Abstract
Treatment of mice with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons results in the induction of P1-450 and P3-450 forms of cytochrome P-450. The genes for both cytochromes have recently been cloned and shown to be coordinately regulated by the Ah receptor. The mouse analogues of P1-450 and P3-450 can be distinguished from their hamster counterparts by Southern blot analysis with Kpn I-digested DNA fragments. DNA from hamster-mouse somatic cell hybrids that have selectively lost mouse chromosomes was used in Southern blots to map the location of the two mouse genes. Chromosome segregation analysis of 12 hybrid clones demonstrated that the structural genes for both P1-450 and P3-450 can be assigned to mouse chromosome 9.
Full text
PDF
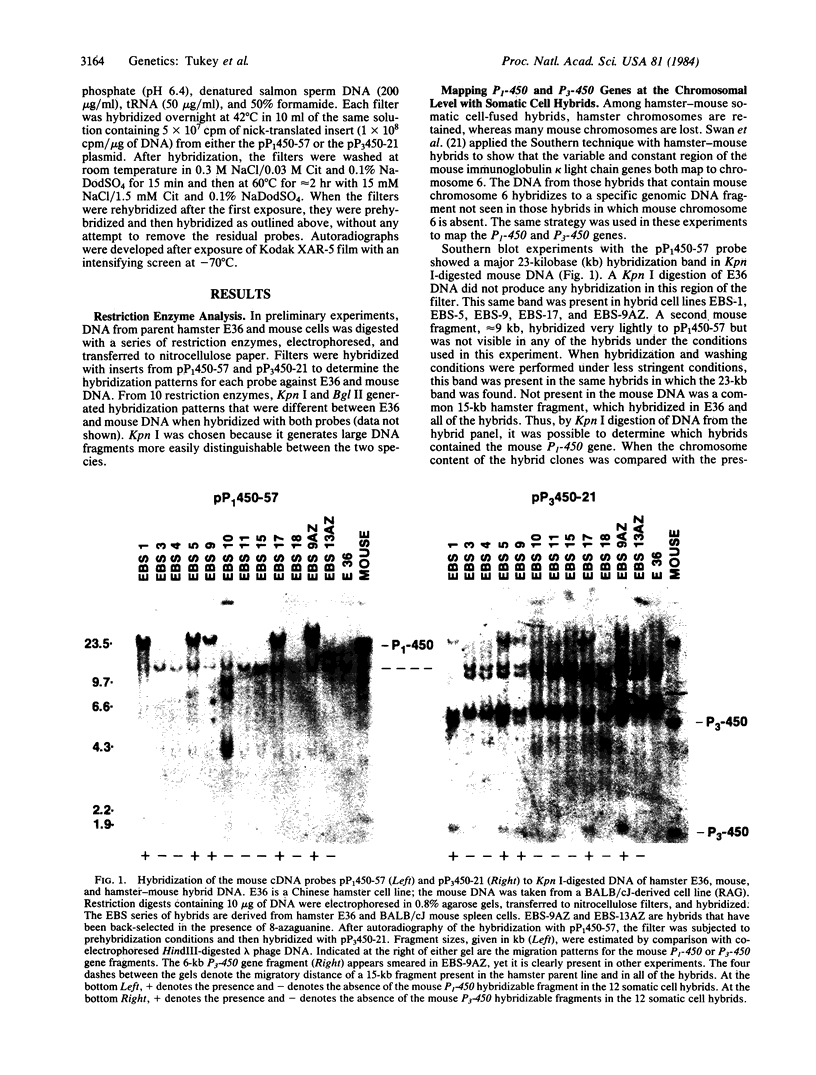
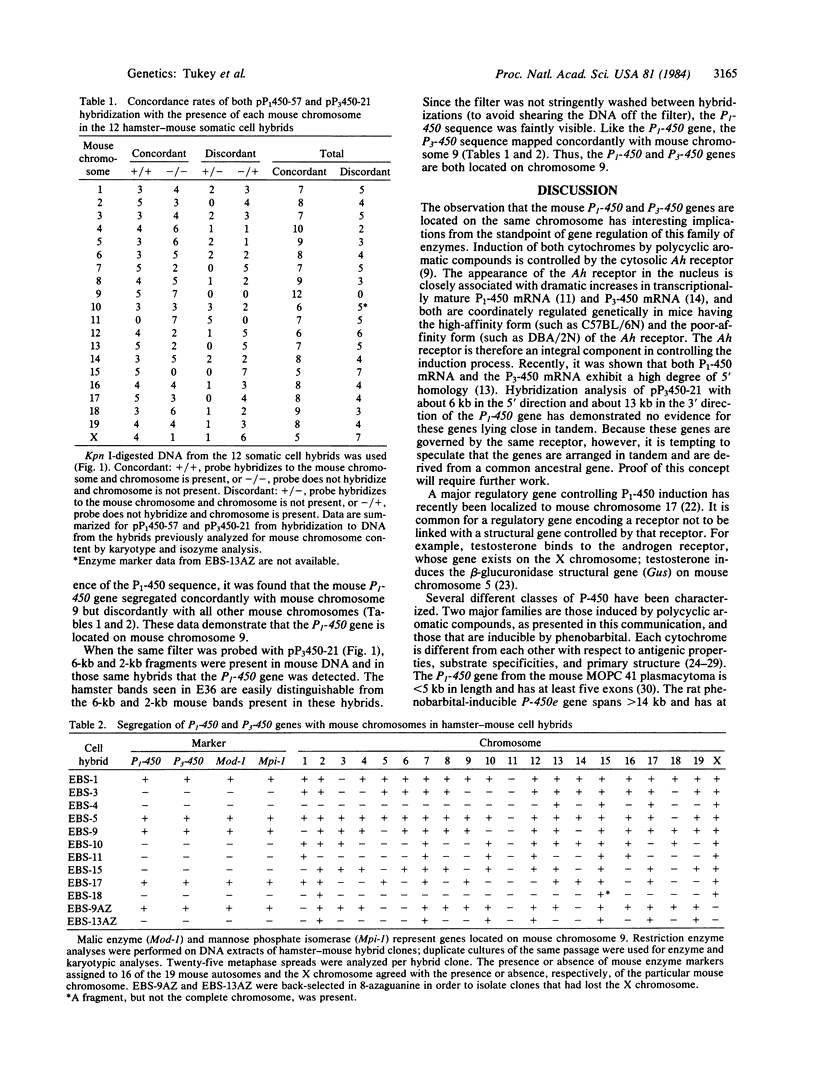

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atchison M., Adesnik M. A cytochrome P-450 multigene family. Characterization of a gene activated by phenobarbital administration. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11285–11295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boström H., Hansson R., Jönsson K. H., Wikvall K. Cytochromes P-450 LM3b and LM4 in biosynthesis of bile acids. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):29–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capdevila J., Chacos N., Werringloer J., Prough R. A., Estabrook R. W. Liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 and the oxidative metabolism of arachidonic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5362–5366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H. Induction of microsomal enzymes by foreign chemicals and carcinogenesis by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: G. H. A. Clowes Memorial Lecture. Cancer Res. 1982 Dec;42(12):4875–4917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. Y., Schleyer H., Levin S. S., Eisenhardt R. H., Novack B. G., Rosenthal O. A reevaluation of the role of cytochrome P-450 as the terminal oxidase in hepatic microsomal mixed function oxidase catalyzed reactions. Drug Metab Rev. 1979;10(2):153–185. doi: 10.3109/03602537908997467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Lalley P. A., Moss W., Ivy J., Minna J. D. Gene mapping in Mus musculus by interspecific cell hybridization: assignment of the genes for tripeptidase-1 to chromosome 10, dipeptidase-2 to chromosome 18, acid phosphatase-1 to chromosome 12, and adenylate kinase-1 to chromosome 2. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1977;19(2-3):57–84. doi: 10.1159/000130799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Kasper C. B. Cloning of DNA complementary to rat liver NADPH-cytochrome c (P-450) oxidoreductase and cytochrome P-450b mRNAs. Evidence that phenobarbital augments transcription of specific genes. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5962–5968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Wang P., Davidson N. K. Estimation of isozymes of microsomal cytochrome P-450 in rats, rabbits, and humans using immunochemical staining coupled with sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 30;21(7):1698–1706. doi: 10.1021/bi00536a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson R., Wikvall K. Hydroxylations in biosynthesis and metabolism of bile acids. Catalytic properties of different forms of cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1643–1649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann F. S., Ozols J. The complete amino acid sequence of rabbit phenobarbital-induced liver microsomal cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4195–4201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Whitlock J. P., Jr Induction of mRNA specific for cytochrome P1-450 in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10390–10394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. F. Isolation and characterization of a constitutive form of rabbit liver microsomal cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):304–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumaki K., Jensen N. M., Shire J. G., Nebert D. W. Genetic differences in induction of cytosol reduced-NAD(P):menadione oxidoreductase and microsomal aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase in the mouse. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):157–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Minna J. D., Francke U. Conservation of autosomal gene synteny groups in mouse and man. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):160–163. doi: 10.1038/274160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. Y., West S. B. Multiplicity of mammalian microsomal cytochromes P-45. Pharmacol Rev. 1979 Dec;31(4):277–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J. D., Marshall T. H., Shaffer-Berman P. V. Chinese hamster X mouse hybrid cells segregating mouse chromosomes and isozymes. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Oct;1(4):355–369. doi: 10.1007/BF01538667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami Y., Sogawa K., Suwa Y., Muramatsu M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Gene structure of a phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 in rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3958–3962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M., Negishi M., Altieri M., Chen Y. T., Ikeda T., Tukey R. H., Nebert D. W. Structure of the mouse cytochrome P1-450 genomic gene. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 15;134(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Negishi M., Lang M. A., Hjelmeland L. M., Eisen H. J. The Ah locus, a multigene family necessary for survival in a chemically adverse environment: comparison with the immune system. Adv Genet. 1982;21:1–52. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60296-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi M., Nebert D. W. Structural gene products of the Ah locus. Genetic and immunochemical evidence for two forms of mouse liver cytochrome P-450 induced by 3-methylcholanthrene. