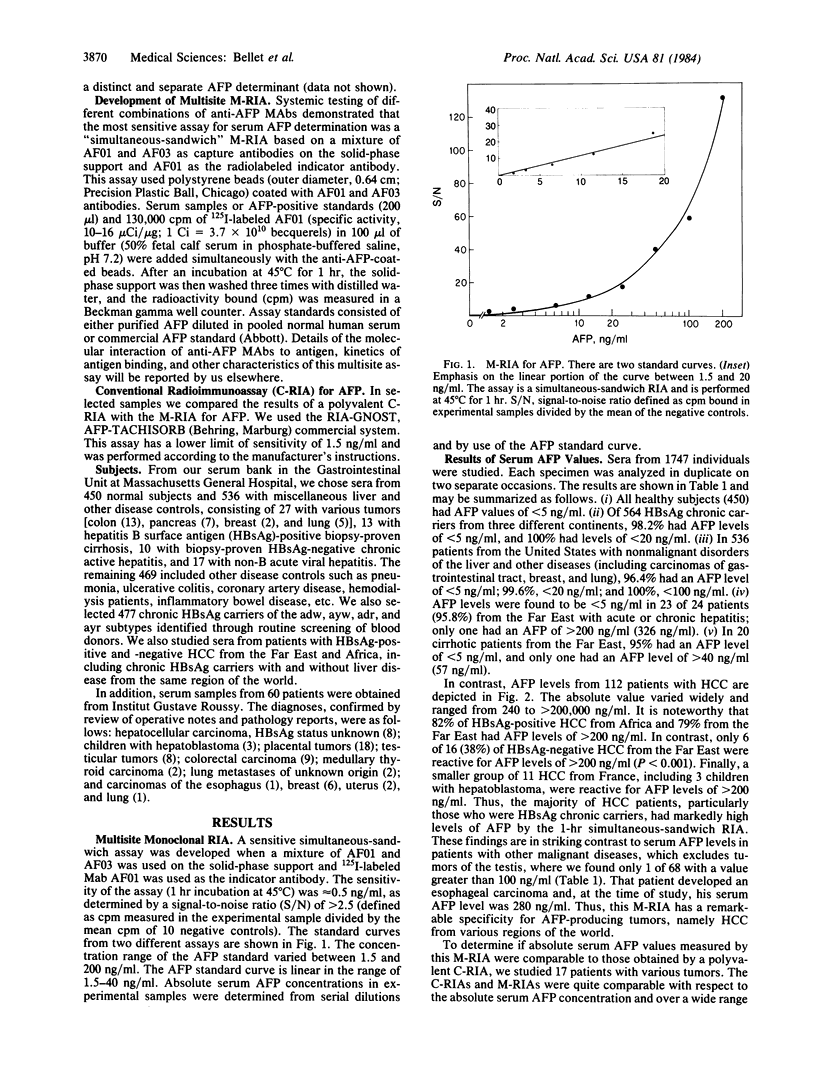
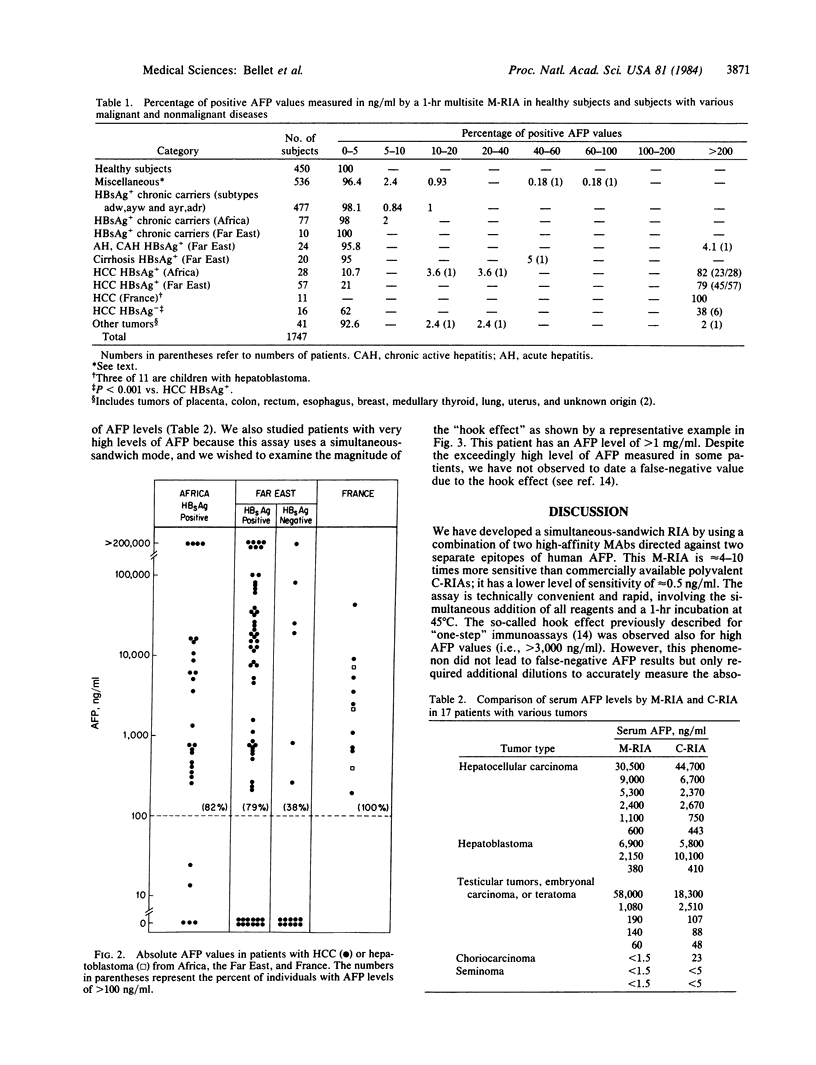
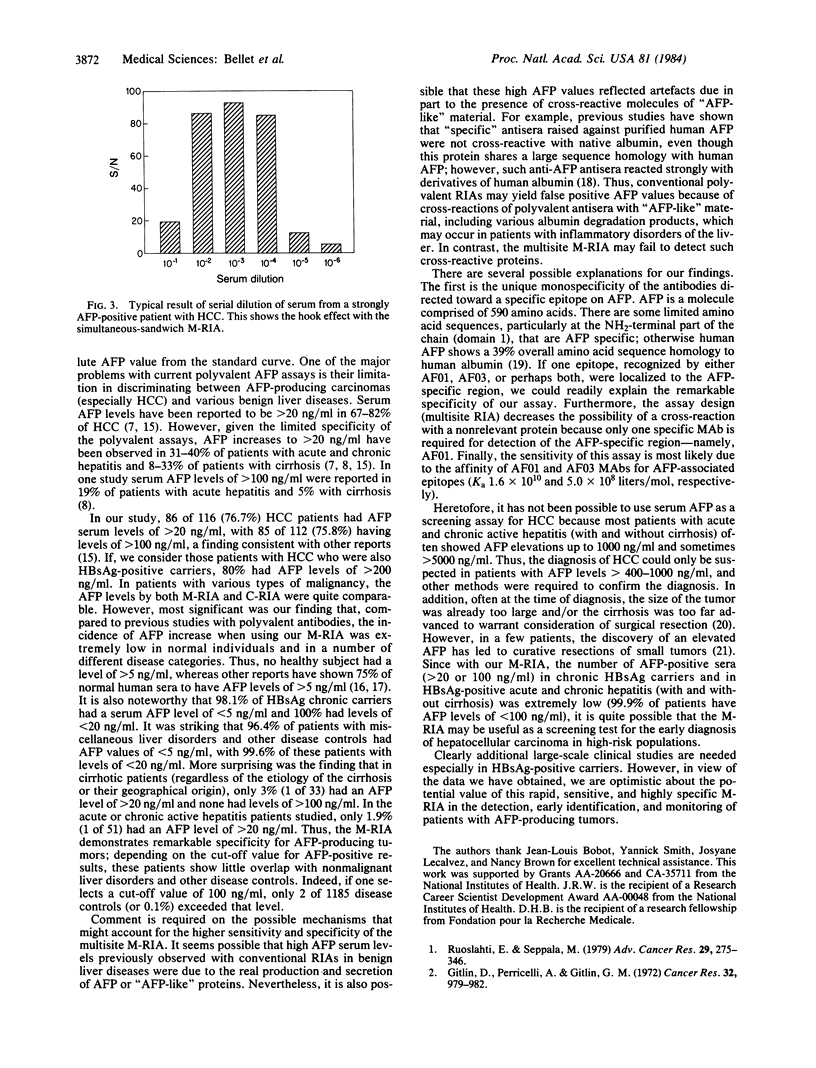
Abstract
A rapid multisite radioimmunoassay for measurement of human alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) that uses two high-affinity monoclonal antibodies directed against distinct and separate determinants on the protein was developed and designated M-RIA. The sensitivity of the "simultaneous-sandwich" M-RIA is approximately equal to 0.5 ng/ml of serum after a 1-hr incubation period. Serum AFP levels have been measured in 1747 individuals with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection, chronic hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)-carrier states, cirrhosis, other malignant tumors, and normal and disease controls to determine the specificity of the assay. Eighty percent (68/85) of patients with HBsAg-positive HCC had AFP levels of greater than 200 ng/ml (range, 260 to greater than 200,000 ng/ml). In contrast, all 450 normal subjects and 477 chronic HBsAg-positive carriers had levels of less than 20 ng/ml. More importantly, in acute and chronic hepatitis B, cirrhosis, and other malignant tumors and in the remaining disease controls, AFP levels were less than 20 ng/ml in 99.3% of the subjects, the great majority (greater than 96%) being less than 5 ng/ml. Indeed only two of 1635 individuals, one with acute hepatitis and the other with carcinoma of the esophagus had AFP levels of greater than 100 ng/ml. These observations are at variance with previous studies with conventional polyvalent RIAs of AFP levels of greater than 20 ng/ml in approximately equal to 40% of acute and chronic hepatitis and in 30% of cirrhosis. This striking specificity of the M-RIA is probably due in part to recognition of epitopes unique to AFP and suggest that such an assay may be used in the detection, early identification, and monitoring of AFP-producing tumors in high-risk populations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelev G. I. Production of embryonal serum alpha-globulin by hepatomas: review of experimental and clinical data. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1344–1350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpert E., Feller E. R. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in benign liver disease. Evidence that normal liver regeneration does not induce AFP synthesis. Gastroenterology. 1978 May;74(5 Pt 1):856–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpert E., Hershberg R., Schur P. H., Isselbacher K. J. -fetoprotein in human hepatoma: improved detection in serum, and quantitative studies using a new sensitive technique. Gastroenterology. 1971 Aug;61(2):137–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellet D., Schlumberger M., Bidart J. M., Assicot M., Caillou B., Motte P., Vignal A., Bohuon C. Production and in vitro utilization of monoclonal antibodies to human thyroglobulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Mar;56(3):530–533. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-3-530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin D., Perricelli A., Gitlin G. M. Synthesis of -fetoprotein by liver, yolk sac, and gastrointestinal tract of the human conceptus. Cancer Res. 1972 May;32(5):979–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedin A., Carlsson L., Berglund A., Hammarström S. A monoclonal antibody-enzyme immunoassay for serum carcinoembryonic antigen with increased specificity for carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3470–3474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Okuda K., Musha H., Nakashima T. Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma during a clinical follow-up of chronic liver disease: observations in 31 patients. Gastroenterology. 1978 Mar;74(3):578–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurman R. J., Scardino P. T., McIntire K. R., Waldmann T. A., Javadpour N. Cellular localization of alpha-fetoprotein and human chorionic gonadotropin in germ cell tumors of the testis using and indirect immunoperoxidase technique. Cancer. 1977 Nov;40(5):2136–2151. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197711)40:5<2136::aid-cncr2820400524>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange P. H., McIntire K. R., Waldmann T. A., Hakala T. R., Fraley E. E. Serum alpha fetoprotein and human chorionic gonadotropin in the diagnosis and management of nonseminomatous germ-cell testicular cancer. N Engl J Med. 1976 Nov 25;295(22):1237–1240. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197611252952207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morinaga T., Sakai M., Wegmann T. G., Tamaoki T. Primary structures of human alpha-fetoprotein and its mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4604–4608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Imai M., Usuda S., Nakamura T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. A pitfall in two-site sandwich 'one-step' immunoassay with monoclonal antibodies for the determination of human alpha-fetoprotein. J Immunol Methods. 1983;56(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90044-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Engvall E. Immunological crossreaction between alpha-fetoprotein and albumin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4641–4644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Salaspuro M., Pihko H., Andersson L., Seppälä M. Serum alpha-fetoprotein: diagnostic significance in liver disease. Br Med J. 1974 Jun 8;2(5918):527–529. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5918.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Seppälä M. -Foetoprotein in normal human serum. Nature. 1972 Jan 21;235(5334):161–162. doi: 10.1038/235161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Seppälä M. Studies of carcino-fetal proteins. 3. Development of a radioimmunoassay for -fetoprotein. Demonstration of -fetoprotein in serum of healthy human adults. Int J Cancer. 1971 Nov 15;8(3):374–383. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910080304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Seppälä M. alpha-Fetoprotein in cancer and fetal development. Adv Cancer Res. 1979;29:275–346. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60849-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wands J. R., Marciniak R. A., Isselbacher K. J., Varghese M., Don G., Halliday J. W., Powell L. W. Demonstration of previously undetected hepatitis B viral determinants in an Australian Aboriginal population by monoclonal anti-hbs antibody radioimmunoassays. Lancet. 1982 May 1;1(8279):977–980. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91988-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



