Abstract
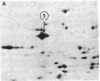
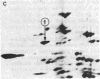
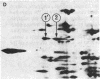
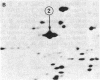
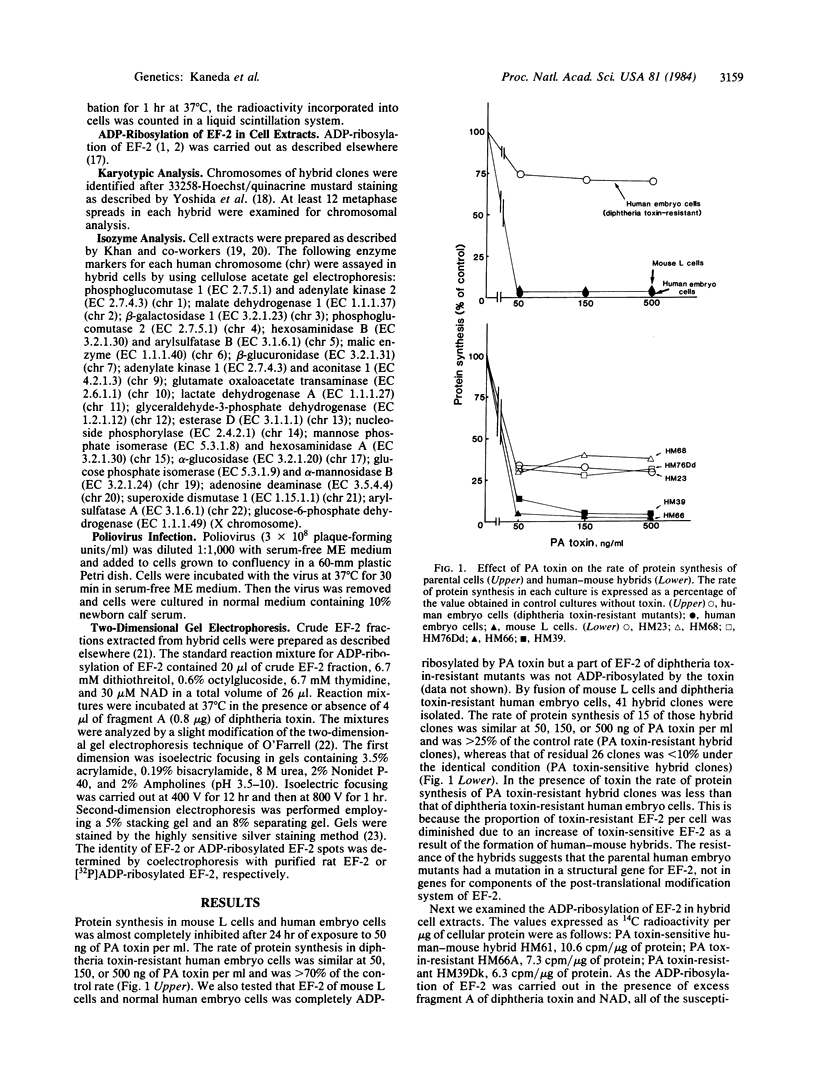
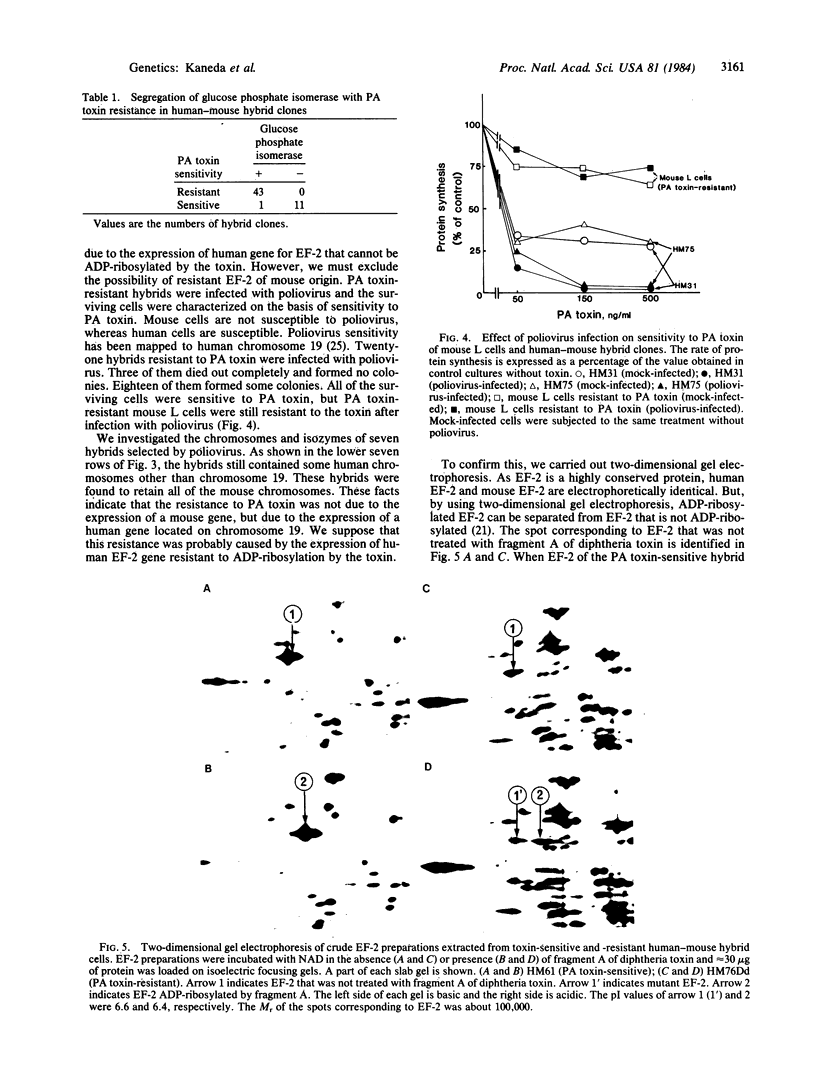
Elongation factor 2 (EF-2), polypeptidyl -tRNA translocase, is an essential factor for protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells and Archebacteria . We isolated diphtheria toxin-resistant human primary embryo cells that contain EF-2 that cannot be ADP-ribosylated by diphtheria toxin and Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PA toxin). Somatic cell hybrids were constructed from mouse L cells and toxin-resistant human embryo cell mutants. Forty-one hybrid clones were isolated, of which 15 clones were resistant to PA toxin. Karyotypic analysis and isozyme studies revealed that there was an absolute correlation between human chromosome 19 and resistance to PA toxin in the hybrids. On subcloning of PA toxin-resistant hybrid cells, we obtained one PA toxin-resistant hybrid subclone containing human chromosome 19 as the only human chromosome. Furthermore, the resistance to PA toxin of hybrid cell strains was lost after infection with poliovirus, for which sensitivity is conferred by human chromosome 19. It was confirmed by using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis that PA toxin resistance in hybrid cells was caused by the presence of EF-2 resistant to ADP-ribosylation by fragment A of diphtheria toxin. These facts suggest that the gene encoding EF-2 is located on human chromosome 19.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARLINGHAUS R., SHAEFER J., SCHWEET R. MECHANISM OF PEPTIDE BOND FORMATION IN POLYPEPTIDE SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1291–1299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creagan R. P., Chen S., Ruddle F. H. Genetic analysis of the cell surface: association of human chromosome 5 with sensitivity to diphtheria toxin in mouse-human somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2237–2241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Young B. D., Elles R. G., Hill M. E., Williamson R. Cloning of a representative genomic library of the human X chromosome after sorting by flow cytometry. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):374–376. doi: 10.1038/293374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper R. K., Chin D., Eurey-Owens D., Scheffler I. E., Simon M. I. Biochemical and genetic characterization of three hamster cell mutants resistant to diphtheria toxin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):116–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Brown R., Kurnick J. T. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. VII. Toxin-stimulated hydrolysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in mammalian cell extracts. J Exp Med. 1969 Jan 1;129(1):1–21. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Siminovitch L. Diphtheria-toxin-resistant mutants of CHO cells affected in protein synthesis: a novel phenotype. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 Sep;4(5):553–571. doi: 10.1007/BF01542926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Hayaishi O. Diphtheria toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3553–3555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Jeanpierre M., Young B. D. Construction and characterization of genomic libraries from specific human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2971–2975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMorris F. A., Chen T. R., Ricciuti F., Tischfield J., Creagan R., Ruddle F. Chromosome assignments in man of the genes for two hexosephosphate isomerases. Science. 