Abstract
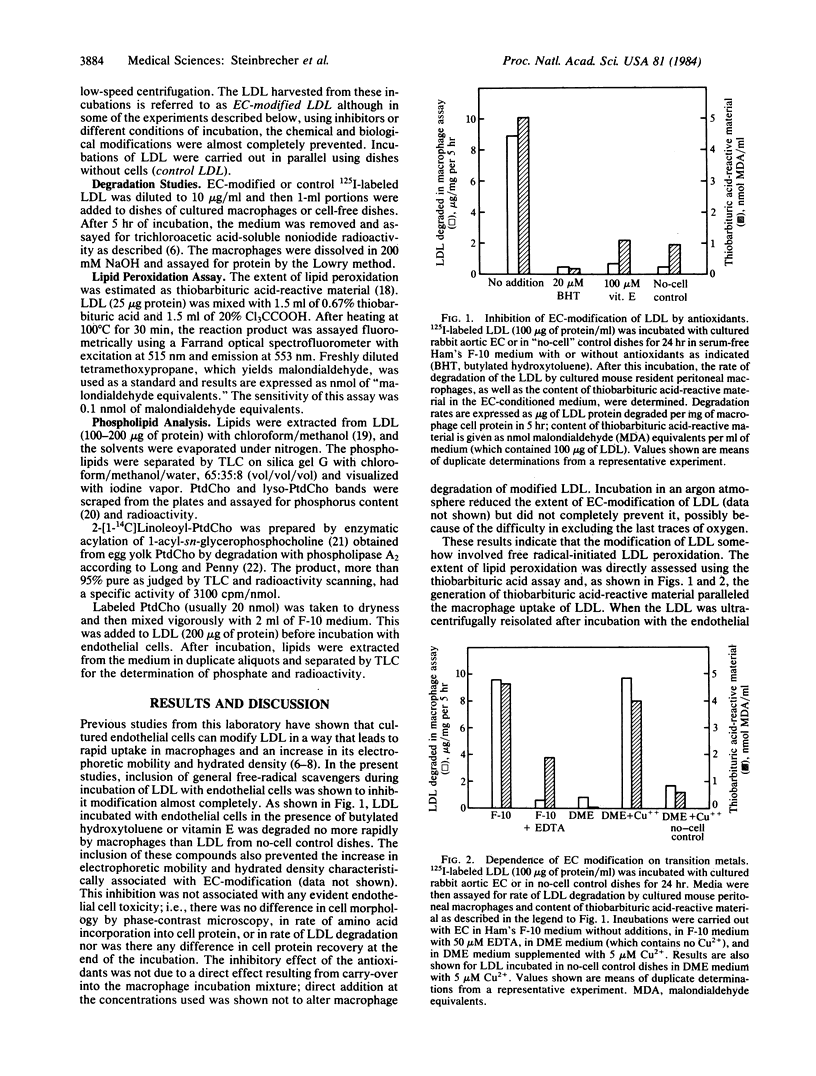
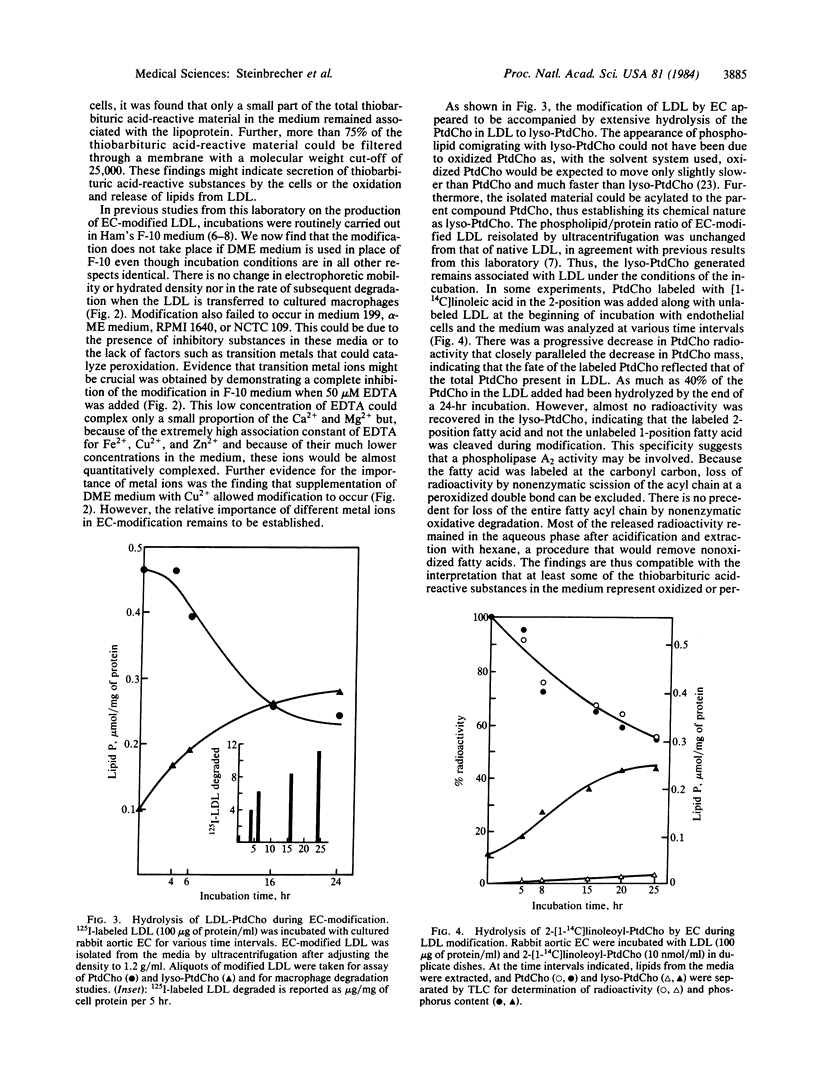
Low density lipoprotein (LDL) incubated with cultured endothelial cells from rabbit aorta or human umbilical vein is altered in several ways (EC-modified): (i) It is degraded by macrophages much faster than LDL similarly incubated in the absence of cells or incubated with fibroblasts. (ii) Its electrophoretic mobility is increased. (iii) Its density is increased. We report here that antioxidants completely prevent these changes. We also report that these changes do not take place if transition metals in the medium are chelated with EDTA. During EC-modification as much as 40% of the LDL phosphatidylcholine is degraded to lysophosphatidylcholine by a phospholipase A2-like activity. When incubation conditions in the absence of cells were selected to favor oxidation--for example, by extending the time of incubation of LDL at low concentrations, or by increasing the Cu2+ concentration--LDL underwent changes very similar to those occurring in the presence of cells, including degradation of phosphatidylcholine. Hence, some phospholipase activity appears to be associated with the isolated LDL used in these studies. The results suggest a complex process in which endothelial cells modify LDL by mechanisms involving generation of free radicals and action of phospholipase (s).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aron L., Jones S., Fielding C. J. Human plasma lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase. Characterization of cofactor-dependent phospholipase activity. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7220–7226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonassisi V., Venter J. C. Hormone and neurotransmitter receptors in an established vascular endothelial cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1612–1616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evensen S. A., Galdal K. S., Nilsen E. LDL-induced cytotoxicity and its inhibition by anti-oxidant treatment in cultured human endothelial cells and fibroblasts. Atherosclerosis. 1983 Oct;49(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(83)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler S., Shio H., Haley N. J. Characterization of lipid-laden aortic cells from cholesterol-fed rabbits. IV. Investigation of macrophage-like properties of aortic cell populations. Lab Invest. 1979 Oct;41(4):372–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Ho Y. K., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Binding site on macrophages that mediates uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Hoff H. F., Ho Y. K., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Stimulation of cholesteryl ester synthesis in macrophages by extracts of atherosclerotic human aortas and complexes of albumin/cholesteryl esters. Arteriosclerosis. 1981 May-Jun;1(3):210–226. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.1.3.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen T., Mahoney E. M., Steinberg D. Enhanced macrophage degradation of biologically modified low density lipoprotein. Arteriosclerosis. 1983 Mar-Apr;3(2):149–159. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.3.