Abstract
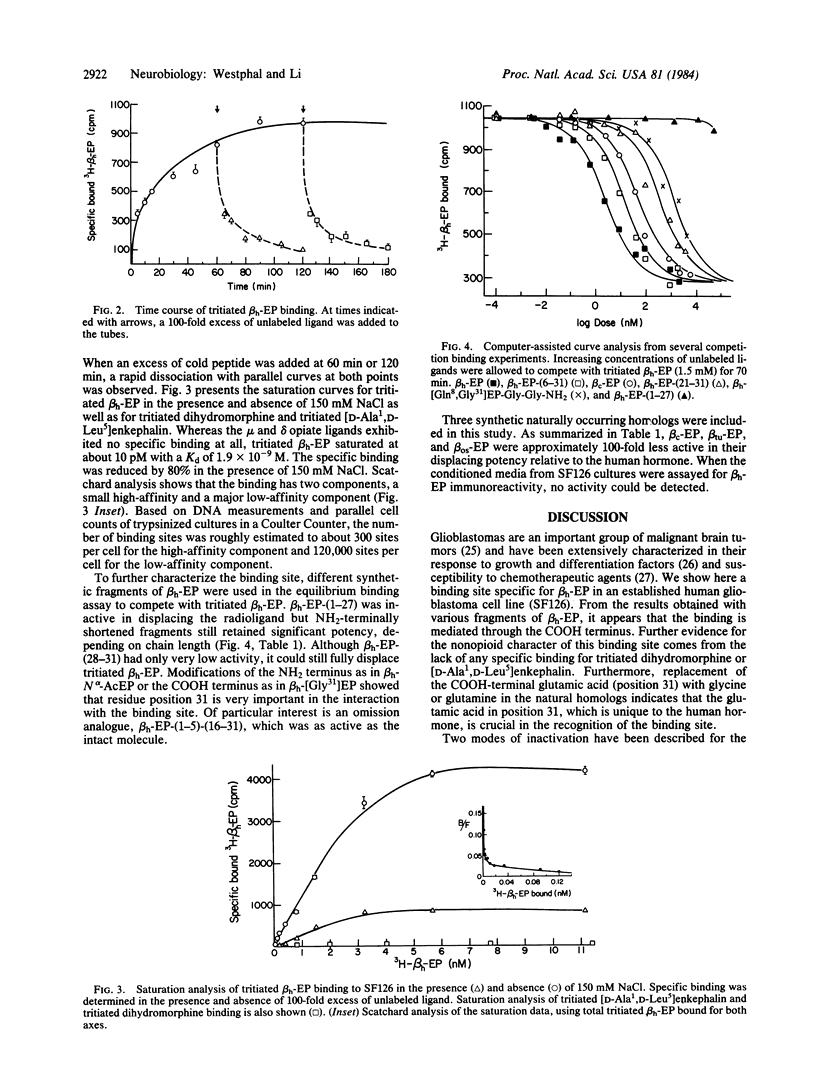
The established human glioblastoma cell line SF126 was found to bind tritiated human beta-endorphin (beta h-EP) in a saturable fashion. From displacement studies, the ED50 was estimated to be about 2.5 nM. The Kd was estimated as 1.9 X 10(-9) M and Scatchard analysis showed a biphasic pattern with a predominant low-affinity component. Binding reached a maximum at about 90 min at 22 degrees C and was instantaneously reversible. Tritiated [D-Ala2,D-Leu5]enkephalin and tritiated dihydromorphine did not bind to the cells. Sodium at a concentration of 150 mM decreased the specific binding by 80%. The interaction with the cellular binding site appeared to be mediated by the COOH-terminal segment of beta h-EP, as beta h-EP-(6-31) retained a high potency for displacing tritiated beta h-EP, and beta h-EP-(1-27) has no activity. Camel beta-EP was only about 1% as active as the human hormone.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akil H., Hewlett W. A., Barchas J. D., Li C. H. Binding of 3H-beta-endorphin to rat brain membranes: characterization of opiate properties and interaction with ACTH. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 May 30;64(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90363-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bewley T. A., Li C. H. Evidence for tertiary structure in aqueous solutions of human beta-endorphin as shown by difference absorption spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1983 May 24;22(11):2671–2675. doi: 10.1021/bi00280a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigner D. D. Biology of gliomas: potential clinical implications of glioma cellular heterogeneity. Neurosurgery. 1981 Sep;9(3):320–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E. The endorphins: a growing family of pharmacologically pertinent peptides. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:151–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deakin J. F., Doströvsky J. O., Smyth D. G. Influence of N-terminal acetylation and C-terminal proteolysis on the analgesic activity of beta-endorphin. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):501–506. doi: 10.1042/bj1890501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara P., Houghten R., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: characteristics of binding sites in the rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):786–792. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91847-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds R. G., Jr, Ferrara P., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: characteristics of binding sites in a neuroblastoma--glioma hybrid cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2218–2220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds R. G., Jr, Li C. H. Human beta-endorphin: specific binding in neuroblastoma N18TG2 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6764–6765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho C. L., Hammonds R. G., Jr, Li C. H. beta-endorphin: characteristics of binding sites in the rabbit cerebellar and brain membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):1096–1104. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91412-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Chang W. C., Li C. H. Human beta-endorphin: synthesis and characterization of analogs iodinated and tritiated at tyrosine residues 1 and 27. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1980 Oct;16(4):311–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1980.tb02592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law P. Y., Hom D. S., Loh H. H. Opiate regulation of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate level in neuroblastoma X glioma NG108-15 hybrid cells. Relationship between receptor occupancy and effect. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;23(1):26–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law P. Y., Loh H. H., Li C. H. Properties and localization of beta-endorphin receptor in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5455–5459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Lemaire S., Yamashiro D., Doneen B. A. The synthesis and opiate activity of beta-endorphin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 12;71(1):19–25. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Tseng L. F., Yamashiro D. beta-Endorphin: complete primary structure is required for full analgesic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 29;85(2):795–800. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Yamashiro D., Tseng L. F., Chang W. C., Ferrara P. beta-Endorphin: synthesis of analogs modified at the carboxyl terminus with increased activites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3276–3278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Yamashiro D., Tseng L. F., Loh H. H. Synthesis and analgesic activity of human beta-endorphin. J Med Chem. 1977 Mar;20(3):325–328. doi: 10.1021/jm00213a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Yamashiro D., Tseng L. F., Loh H. H. beta-endorphin: synthesis and biological activity of shortened peptide chains. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1978 Feb;11(2):154–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1978.tb02834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H. beta-Endorphin. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):504–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90305-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin-Shiau S. Y., Hammonds R. G., Jr, Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: characteristics of binding sites in the mouse brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Feb 18;87(2-3):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90341-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michler-Stuke A., Bottenstein J. E. Proliferation of glial-derived cells in defined media. J Neurosci Res. 1982;7(2):215–228. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490070212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Frazier G. R. Statistical analysis of radioligand assay data. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:3–22. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum M. L., Gerosa M. A., Wilson C. B., Barger G. R., Pertuiset B. F., de Tribolet N., Dougherty D. V. Stem cell studies of human malignant brain tumors. Part 1: Development of the stem cell assay and its potential. J Neurosurg. 1983 Feb;58(2):170–176. doi: 10.3171/jns.1983.58.2.0170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigerer L., Bhakdi S., Teschemacher H. Specific non-opiate binding sites for human beta-endorphin on the terminal complex of human complement. Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):572–574. doi: 10.1038/296572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigerer L., Teschemacher H., Bhakdi S., Lederle M. Interaction of human beta-endorphin with nonopiate binding sites on the terminal SC5b-9 complex of human complement. Significance of COOH-terminal beta H-endorphin fragments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12287–12292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vivekanandan S., Rao A. P., Sampathkumar M. M., Kanaka T. S. Presence of immunoreactive beta-endorphin in human brain tumor cyst fluids. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Apr;59(1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro D., Ferrara P., Li C. H. Synthesis and radioreceptor binding activity of turkey beta-endorphin and deacetylated salmon endorphin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1980 Jul;16(1):75–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1980.tb02938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro D., Ferrara P., Li C. H. beta-endorphin: synthesis of analogs with extension at the carboxyl terminus with high radioreceptor binding activity. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1980 Jul;16(1):70–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1980.tb02937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro D., Hammonds R. G., Jr, Li C. H. Beta-Endorphin. Synthesis and radioreceptor-binding activity of the ostrich hormone. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 Mar;19(3):251–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaoral M., Yamashiro D., Hammonds R. G., Jr, Li C. H. Beta-Endorphin: synthesis and radioreceptor binding activity of Beta h-endorphin-(1-27) and its analogs. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1981 Mar;17(3):292–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1981.tb01995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]