1973 Mar 16;179(4078):1129–1131. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4078.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P. Enzyme electrophoresis on cellulose acetate gel: zymogram patterns in mgh-mouse and man--Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Aug;145(2):470–483. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(71)80007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekada E., Uchida T., Okada Y. Modification of the cell surface with neuraminidase increases the sensitivities of cells to diphtheria toxin and Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 1;123(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. Characterization of the diphtheria toxin-resistance system in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Jul;5(4):453–468. doi: 10.1007/BF01538880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Danley D. E., Moehring J. M. Codominant translational mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells selected with diphtheria toxin. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Jul;5(4):469–480. doi: 10.1007/BF01538881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKADA Y. Analysis of giant polynuclear cell formation caused by HVJ virus from Ehrlich's ascites tumor cells. I. Microscopic observation of giant polynuclear cell formation. Exp Cell Res. 1962 Feb;26:98–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. A., Henriksen O., Maxwell E. S. Elongation factor 2. Amino acid sequence at the site of adenosine diphosphate ribosylation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5088–5093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogerson L., Moldave K. The binding of aminoacyl transferase II to ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Jun 9;27(5):568–572. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Mutation in the structural gene for diphtheria toxin carried by temperate phage . Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 1;233(35):8–11. doi: 10.1038/newbio233008a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Kim J., Yamaizumi M., Miyake Y., Okada Y. Reconstitution of lipid vesicles associated with HVJ (Sendai virus) sikes. Purification and some properties of vesicles containing nontoxic fragment A of diphtheria toxin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jan;80(1):10–20. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Howard J. B., Bodley J. W. ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 by diphtheria toxin. NMR spectra and proposed structures of ribosyl-diphthamide and its hydrolysis products. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10710–10716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Someren H., Beijersbergen van Henegouwen H., Los W., Wurzer-Figurelli E., Doppert B., Vervloet M., Meera Khan P. Enzyme electrophoresis on cellulose acetate gel. II. Zymogram patterns in man-Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids. Humangenetik. 1974;25(3):189–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00281426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]