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen T., Mahoney E. M., Steinberg D. Enhanced macrophage degradation of low density lipoprotein previously incubated with cultured endothelial cells: recognition by receptors for acetylated low density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6499–6503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriksen T., Mahoney E. M., Steinberg D. Interactions of plasma lipoproteins with endothelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;401:102–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L., Deykin D. Activation of phospholipases A2 and C in pig aortic endothelial cells synthesizing prostacyclin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7151–7154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONG C., PENNY I. F. The structure of the naturally occurring phosphoglycerides. III. Action of moccasin-venom phospholipase A on ovolecithin and related substances. Biochem J. 1957 Feb;65(2):382–389. doi: 10.1042/bj0650382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. M. Malondialdehyde formation in stored plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 29;95(4):1663–1672. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Weisgraber K. B., Oh S. Y. Altered metabolism (in vivo and in vitro) of plasma lipoproteins after selective chemical modification of lysine residues of the apoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):743–750. doi: 10.1172/JCI109518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel D. W., Hessler J. R., Chisolm G. M. Low density lipoprotein cytotoxicity induced by free radical peroxidation of lipid. J Lipid Res. 1983 Aug;24(8):1070–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON A. F., LANDS W. E. Positional specificites in phospholipid hydrolyses. Biochemistry. 1962 Sep;1:804–810. doi: 10.1021/bi00911a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond T. L., Reynolds S. A. Lipoproteins of the extravascular space: alterations in low density lipoproteins of interstitial inflammatory fluid. J Lipid Res. 1983 Feb;24(2):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner T., Taylor K., Bartucci E. J., Fischer-Dzoga K., Beeson J. H., Glagov S., Wissler R. W. Arterial foam cells with distinctive immunomorphologic and histochemical features of macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jul;100(1):57–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh J., Fairclough G. F., Jr, Haschemeyer R. H. Oxygen-mediated heterogeneity of apo-low-density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3173–3177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevanian A., Muakkassah-Kelly S. F., Montestruque S. The influence of phospholipase A2 and glutathione peroxidase on the elimination of membrane lipid peroxides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jun;223(2):441–452. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90608-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter I., Fogelman A. M., Haberland M. E., Seager J., Hokom M., Edwards P. A. The metabolism of native and malondialdehyde-altered low density lipoproteins by human monocyte-macrophages. J Lipid Res. 1981 Jan;22(1):63–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., Kaduce T. L., Hoak J. C., Fry G. L. Utilization of arachidonic and linoleic acids by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1003–1011. doi: 10.1172/JCI110322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. B., Carew T. E., Steinberg D. Uptake and degradation of low density lipoprotein by swine arterial smoot muscle cells with inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 26;424(3):404–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K. A simple fluorometric assay for lipoperoxide in blood plasma. Biochem Med. 1976 Apr;15(2):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(76)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



