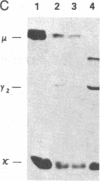
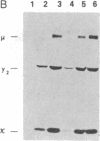
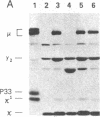
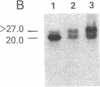
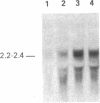
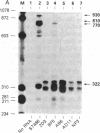
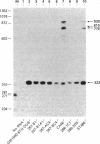
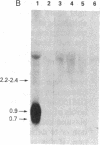
Abstract
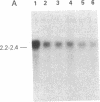
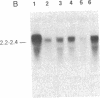
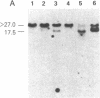
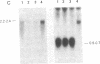
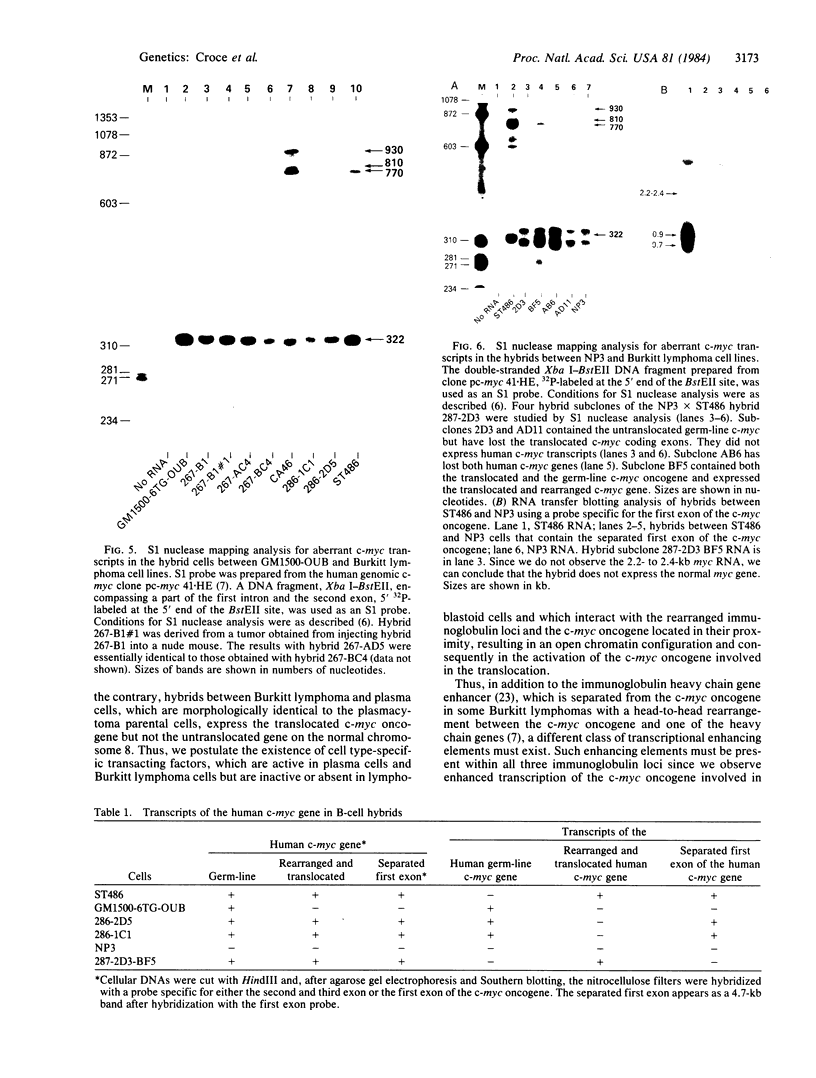
We examined somatic cell hybrids between Burkitt lymphoma cells and either human lymphoblastoid cells or mouse plasmacytoma cells for the expression of the translocated c-myc oncogene. The results of this study indicate that the translocated c-myc oncogene is transcribed in plasma cells but is repressed in lymphoblastoid cells. Thus, the factors necessary for translocated c-myc transcription are present in plasma cells and Burkitt lymphoma cells but are absent or inactive in lymphoblastoid cells. Since the distance between the rearranged immunoglobulin loci and the c-myc oncogene can even exceed 30-50 kilobases, we speculate that the translocated c-myc oncogene is under the transcriptional control of enhancer-like elements capable of acting over long distances. The activity of this long-range enhancer may depend on the interaction with transacting factors that are active in plasma cells and in Burkitt lymphoma cells but are not active in lymphoblastoid cells. We also examined the transcription of the first exon of the c-myc oncogene, which becomes separated from the second and third exon because of the chromosomal break involving the first intron. This exon is transcribed at high levels in ST486 Burkitt lymphoma cells with the t(8;14) chromosome translocation. Hybrids between lymphoblastoid and ST486 cells expressed high levels of transcripts of the first exon, whereas hybrids between plasma cells and ST486 cells did not. Thus, transcription of the separated first exon can be enhanced in lymphoblastoid and Burkitt lymphoma cells because of its close proximity to the heavy chain enhancer that is normally located between the joining and the switch region of the C mu gene. Such enhancement, however, does not occur in plasma cells, possibly because these cells are able to suppress completely the c-myc oncogene, unless it has been placed in the proximity of a rearranged immunoglobulin constant region gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ar-Rushdi A., Tan K. B., Croce C. M. Transcriptional control of the expression of mouse globin genes in myeloma x erythroleukemia cell hybrids. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Mar;8(2):151–161. doi: 10.1007/BF01538674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M. Assignment of the integration site for simian virus 40 to chromosome 17 in GM54VA, a human cell line transformed by simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):315–318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Linnenbach A., Hall W., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Production of human hybridomas secreting antibodies to measles virus. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):488–489. doi: 10.1038/288488a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Shander M., Martinis J., Cicurel L., D'Ancona G. G., Dolby T. W., Koprowski H. Chromosomal location of the genes for human immunoglobulin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3416–3419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Thierfelder W., Erikson J., Nishikura K., Finan J., Lenoir G. M., Nowell P. C. Transcriptional activation of an unrearranged and untranslocated c-myc oncogene by translocation of a C lambda locus in Burkitt. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6922–6926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Bregni M., Erikson J., Patterson D., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M. Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7824–7827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Martinotti S., Gallo R. C., Erikson J., Croce C. M. Translocation and rearrangements of the c-myc oncogene locus in human undifferentiated B-cell lymphomas. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):963–967. doi: 10.1126/science.6401867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel B. S., Selden J. R., Chaganti R. S., Jhanwar S., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. The 2p breakpoint of a 2;8 translocation in Burkitt lymphoma interrupts the V kappa locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2444–2446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Croce C. M. Secretion of human immunoglobulins by mouse myeloma x Daudi somatic cell hybrids. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Aug;12(8):697–701. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Finan J., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Translocation of immunoglobulin VH genes in Burkitt lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5611–5615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Martinis J., Croce C. M. Assignment of the genes for human lambda immunoglobulin chains to chromosome 22. Nature. 1981 Nov 12;294(5837):173–175. doi: 10.1038/294173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Nishikura K., ar-Rushdi A., Finan J., Emanuel B., Lenoir G., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Translocation of an immunoglobulin kappa locus to a region 3' of an unrearranged c-myc oncogene enhances c-myc transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7581–7585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozbor D., Lagarde A. E., Roder J. C. Human hybridomas constructed with antigen-specific Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6651–6655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Battey J., Lenoir G., Moulding C., Murphy W., Potter H., Stewart T., Taub R. Translocations among antibody genes in human cancer. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):765–771. doi: 10.1126/science.6356357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., van deSande H. Chain length determination of small double- and single-stranded DNA molecules by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3787–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Wang X. F., Olsen J., Calame K. Transcriptional enhancer elements in the mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.6306772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., ar-Rushdi A., Erikson J., Watt R., Rovera G., Croce C. M. Differential expression of the normal and of the translocated human c-myc oncogenes in B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4822–4826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., ar-Rushdi A., Erikson J., Watt R., Rovera G., Croce C. M. Differential expression of the normal and of the translocated human c-myc oncogenes in B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4822–4826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific enhancer in the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):80–82. doi: 10.1038/307080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Hayday A. C., Wiman K., Hayward W. S., Tonegawa S. Activation of the c-myc gene by translocation: a model for translational control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Berk A. J., Berget S. M. Transcription maps of adenovirus. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):750–768. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ar-Rushdi A., Nishikura K., Erikson J., Watt R., Rovera G., Croce C. M. Differential expression of the translocated and the untranslocated c-myc oncogene in Burkitt lymphoma. Science. 1983 Oct 28;222(4622):390–393. doi: 10.1126/science.6414084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]