Abstract
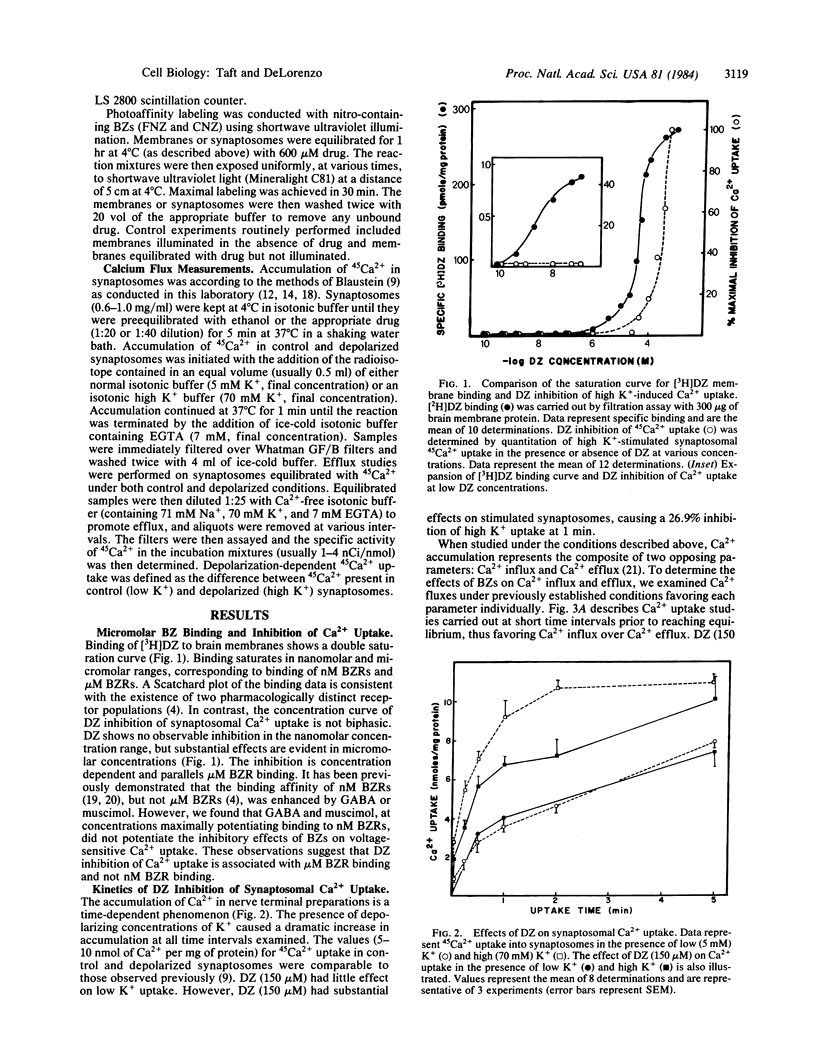
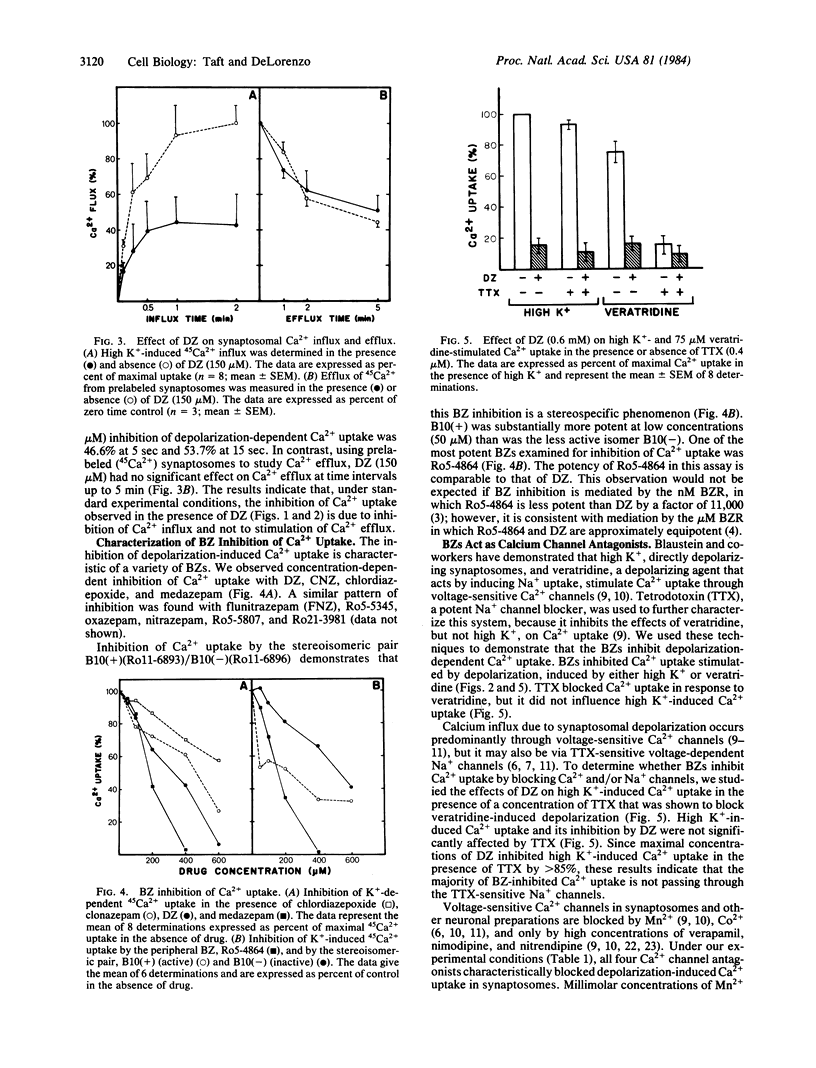
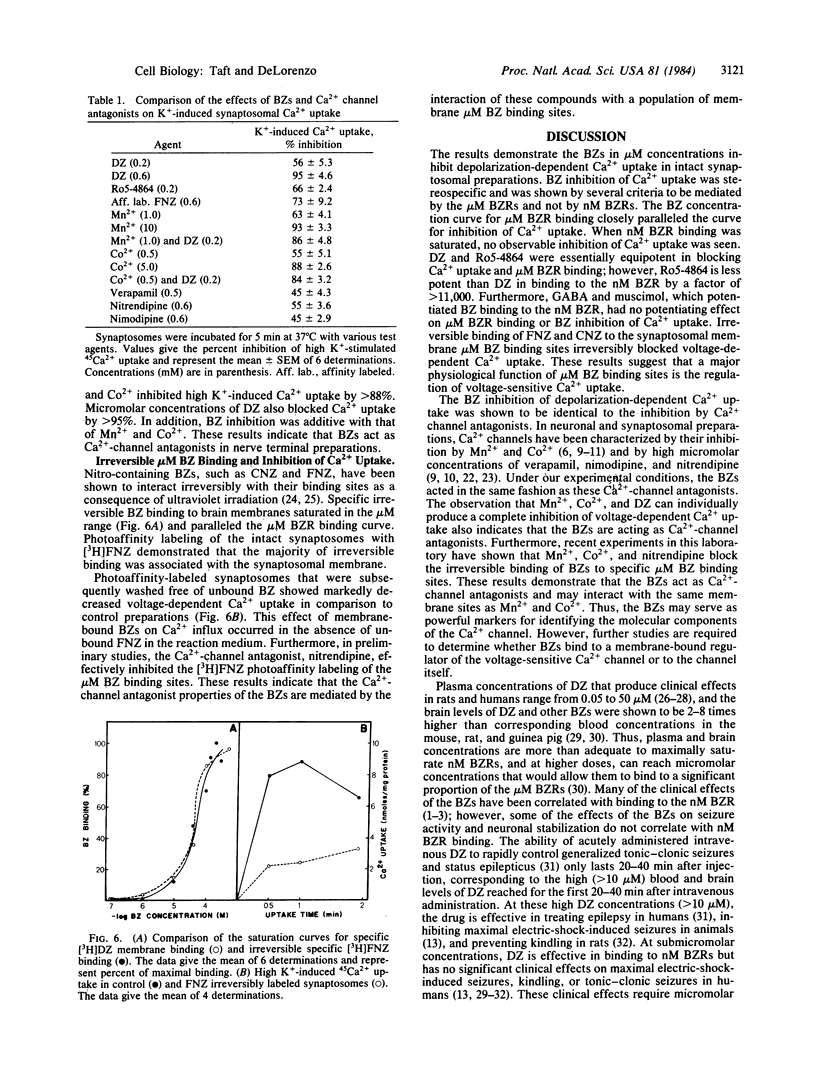
Benzodiazepines in micromolar concentrations significantly inhibit depolarization-sensitive Ca2+ uptake in intact nerve-terminal preparations. Benzodiazepine inhibition of Ca2+ uptake is concentration dependent and stereospecific. Micromolar-affinity benzodiazepine receptors have been identified and characterized in brain membrane and shown to be distinct from nanomolar-affinity benzodiazepine receptors. Evidence is presented that micromolar, and not nanomolar, benzodiazepine binding sites mediate benzodiazepine inhibition of Ca2+ uptake. Irreversible binding to micromolar benzodiazepine binding sites also irreversibly blocked depolarization-dependent Ca2+ uptake in synaptosomes, indicating that these compounds may represent a useful marker for identifying the molecular components of Ca2+ channels in brain. Characterization of benzodiazepine inhibition of Ca2+ uptake demonstrates that these drugs function as Ca2+ channel antagonists, because benzodiazepines effectively blocked voltage-sensitive Ca2+ uptake inhibited by Mn2+, Co2+, verapamil, nitrendipine, and nimodipine. These results indicate that micromolar benzodiazepine binding sites regulate voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels in brain membrane and suggest that some of the neuronal stabilizing effects of micromolar benzodiazepine receptors may be mediated by the regulation of Ca2+ conductance.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Effects of manganese and other agents on the calcium uptake that follows depolarization of squid axons. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):511–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Ector A. C. Carrier-mediated sodium-dependent and calcium-dependent calcium efflux from pinched-off presynaptic nerve terminals (synaptosomes) in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 21;419(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90355-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. Effects of potassium, veratridine, and scorpion venom on calcium accumulation and transmitter release by nerve terminals in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;247(3):617–655. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booker H. E., Celesia G. G. Serum concentrations of diazepam in subjects with epilepsy. Arch Neurol. 1973 Sep;29(3):191–194. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490270073012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth R. F., Clark J. B. A rapid method for the preparation of relatively pure metabolically competent synaptosomes from rat brain. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):365–370. doi: 10.1042/bj1760365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowling A. C., DeLorenzo R. J. Micromolar affinity benzodiazepine receptors: identification and characterization in central nervous system. Science. 1982 Jun 11;216(4551):1247–1250. doi: 10.1126/science.6281893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B. E., DeLorenzo R. J. Ca2+- and calmodulin-stimulated endogenous phosphorylation of neurotubulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):991–995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa T., Rodbard D., Pert C. B. Is the benzodiazepine receptor coupled to a chloride anion channel? Nature. 1979 Jan 25;277(5694):315–317. doi: 10.1038/277315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorenzo R. J., Freedman S. D., Yohe W. B., Maurer S. C. Stimulation of Ca2+-dependent neurotransmitter release and presynaptic nerve terminal protein phosphorylation by calmodulin and a calmodulin-like protein isolated from synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1838–1842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorenzo R. J. The calmodulin hypothesis of neurotransmission. Cell Calcium. 1981 Aug;2(4):365–385. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(81)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPolo R., Caputo C., Bezanilla F. Voltage-dependent calcium channel in the squid axon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1743–1745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrendelli J. A., Daniels-McQueen S. Comparative actions of phenytoin and other anticonvulsant drugs on potassium- and veratridine-stimulated calcium uptake in synaptosomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Jan;220(1):29–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASTAUT H., NAQUET R., POIRE R., TASSINARI C. A. TREATMENT OF STATUS EPILEPTICUS WITH DIAZEPAM (VALIUM). Epilepsia. 1965 Jun;6:167–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1965.tb03786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Woo E., Allen M. D., Orsulak P. J., Shader R. I. Rapid recovery from massive diazepam overdose. JAMA. 1978 Oct 20;240(17):1872–1874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillestad L., Hansen T., Melsom H., Drivenes A. Diazepam metabolism in normal man. I. Serum concentrations and clinical effects after intravenous, intramuscular, and oral administration. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Sep;16(3):479–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie S. W., Friedman M. B., Coleman R. R. Effects of chlordiazepoxide on depolarization-induced calcium influx into synaptosomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Sep 15;29(18):2439–2443. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90347-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lister R. G., File S. E., Greenblatt D. J. The behavioural effects of lorazepam are poorly related to its concentration in the brain. Life Sci. 1983 Apr 25;32(17):2033–2040. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Presynaptic calcium currents and their relation to synaptic transmission: voltage clamp study in squid giant synapse and theoretical model for the calcium gate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer E. M., Cooper J. R. Cobalt-ions dissociate between calcium uptake through voltage-dependent sodium and calcium channels in synaptosomes. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 11;265(1):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91352-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Battersby M. K., Richards J. G. Benzodiazepine receptor protein identified and visualized in brain tissue by a photoaffinity label. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1666–1670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachshen D. A., Blaustein M. P. The effects of some organic "calcium antagonists" on calcium influx in presynaptic nerve terminals. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;16(2):576–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Ogura A. Dihydropyridines as potent calcium channel blockers in neuronal cells. FEBS Lett. 1983 Feb 21;152(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80377-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallman J. F., Paul S. M., Skolnick P., Gallager D. W. Receptors for the age of anxiety: pharmacology of the benzodiazepines. Science. 1980 Jan 18;207(4428):274–281. doi: 10.1126/science.6101294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallman J. F., Thomas J. W., Gallager D. W. GABAergic modulation of benzodiazepine binding site sensitivity. Nature. 1978 Jul 27;274(5669):383–385. doi: 10.1038/274383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. W., Tallman J. F. Characterization of photoaffinity labeling of benzodiazepine binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9838–9842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toll L. Calcium antagonists High-affinity binding and inhibition of calcium transport in a clonal cell line. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13189–13192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



