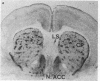
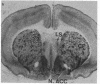
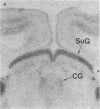
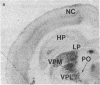
Abstract
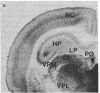
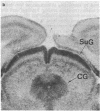
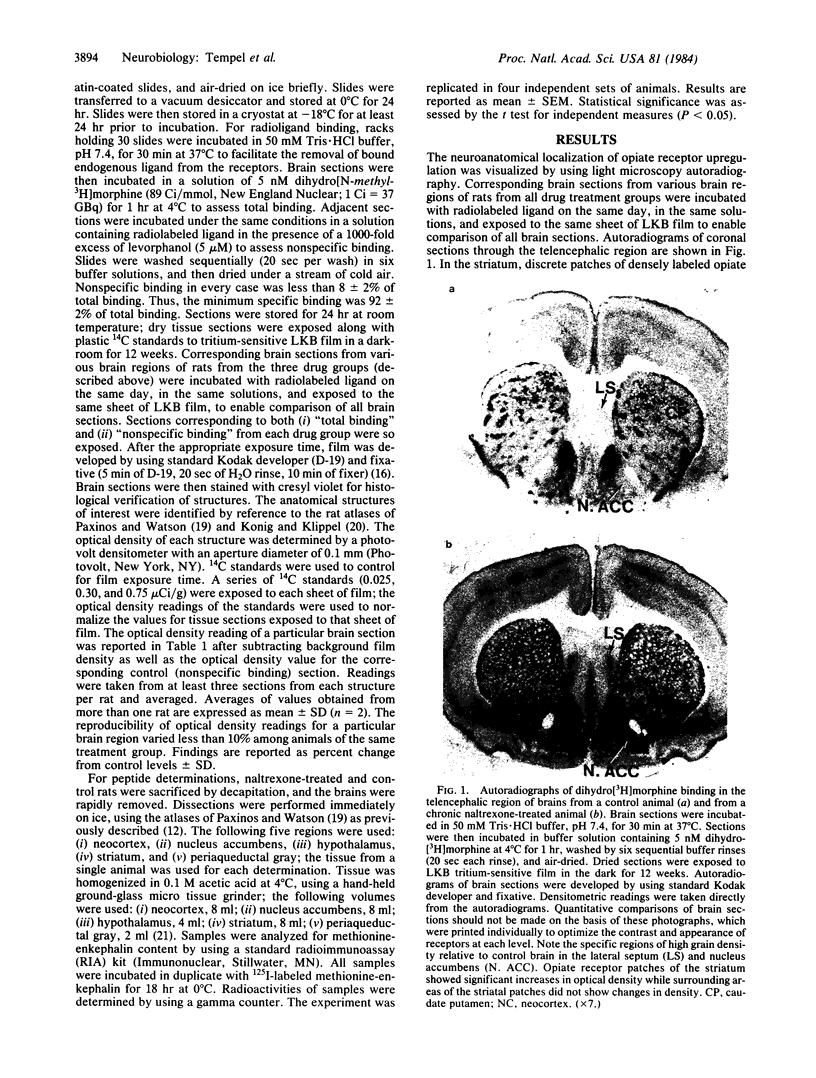
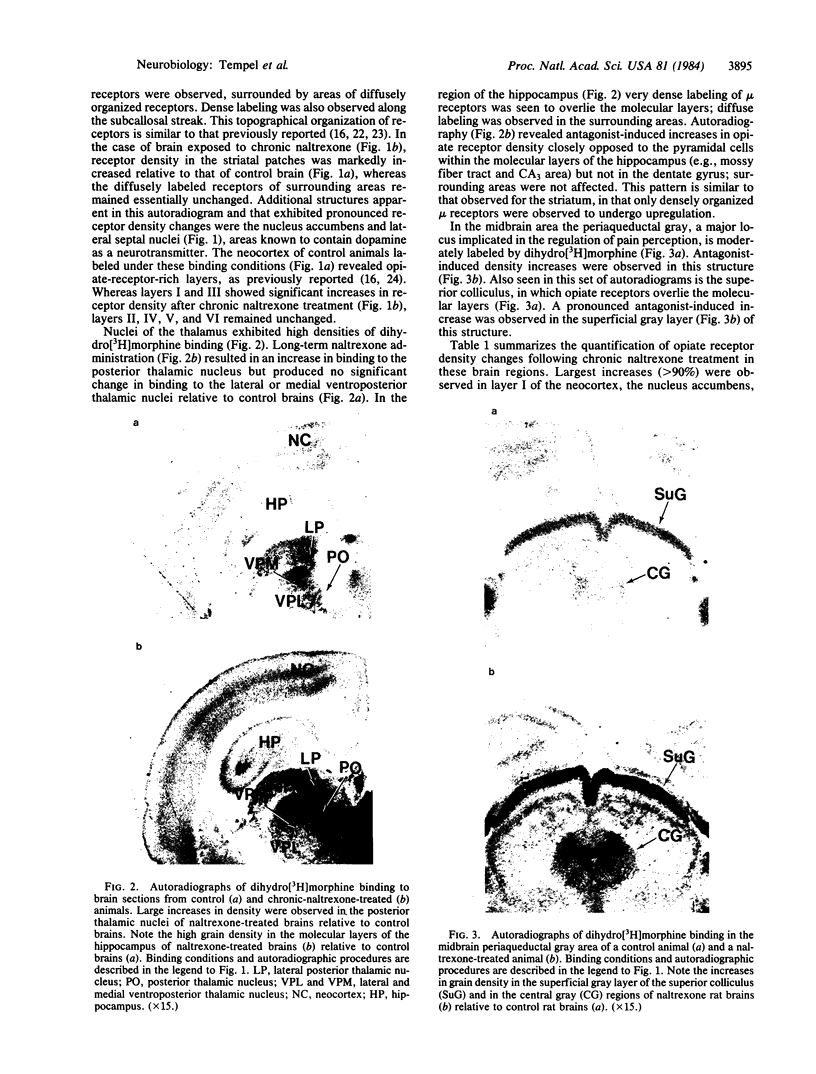
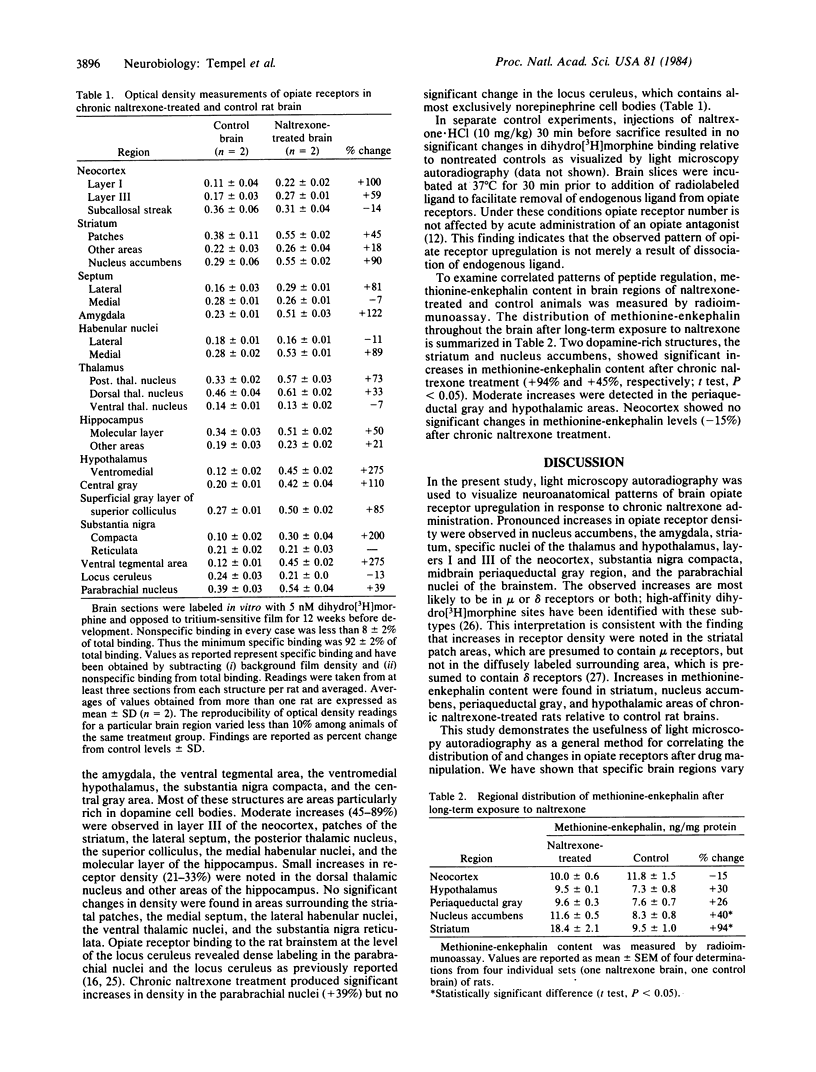
Light microscopy autoradiography has been used to visualize neuroanatomical patterns of brain opiate receptor upregulation in response to chronic naltrexone administration. Slide-mounted brain sections of frozen rat brain were labeled in vitro with dihydro[3H]morphine, a relatively selective mu opioid ligand. The greatest relative increases in opiate receptor density were observed in the nucleus accumbens, the amygdala, striatal patches, nuclei of the thalamus and hypothalamus, layers I and III of neocortex, substantia nigra compacta, midbrain periaqueductal gray regions, and the parabrachial nuclei of the brainstem. The substantia nigra reticulata, surrounding areas of striatal patches, and the locus ceruleus, were not affected by this drug treatment. These findings demonstrate that chronically administered naltrexone differentially regulates opiate receptors throughout the brain. In particular, three brain systems appear to be target areas of receptor upregulation : (i) the dopamine A9/A10 systems, (ii) the limbic system, and (iii) structures that receive input from afferent sensory pathways. Two possible mechanisms to account for this finding are (i) that the drug does not have uniform effects throughout the brain or (ii) that the receptors themselves may be associated with different functional systems. Receptor density changes are paralleled by increases in methionine-enkephalin content in the striatum, nucleus accumbens, periaqueductal gray, and hypothalamic areas of chronic naltrexone-treated rats relative to control rats. Thus opiate receptors and opioid peptides appear to be subject to regulatory mechanisms similar to those that modulate other neurotransmitters and their receptors. These results document in a visual manner brain patterns of opiate receptor upregulation .