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11015–11023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliw E. H., Guengerich F. P., Oates J. A. Oxygenation of arachidonic acid by hepatic monooxygenases. Isolation and metabolism of four epoxide intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3771–3781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens I. S. Genetic regulation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase induction by polycyclic aromatic compounds in mice. Co-segregation with aryl hydrocarbon (benzo(alpha)pyrene) hydroxylase induction. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2827–2833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D. E., Thomas P. E., Levin W. Hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450 from rats treated with isosafrole. Purification and characterization of four enzymic forms. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7941–7955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. L., Kasper C. B. Genetic polymorphisms for a phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 map to the Coh locus in mice. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9585–9588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan D., D'Eustachio P., Leinwand L., Seidman J., Keithley D., Ruddle F. H. Chromosomal assignment of the mouse kappa light chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2735–2739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr G. E., Black S. D., Fujita V. S., Coon M. J. Complete amino acid sequence and predicted membrane topology of phenobarbital-induced cytochrome P-450 (isozyme 2) from rabbit liver microsomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6552–6556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Reik L. M., Ryan D. E., Levin W. Regulation of three forms of cytochrome P-450 and epoxide hydrolase in rat liver microsomes. Effects of age, sex, and induction. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1044–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tukey R. H., Hannah R. R., Negishi M., Nebert D. W., Eisen H. J. The Ah locus: correlation of intranuclear appearance of inducer-receptor complex with induction of cytochrome P1-450 mRNA. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):275–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tukey R. H., Nebert D. W., Negishi M. Structural gene product of the [Ah] complex. Evidence for transcriptional control of cytochrome P1-450 induction by use of a cloned DNA sequence. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6969–6974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. W., Taylor B. A. Genetic regulation of coumarin hydroxylase activity in mice. Evidence for single locus control on chromosome. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5647–5651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan P. M., Ryan D. E., Levin W., Shively J. E. Identification and localization of amino acid substitutions between two phenobarbital-inducible rat hepatic microsomal cytochromes P-450 by micro sequence analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1169–1173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]