Abstract
Evidence is presented that has led us to abandon the hypothesis that receptor-mediated cyclic GMP formation in cultured nerve cells occurs via the influx of extracellular calcium ions and an increase in the cytosolic free calcium ion concentration. While the cyclic GMP response is absolutely dependent on the presence of Ca2+, there is no increase in free intracellular Ca2+ subsequent to agonist stimulation. Instead, we have found that muscarinic or histamine H1 receptor stimulation elicits the release of arachidonic acid through a quinacrine-sensitive mechanism, possibly phospholipase A2. Inhibition of the release or metabolism of arachidonate by the lipoxygenase pathway prevents receptor-mediated cyclic GMP formation. We hypothesize that neurotransmitter receptors that mediate cyclic GMP synthesis function by releasing arachidonic acid and that an oxidative metabolite of arachidonic acid then stimulates soluble guanylate cyclase.
Full text
PDF

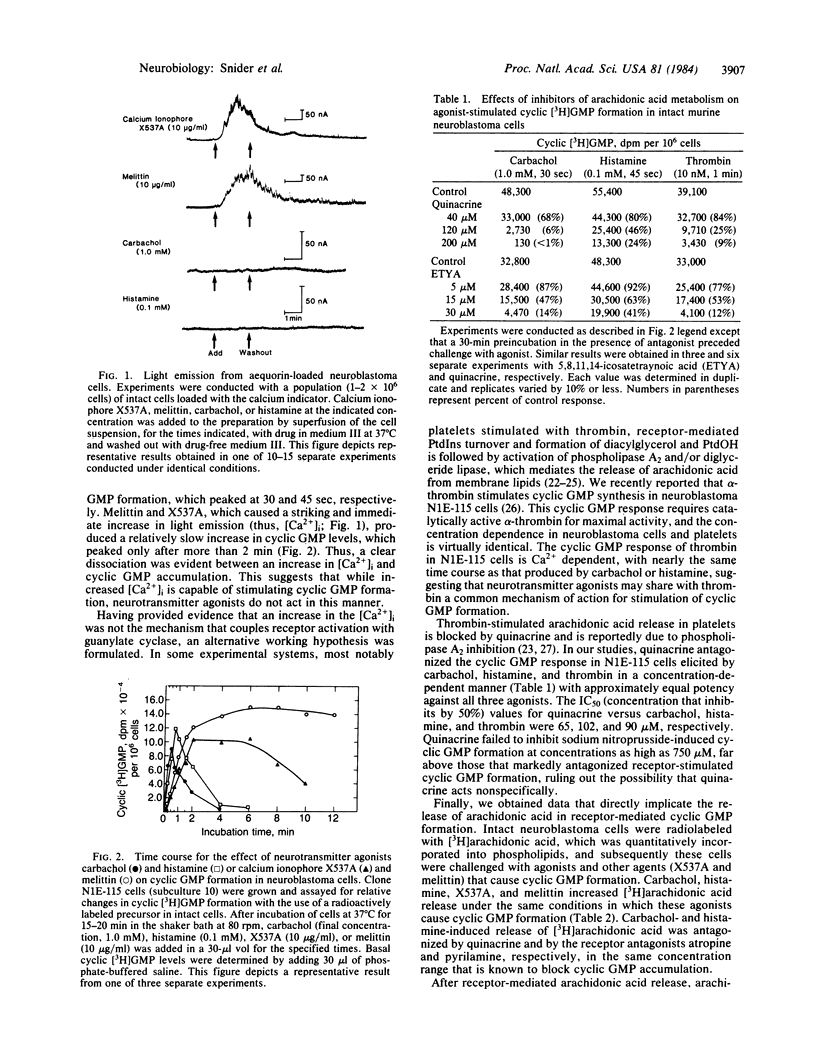
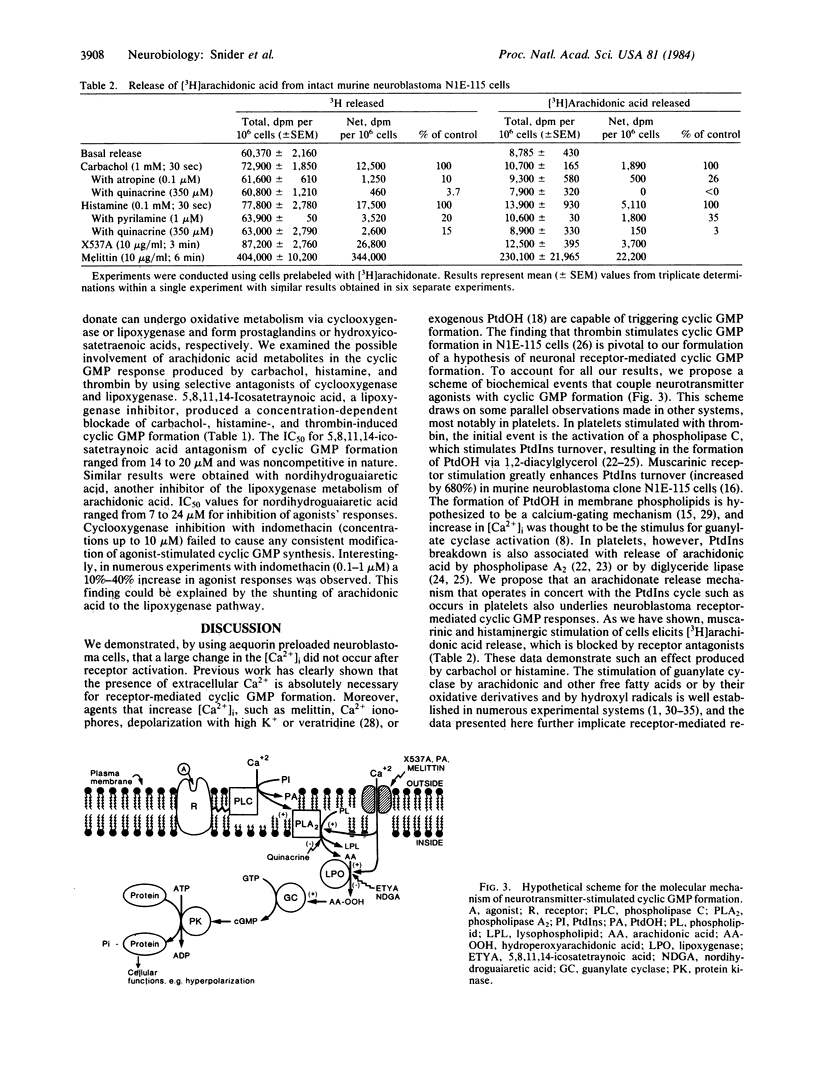

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agranoff B. W., Murthy P., Seguin E. B. Thrombin-induced phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2076–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfai T., Breakefield X. O., Greengard P. Regulation of synthesis of guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in neuroblastoma cells. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 15;176(1):119–127. doi: 10.1042/bj1760119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis: a multifunctional transducing mechanism. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Nov;24(2):115–140. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G. Formation of lysophosphatidylinositol in platelets stimulated with thrombin or ionophore A23187. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5196–5200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Wier W. G., Hess P., Prendergast F. G. Measurement of Ca2+ concentrations in living cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;40(1-2):1–114. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen N. M., Schmidt D. M., McGlennen R. C., Klein W. L. Receptor-mediated increases in phosphatidylinositol turnover in neuron-like cell lines. J Neurochem. 1983 Feb;40(2):547–554. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb11317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., DeRubertis F. R. Ca2+.Calmodulin-dependent release of arachidonic acid for renal medullary prostaglandin synthesis. Evidence for involvement of phospholipases A2 and C. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4814–4823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., DeRubertis F. R. Calcium and O2-dependent control of inner medullary cGMP: possible role for Ca2+-dependent arachiodonate release and prostaglandin synthesis in expression of the action of osmolality on renal inner medullary guanosine 3'5' monophosphate. Metabolism. 1980 Sep;29(9):842–853. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90123-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P. Receptor-stimulated inositol phospholipid metabolism in the central nervous system. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):413–428. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes P., Michell R. H. Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate: lipids in search of a function. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):467–502. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Fakahany E., Richelson E. Effect of some calcium antagonists on muscarinic receptor-mediated cyclic GMP formation. J Neurochem. 