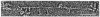Abstract
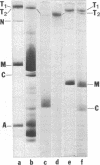
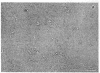
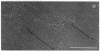
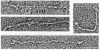
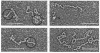
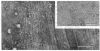
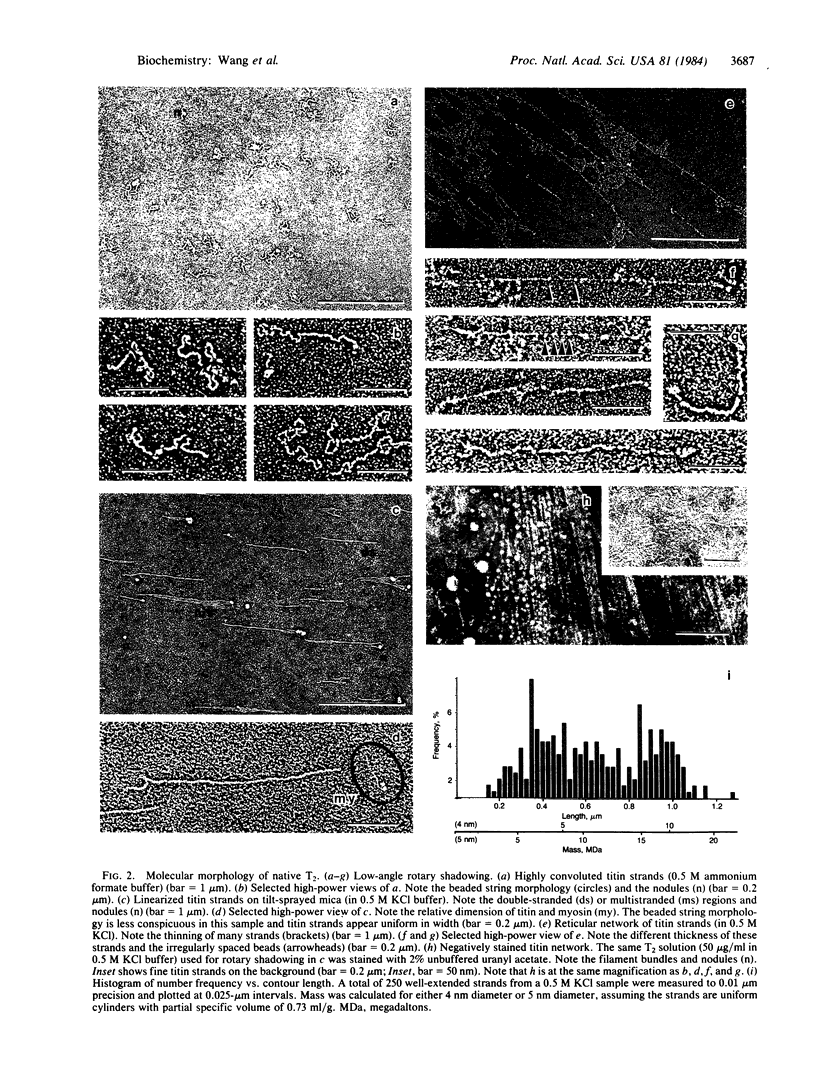
" Titin " is a term used to describe a pair of closely related megadalton polypeptides that together are the third most abundant myofibrillar protein in a wide range of striated muscles. It has been proposed that titin and another giant protein, nebulin , are the major components of an elastic cytoskeletal lattice within the sarcomere. We have now purified the leading band, titin -2 (T2), of the titin doublet in native forms by extraction with Guba -Straub solution followed by chromatography. Electron microscopy of low-angle-shadowed and negatively stained specimens revealed that T2 chains self-assembled into extremely long (from 0.1 micron to over 1.0 micron), flexible, and extensible slender strands (4-5 nm in diameter) with axial periodicity. Furthermore, these strands tended to associate to form filamentous bundles and meshworks. Thus, titin appears to be ideally suited as a component of an elastic lattice that serves as an organizing scaffold or template for thick and thin filaments.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Erickson H. P., Carrell N., McDonagh J. Fibronectin molecule visualized in electron microscopy: a long, thin, flexible strand. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):673–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDIES ON THE STRUCTURE OF NATURAL AND SYNTHETIC PROTEIN FILAMENTS FROM STRIATED MUSCLE. J Mol Biol. 1963 Sep;7:281–308. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E. Procedure for freeze-drying molecules adsorbed to mica flakes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):155–195. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Maruyama K. Preparation of native connectin from chicken breast muscle. J Biochem. 1983 Dec;94(6):2083–2085. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker R. H., Leet N. G. Histology of highly-stretched beef muscle. I. The fine structure of grossly stretched single fibers. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 Jul;52(1):64–75. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)80022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offer G., Moos C., Starr R. A new protein of the thick filaments of vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Extractions, purification and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):653–676. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr R., Offer G. Preparation of C-protein, H-protein, X-protein, and phosphofructokinase. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):130–138. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinick J. A. End-filaments: a new structural element of vertebrate skeletal muscle thick filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 15;151(2):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90517-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinick J., Elliott A. Electron microscope studies of thick filaments from vertebrate skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 15;131(1):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. M., Anderson J. M., Branton D. Structural comparison of several actin-binding macromolecules. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):489–495. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. M., Branton D. Rotary shadowing of extended molecules dried from glycerol. J Ultrastruct Res. 1980 May;71(2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(80)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., McClure J., Tu A. Titin: major myofibrillar components of striated muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3698–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K. Purification of titin and nebulin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):264–274. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Williamson C. L. Identification of an N2 line protein of striated muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3254–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]