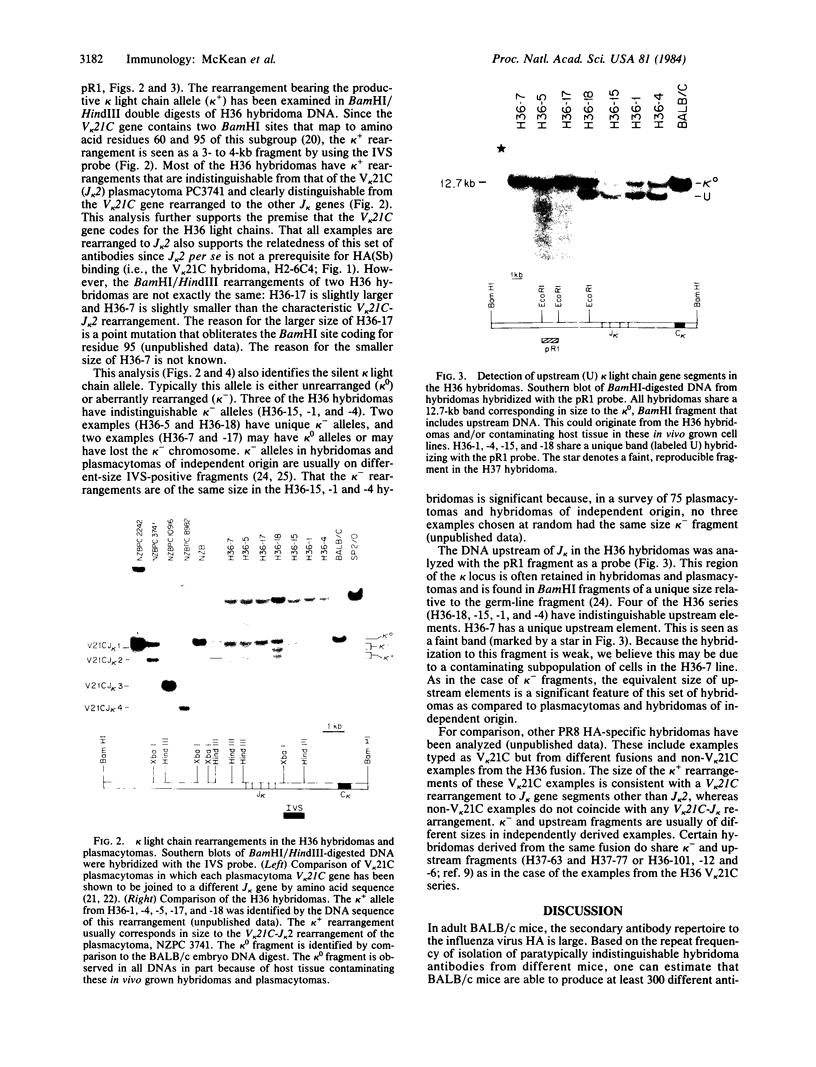
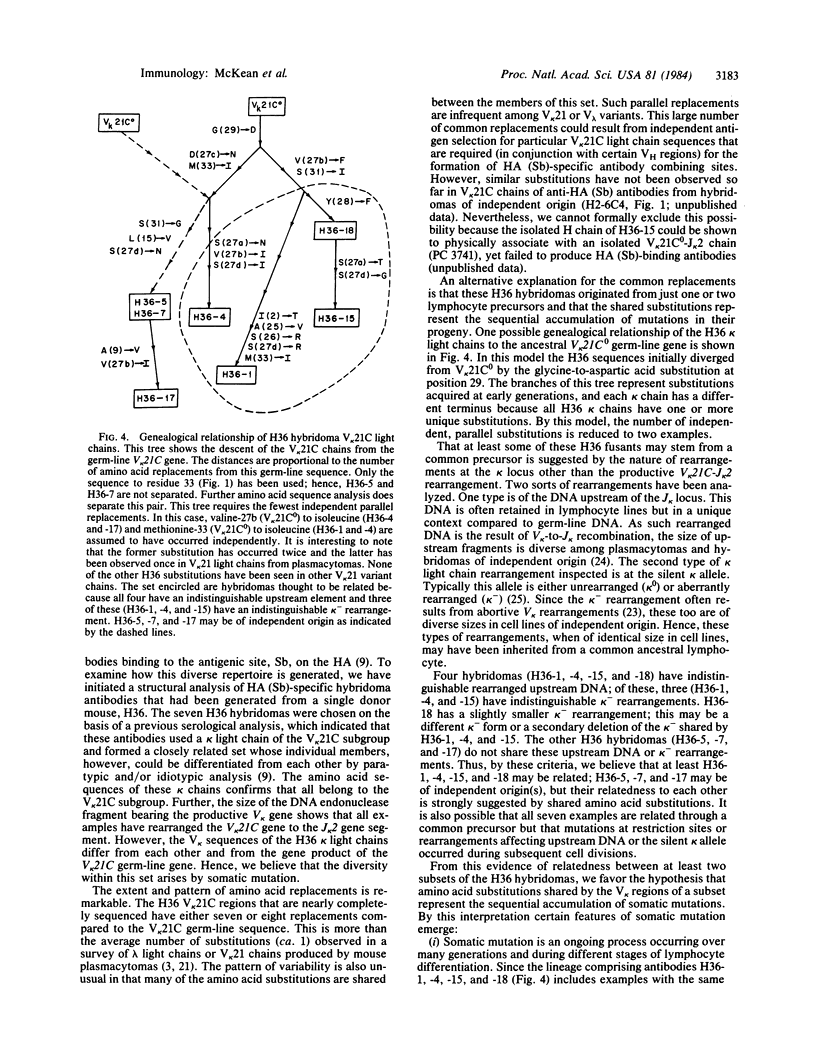
Abstract
We have examined the amino-terminal sequence of the kappa light chains of a set of monoclonal antibodies specific for one of the major antigenic determinants (Sb) on the influenza virus PR8[A/PR/8/34(H1N1)] hemagglutinin molecule. This set was believed to be structurally related from earlier serological analysis that typed these kappa chains as members of the variable (V) region V kappa 21 group [ Staudt , L. M. & Gerhard , W. (1983) J. Exp. Med. 157, 678-704]. Our sequence analysis confirms and extends this conclusion; all examples of this set belong to a subgroup of the V kappa 21 group, V kappa 21C . A special feature of this set of kappa light chains is that all examples were derived from the same mouse (designated H36 ). This sequence analysis along with the characterization of gene rearrangements at the kappa light chain loci of these hybridomas is consistent with the idea that certain members of this set are the progeny of one or two lymphocytes. Because of this potential clonal relationship, we can reach several conclusions about the diversity observed among these kappa light chains: (i) the diversity is due to somatic mutation, (ii) somatic mutations occur sequentially and accumulate in the first complementarity-determining region, and (iii) the extent of somatic variation in this sample is high, suggesting a somatic mutation rate of about 10(-3) per base pair per generation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Gene conversion: some implications for immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):592–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Somatic mutation gains its place among the generators of diversity. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):295–296. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90196-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S., Milstein C. Origin of antibody variation. Nature. 1966 Jul 16;211(5046):242–243. doi: 10.1038/211242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleclough C., Perry R. P., Karjalainen K., Weigert M. Aberrant rearrangements contribute significantly to the allelic exclusion of immunoglobulin gene expression. Nature. 1981 Apr 2;290(5805):372–378. doi: 10.1038/290372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. D., Scharff M. D. Antigen-binding mutants of mouse myeloma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5687–5691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearhart P. J., Johnson N. D., Douglas R., Hood L. IgG antibodies to phosphorylcholine exhibit more diversity than their IgM counterparts. Nature. 1981 May 7;291(5810):29–34. doi: 10.1038/291029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich G., Traunecker A., Tonegawa S. Somatic mutation creates diversity in the major group of mouse immunoglobulin kappa light chains. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):417–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. V., Bond M. W., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E. Cleavage at tryptophanyl residues with dimethyl sulfoxide-hydrochloric acid and cyanogen bromide. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:318–324. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppi K., Julius M., Staudt L., Gerhard W., Weigert M. The idiotypes of V kappa 21 light chains. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1984 Jan-Feb;135C(1):181–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Davis M., Sinn E., Patten P., Hood L. Antibody diversity: somatic hypermutation of rearranged VH genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90399-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Lang R. B., Stanton L. W., Harris L. J. A model for the molecular requirements of immunoglobulin heavy chain class switching. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):87–89. doi: 10.1038/298087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E., Schibler U., Huebner K., Croce C. M. Selective suppression of the transcription of ribosomal genes in mouse-human hybrid cells. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Mar;98(3):553–559. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040980313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Nau M. M., Norman B., Kwan S. P., Scharff M., Leder P. Immunoglobulin V/J recombination is accompanied by deletion of joining site and variable region segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6022–6026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Gerhard W. Generation of antibody diversity in the immune response of BALB/c mice to influenza virus hemagglutinin. I. Significant variation in repertoire expression between individual mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):687–704. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Coleclough C., Perry R. P., Weigert M. DNA between variable and joining gene segments of immunoglobulin kappa light chain is frequently retained in cells that rearrange the kappa locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):262–266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness B. G., Weigert M., Coleclough C., Mather E. L., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Transcription of the unrearranged mouse C kappa locus: sequence of the initiation region and comparison of activity with a rearranged V kappa-C kappa gene. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):593–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90401-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M. G., Cesari I. M., Yonkovich S. J., Cohn M. Variability in the lambda light chain sequences of mouse antibody. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1045–1047. doi: 10.1038/2281045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigert M., Gatmaitan L., Loh E., Schilling J., Hood L. Rearrangement of genetic information may produce immunoglobulin diversity. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):785–790. doi: 10.1038/276785a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]