1983 Mar;40(3):705–710. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Fakahany E., Richelson E. Involvement of calcium channels in short-term desensitization of muscarinic receptor-mediated cyclic GMP formation in mouse neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6897–6901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Fakahany E., Richelson E. Regulation of muscarinic receptor-mediated cyclic GMP synthesis by cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem. 1980 Oct;35(4):941–948. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb07093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerzer R., Hamet P., Ross A. H., Lawson J. A., Hardman J. G. Calcium-induced release from platelet membranes of fatty acids that modulate soluble guanylate cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jul;226(1):180–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerzer R., Hamet P., Ross A. H., Lawson J. A., Hardman J. G. Calcium-induced release from platelet membranes of fatty acids that modulate soluble guanylate cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jul;226(1):180–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg N. D., Haddox M. K. Cyclic GMP metabolism and involvement in biological regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:823–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Asano T. Stimulation of human platelet guanylate cyclase by unsaturated fatty acid peroxides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3657–3661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Billah M. M., Cuatrecasas P. The initial action of thrombin on platelets. Conversion of phosphatidylinositol to phosphatidic acid preceding the production of arachidonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5037–5040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Billah M. M., Cuatrecasas P. The phosphatidylinositol cycle and the regulation of arachidonic acid production. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):367–369. doi: 10.1038/292367a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiber D., Harbon S. The relationship between the carbachol stimulatory effect on cyclic GMP content and activation by fatty acid hydroperoxides of a soluble guanylate cyclase in the guinea pig myometrium. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 May;21(3):654–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzawa H., Nirenberg M. Receptor-mediated shifts in cGMP and cAMP levels in neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3472–3476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClellan G. B., Winegrad S. The regulation of the calcium sensitivity of the contractile system in mammalian cardiac muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Dec;72(6):737–764. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.6.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Vascular smooth muscle: the first recorded Ca2+ transients. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):75–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00584972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld E. J., Majerus P. W. Arachidonate release and phosphatidic acid turnover in stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2461–2467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsako S., Deguchi T. Stimulation of phosphatidic acid of calcium influx and cyclic GMP synthesis in neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10945–10948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. M., Majerus P. W. Characterization of 1,2-diacylglycerol hydrolysis in human platelets. Demonstration of an arachidonoyl-monoacylglycerol intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):764–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelson E. Antipsychotics block muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated cyclic GMP formation in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. Nature. 