in human-mouse cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3600–3604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Hobgood K. K., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. The LDL receptor locus in familial hypercholesterolemia: multiple mutations disrupt transport and processing of a membrane receptor. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vora S., Francke U. Assignment of the human gene for liver-type 6-phosphofructokinase isozyme (PFKL) to chromosome 21 by using somatic cell hybrids and monoclonal anti-L antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3738–3742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead A. S., Solomon E., Chambers S., Bodmer W. F., Povey S., Fey G. Assignment of the structural gene for the third component of human complement to chromosome 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F., Lum J. B., McGill J. R., Moore C. M., Naylor S. L., van Bragt P. H., Baldwin W. D., Bowman B. H. Human transferrin: cDNA characterization and chromosomal localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2752–2756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