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. III. The telencephalon. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 14;134(3):393–405. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90817-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardo M. T., Bhatnagar R. K., Gebhart G. F. Differential effects of chronic morphine and naloxone on opiate receptors, monoamines, and morphine-induced behaviors in preweanling rats. Brain Res. 1982 Jun;256(2):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(82)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggio G., Casu M., Corda M. G., Di Bello C., Gessa G. L. Stimulation of dopamine synthesis in caudate nucleus by intrastriatal enkephalins and antagonism by naloxone. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):552–554. doi: 10.1126/science.205949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard S. G., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Characterization of the association of tritiated enkephalin with neuroblastoma cells under conditions optimal for receptor down regulation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1092–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Eckel R. W., Blanchard S. G. Opioid peptides induce reduction of enkephalin receptors in cultured neuroblastoma cells. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):446–448. doi: 10.1038/296446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner E. L., Zukin R. S., Makman M. H. Modulation of opiate receptor binding in striatum and amygdala by selective mesencephalic lesions. Brain Res. 1980 Jul 21;194(1):232–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Snyder S. H. Kappa opiate receptors localized by autoradiography to deep layers of cerebral cortex: relation to sedative effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5703–5707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Snyder S. H., Kuhar M. J., Young W. S., 3rd Differentiation of delta and mu opiate receptor localizations by light microscopic autoradiography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6239–6243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Pert C. B. In vitro autoradiography of opiate receptors in rat brain suggests loci of "opiatergic" pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5532–5536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Pert C. B. Light microscopic localization of brain opiate receptors: a general autoradiographic method which preserves tissue quality. J Neurosci. 1982 Aug;2(8):1129–1149. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-08-01129.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzemann R. J., Hitzemann B. A., Loh H. H. Binding of 3H-naloxone in the mouse brain: effect of ions and tolerance development. Life Sci. 1974 Jun 16;14(12):2393–2404. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holaday J. W., Hitzemann R. J., Curell J., Tortella F. C., Belenky G. L. Repeated electroconvulsive shock or chronic morphine treatment increases the number of 3H-D-Ala2,D-Leu5-enkephalin binding sites in rat brain membranes. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 15;31(20-21):2359–2362. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Yang H. Y., Fratta W., Costa E. Determination of methionine enkephalin in discrete regions of rat brain. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 7;134(2):383–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee W. A., Streaty R. A. Narcotic receptor sites in morphine-dependent rats. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):61–63. doi: 10.1038/248061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer D. J., Liebeskind J. C. Pain reduction by focal electrical stimulation of the brain: an anatomical and behavioral analysis. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 15;68(1):73–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90534-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer D. J., Price D. D. Central nervous system mechanisms of analgesia. Pain. 1976 Dec;2(4):379–404. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(76)90080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan H. S., Frey K. A., Young A. B., Penney J. B., Jr Changes in [3H]muscimol binding in substantia nigra, entopeduncular nucleus, globus pallidus, and thalamus after striatal lesions as demonstrated by quantitative receptor autoradiography. J Neurosci. 1983 Jun;3(6):1189–1198. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-06-01189.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D. C., Rosenbaum J. S., Sadee W. In vivo binding of 3H-etorphine in morphine-dependent rats. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 20;31(12-13):1405–1408. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90392-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: autoradiographic localization in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3729–3733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Pasternak G., Snyder S. H. Opiate agonists and antagonists discriminated by receptor binding in brain. Science. 1973 Dec 28;182(4119):1359–1361. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4119.1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H., Llorens-Cortes C., Schwartz J. C. Enkephalin receptors on dopaminergic neurones in rat striatum. Nature. 1977 Aug 25;268(5622):745–747. doi: 10.1038/268745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragavan V. V., Wardlaw S. L., Kreek M. J., Frantz A. G. Effect of chronic naltrexone and methadone administration on brain immunoreactive beta-endorphin in the rat. Neuroendocrinology. 1983 Oct;37(4):266–268. doi: 10.1159/000123556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R., Wüster M., Herz A. Supersensitivity to opioids following the chronic blockade of endorphin action by naloxone. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;306(1):93–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00515600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C., Pollard H., Llorens C., Malfroy B., Gros C., Pradelles P., Dray F. Endorphins and endorphin receptors in striatum: relationships with dopaminergic neurons. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1978;18:245–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Hiller J. M. In vitro studies on opiate receptors and their ligands. Fed Proc. 1978 Feb;37(2):141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang A. H., Collins R. J. Enhanced analgesic effects of morphine after chronic administration of naloxone in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Feb 15;47(4):473–474. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin R. S., Sugarman J. R., Fitz-Syage M. L., Gardner E. L., Zukin S. R., Gintzler A. R. Naltrexone-induced opiate receptor supersensitivity. Brain Res. 1982 Aug 12;245(2):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90811-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin R. S., Zukin S. R. Multiple opiate receptors: emerging concepts. Life Sci. 1981 Dec 28;29(26):2681–2690. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90527-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]