1977 Mar 24;266(5600):371–373. doi: 10.1038/266371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelson E. Desensitisation of muscarinic receptor-mediated cyclic GMP formation by cultured nerve cells. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):366–368. doi: 10.1038/272366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelson E., El-Fakahany E. The molecular basis of neurotransmission at the muscarinic receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Nov 1;30(21):2887–2891. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90248-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelson E. Histamine H1 receptor-mediated guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate formation by cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. Science. 1978 Jul 7;201(4350):69–71. doi: 10.1126/science.26974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelson E., Prendergast F. G., Divinetz-Romero S. Muscarinic receptor-mediated cyclic GMP formation by cultured nerve cells--ionic dependence and effects of local anesthetics. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(16):2039–2048. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richelson E. Tricyclic antidepressants block histamine H1 receptors of mouse neuroblastoma cells. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):176–177. doi: 10.1038/274176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rillema J. A. Activation of guanylate cyclase by arachidonic acid in mammary gland homogenates from mice. Prostaglandins. 1978 May;15(5):857–865. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(78)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz G., Hardman J. G., Schultz K., Baird C. E., Sutherland E. W. The importance of calcium ions for the regulation of guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphage levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3889–3893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shier W. T. Activation of high levels of endogenous phospholipase A2 in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):195–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider R. M., Richelson E. Thrombin stimulation of guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate formation in murine neuroblastoma cells (clone N1E-115). Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):566–568. doi: 10.1126/science.6306770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies C., Schultz K. D., Schultz G. Inhibitory effects of mepacrine and eicosatetraynoic acid on cyclic GMP elevations caused by calcium and hormonal factors in rat ductus deferens. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;311(1):71–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00500305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Study R. E., Breakefield X. O., Bartfai T., Greengard P. Voltage-sensitive calcium channels regulate guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate levels in neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6295–6299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. Y., Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin stimulates human platelet phospholipase A2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 27;90(2):473–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



