Abstract
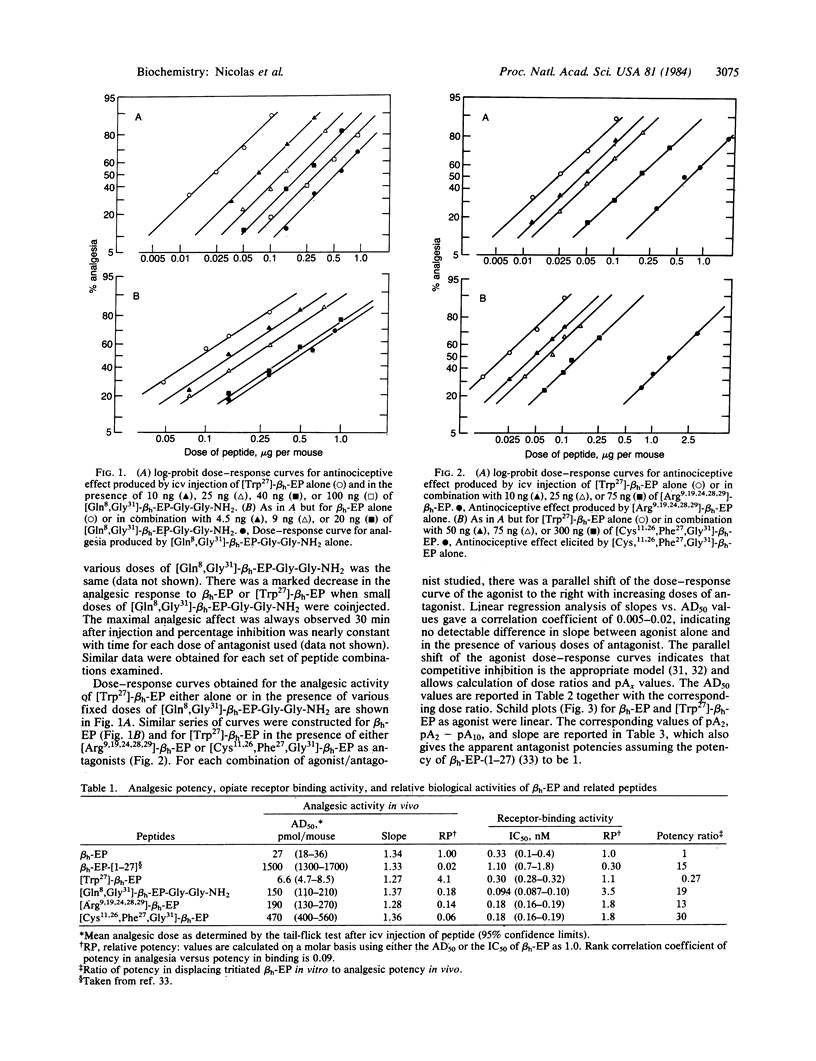
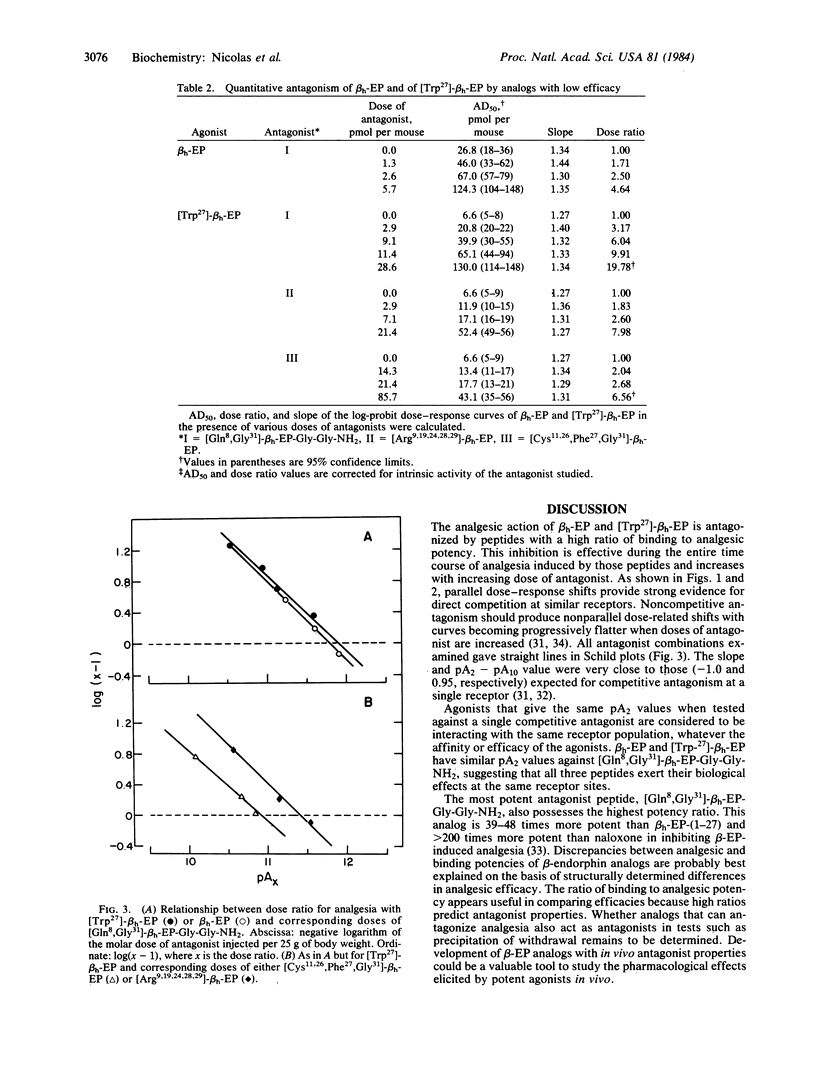
Competitive antagonism of human beta-endorphin (beta h-EP)-induced analgesia by synthetic beta h-EP analogs with high in vitro opiate receptor binding to in vivo analgesic potency ratio has been demonstrated. A parallel shift of the dose-response curve for analgesia to the right was observed when either beta h-EP or [ Trp27 ] -beta h-EP was coinjected with various doses of [Gln8, Gly31 ]-beta h-EP-Gly-Gly-NH2, [Arg9,19,24,28,29]-beta h-EP, or [ Cys11 ,26, Phe27 , Gly31 ]-beta h-EP. It was estimated that the most potent antagonist, [Gln8, Gly31 ]-beta h-EP-Gly-NH2, is at least 200 times more potent than naloxone.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akil H., Hewlett W. A., Barchas J. D., Li C. H. Binding of 3H-beta-endorphin to rat brain membranes: characterization of opiate properties and interaction with ACTH. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 May 30;64(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90363-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsall N. J., Hulme E. C. C fragment of lipotropin has a high affinity for brain opiate receptors. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):793–795. doi: 10.1038/260793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake J., Chang W. C., Li C. H. Synthesis of biological activity of human beta-endorphin analogs with disulfide bridges. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1979;14(3):275–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1979.tb01933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake J., Li C. H., Nicolas P. Beta-endorphin: synthesis and properties of analogs with replacement of lysine residues by arginine. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 Oct;20(4):308–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1982.tb00895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Goldstein A., Hi C. H. Opioid activity of a peptide, beta-lipotropin-(61-91), derived from beta-lipotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1821–1823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Smyth D. G. The C-fragment of lipotropin - a potent analgesic [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;260(2):30P–31P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara P., Houghten R., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: characteristics of binding sites in the rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):786–792. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91847-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf L., Szekely J. I., Ronai A. Z., Dunai-Kovacs Z., Bajusz S. Comparative study on analgesic effect of Met5-enkephalin and related lipotropin fragments. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):240–242. doi: 10.1038/263240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds R. G., Jr, Li C. H. Beta-Endorphin. Opiate receptor-binding activity of synthetic analogs modified in the enkephalin segment in rat brain membrane and neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cell. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 Mar;19(3):254–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds R. G., Jr, Li C. H. Beta-Endorphin. Opiate receptor-binding activity of synthetic analogs modified in the enkephalin segment in rat brain membrane and neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cell. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 Mar;19(3):254–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds R. G., Jr, Nicolas P., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: analgesic and receptor binding activity of non-mammalian homologs. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 May;19(5):556–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1982.tb02642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds R. G., Jr, Nicolas P., Li C. H. beta-endorphin-(1-27) is an antagonist of beta-endorphin analgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1389–1390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Chang W. C., Li C. H. Human beta-endorphin: synthesis and characterization of analogs iodinated and tritiated at tyrosine residues 1 and 27. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1980 Oct;16(4):311–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1980.tb02592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Li C. H. Preparation and properties of tritiated human beta-endorphin with high specific radioactivity. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1978 Nov;12(5):325–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1978.tb02904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson N., Houghten R., Pasternak G. W. Binding of 3H-beta-endorphin in rat brain. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 20;31(12-13):1381–1384. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law P. Y., Loh H. H., Li C. H. Properties and localization of beta-endorphin receptor in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5455–5459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire S., Bérubé A., Derome G., Lemaire I., Magnan J., Regoli D., St Pierre S. Synthesis and biological activity of beta-endorphin and analogues. Additional evidence for multiple opiate receptors. J Med Chem. 1978 Dec;21(12):1232–1235. doi: 10.1021/jm00210a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Chung D. Isolation and structure of an untriakontapeptide with opiate activity from camel pituitary glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1145–1148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Tseng L. F., Ferrara P., Yamashiro D. Beta-Endorphin: dissociation of receptor binding activity from analgesic potency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2303–2304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Yamashiro D., Nicolas P. Beta-endorphin: replacement of tyrosine in position 27 by tryptophan increases analgesic potency--preparation and properties of the 2-nitrophenylsulfenyl derivative. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1042–1044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Yamashiro D., Nicolas P. Beta-endorphin: replacement of tyrosine in position 27 by tryptophan increases analgesic potency--preparation and properties of the 2-nitrophenylsulfenyl derivative. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1042–1044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Yamashiro D., Tseng L. F., Loh H. H. Synthesis and analgesic activity of human beta-endorphin. J Med Chem. 1977 Mar;20(3):325–328. doi: 10.1021/jm00213a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh H. H., Tseng L. F., Wei E., Li C. H. beta-endorphin is a potent analgesic agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2895–2898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas P., Hammonds R. G., Jr, Gomez S., Li C. H. Beta-endorphin: thermodynamics of the binding reaction with rat brain membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Aug;217(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas P., Hammonds R. G., Jr, Li C. H. Beta-endorphin: opiate receptor binding activities of six naturally occurring beta-endorphin homologs studied by using tritiated human hormone and naloxone as primary ligands--effects of sodium ion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2191–2193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori A. E., Hayashi G., Smits S. E. Studies on the quantitative antagonism of analgesics by naloxone and diprenorphine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Oct;20(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori A. E., Kupferberg H. J., Miller J. W. Quantitative studies of the antagonism of morphine by nalorphine and naloxone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Sep;169(1):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng L. F., Loh H. H., Li C. H. Beta-Endorphin as a potent analgesic by intravenous injection. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):239–240. doi: 10.1038/263239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro D., Nicolas P., Li C. H. Synthesis and properties of dermorphin and an analog of beta-endorphin containing the dermorphin sequence. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1983 Mar;21(3):219–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1983.tb03097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro D., Nicolas P., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin: synthesis and properties of analogs modified in positions 8 and 31. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 Jul;20(1):43–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1982.tb02650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



