Abstract
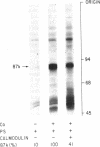
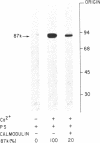
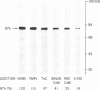
Calmodulin was previously found to inhibit the Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent phosphorylation of an endogenous substrate, called the 87-kilodalton protein, in a crude extract prepared from rat brain synaptosomal cytosol. We investigated the mechanism of this inhibition, using Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase and the 87-kilodalton protein, both of which had been purified to homogeneity from bovine brain. Rabbit brain calmodulin and some other Ca2+-binding proteins inhibited the phosphorylation of the 87-kilodalton protein by this kinase in the purified system. Calmodulin also inhibited the Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent phosphorylation of H1 histone, synapsin I, and the delta subunit of the acetylcholine receptor, with use of purified components. These results suggest that calmodulin may be a physiological regulator of Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cox D. E., Edstrom R. D. Inhibition by calmodulin of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase activation of phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12728–12733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. C., Powell D. W. Calcium/calmodulin inhibition of coupled NaCl transport in membrane vesicles from rabbit ileal brush border. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5248–5252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardot J. M., Kempf J., Cooper D. M. Role of calmodulin in the effect of guanyl nucleotides on rat hippocampal adenylate cyclase: involvement of adenosine and opiates. J Neurochem. 1983 Sep;41(3):848–859. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V. The binding of calmodulin to myelin basic protein and histone H2B. Biochem J. 1980 Aug 1;189(2):227–240. doi: 10.1042/bj1890227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grand R. J., Perry S. V., Weeks R. A. Troponin C-like proteins (calmodulins) from mammalian smooth muscle and other tissues. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 1;177(2):521–529. doi: 10.1042/bj1770521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Multiple phosphorylation sites in protein I and their differential regulation by cyclic AMP and calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itano T., Itano R., Penniston J. T. Interactions of basic polypeptides and proteins with calmodulin. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 1;189(3):455–459. doi: 10.1042/bj1890455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasa Y., Takai Y., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Phosphorylation of calf thymus H1 histone by calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):180–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand C., Clos J., Legrand J., Langley O. K., Ghandour M. S., Labourdette G., Gombos G., Vincendon G. Localization of S100 protein in the rat cerebellum: an immunoelectron microscope study. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1981 Jul-Aug;7(4):299–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1981.tb00101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa M., Hidaka H., Adelstein R. S. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle heavy meromyosin by calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. The effect on actin-activated MgATPase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14069–14072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J., Marangos P. J., Heydorn W. E., Chang G., Verma A., Jacobowitz D. S-100-mediated inhibition of brain protein phosphorylation. J Neurochem. 1983 Oct;41(4):1040–1045. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb09048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J., Marangos P. J. Modulation of brain protein phosphorylation by the S-100 protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 31;109(4):1089–1093. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91888-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Takai Y., Yamanishi J., Nishizuka Y. A role of calcium-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in human platelet activation. Comparison of thrombin and collagen actions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):2010–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzman R. C., Raynor R. L., Fritz R. B., Kuo J. F. Purification to homogeneity, characterization and monoclonal antibodies of phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from spleen. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):435–443. doi: 10.1042/bj2090435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W., Schulman H., Greengard P. Neuronal localization of Ca2+-dependent protein phosphorylation in brain. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):548–553. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer S. A., Lemon R. H., Fairhurst A. S. Calmodulin inhibition of brain membrane phosphorylation. J Neurochem. 1983 Oct;41(4):1090–1093. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb09056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. I. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5155–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. C., Walaas S. I., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Calcium/phospholipid regulates phosphorylation of a Mr "87k" substrate protein in brain synaptosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5249–5253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]