Abstract
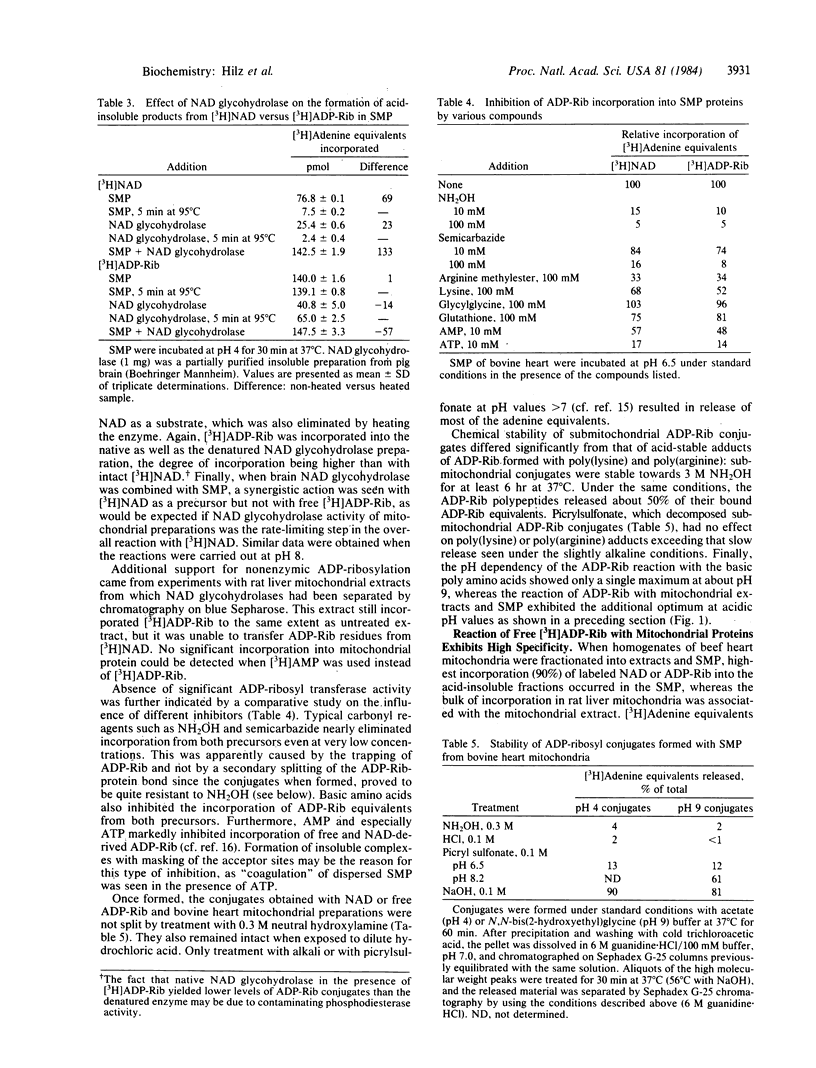
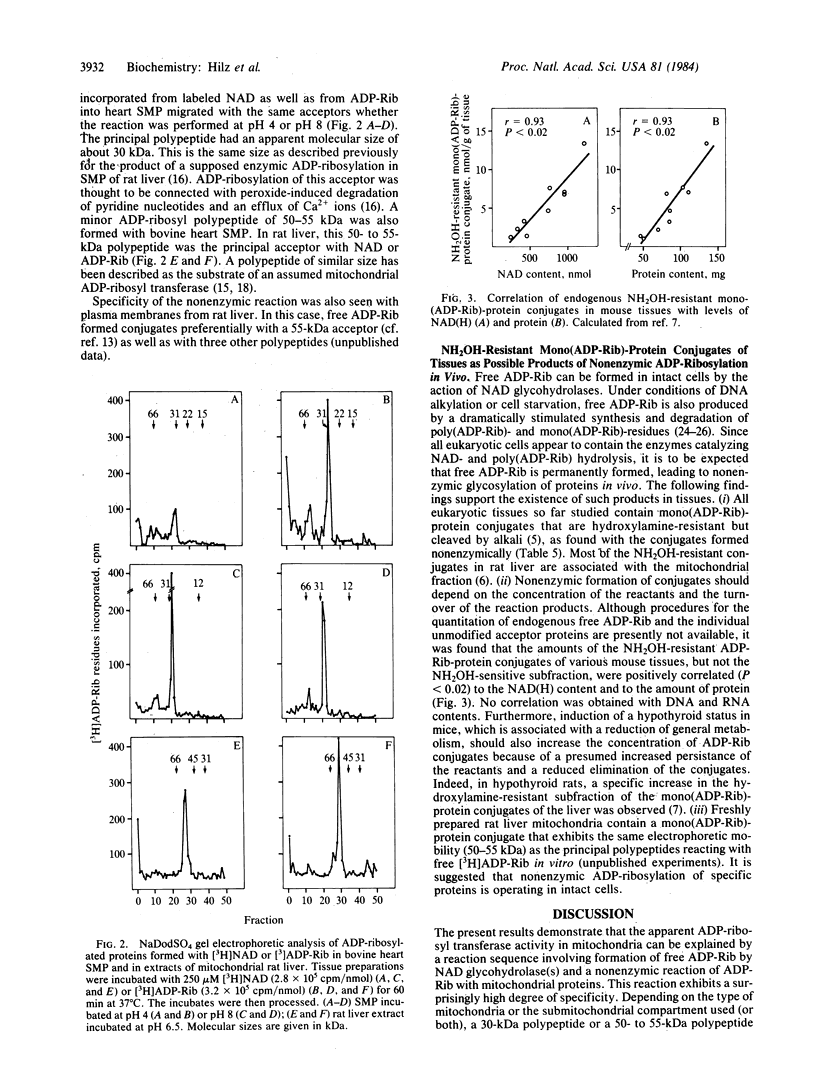
The apparent NAD:protein ADP-ribosyl transferase activity of mitochondria and submitochondrial particles from beef heart and rat liver is simulated by a reaction sequence that consists of an enzymic hydrolysis of NAD to ADP-ribose (ADP-Rib) by NAD glycohydrolase(s) and a nonenzymic ADP-ribosylation of acceptor proteins by the free ADP-Rib formed. The nonenzymic ADP-ribosylation of mitochondrial proteins showed two pH optima and exhibited the same remarkable selectivity as the reaction with NAD. The predominant acceptor in beef heart mitochondria was a 30-kDa protein, whereas in mitochondrial extracts of rat liver a 50-55 kDa polypeptide served as an acceptor. No authentic ADP-Rib transferase activity could be detected even when free ADP-Rib was trapped by NH2OH. Once formed, the mitochondrial ADP-Rib conjugates were resistant to hydroxylamine. NH2OH-resistant mono(ADP-Rib)-protein conjugates as found in most cells may also be products of nonenzymic ADP-ribosylation. In mouse tissues, their amounts relate to protein and NAD contents, and they increase specifically and reversibly in the hypothyroid status. Furthermore, intact rat liver mitochondria contain a mono(ADP-Rib)-polypeptide (50-55 kDa) that appeared to be identical with the polypeptide reacting with ADP-Rib in vitro.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamietz P., Wielckens K., Bredehorst R., Lengyel H., Hilz H. Subcellular distribution of mono(ADP-ribose) protein conjugates in rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jul 16;101(1):96–103. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckner S. K., Blecher M. Endogenous and cholera toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of a plasma membrane protein by RL-PR-C cloned rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 3;673(4):477–486. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90479-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Pfeuffer T. Mechanism of cholera toxin action: covalent modification of the guanyl nucleotide-binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbay K. H., Hasty K., Breslow J. L., Ellison R. C., Bunn H. F., Gallop P. M. Glycosylated hemoglobins and long-term blood glucose control in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 May;44(5):859–864. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-5-859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Meren R. ADP-ribosylation of membrane proteins catalyzed by cholera toxin: basis of the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilz H., Stone P. Poly(ADP-ribose) and ADP-ribosylation of proteins. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1976;76:1-58, 177. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter W., Mühlebach T., Lötscher H. R., Winterhalter K. H., Richter C. ATP prevents both hydroperoxide-induced hydrolysis of pyridine nucleotides and release of calcium in rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(2):361–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Hayaishi O. Diphtheria toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3553–3555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. L., Antol K. M., Juarez-Salinas H., Jacobson M. K. Poly(ADP-ribose) metabolism in ultraviolet irradiated human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):103–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaslow H. R., Johnson G. L., Brothers V. M., Bourne H. R. A regulatory component of adenylate cyclase from human erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3736–3741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreimeyer A., Wielckens K., Adamietz P., Hilz H. DNA repair-associated ADP-ribosylation in vivo. Modification of histone H1 differs from that of the principal acceptor proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):890–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kun E., Chang A. C., Sharma M. L., Ferro A. M., Nitecki D. Covalent modification of proteins by metabolites of NAD+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3131–3135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kun E., Kirsten E., Piper W. N. Stabilization of mitochondrial functions with digitonin. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:115–118. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kun E., Zimber P. H., Chang A. C., Puschendorf B., Grunicke H. Macromolecular enzymatic product of NAD+ in liver mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1436–1440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner C., Hilz H. ADP-ribosyl-protein conjugate subclasses in various tissues. Specific influence of thyroid hormone on liver conjugates. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 15;206(1):61–65. doi: 10.1042/bj2060061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lötscher H. R., Winterhalter K. H., Carafoli E., Richter C. Hydroperoxides can modulate the redox state of pyridine nucleotides and the calcium balance in rat liver mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4340–4344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel P., Okazaki H., Niedergang C. Poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose). Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1982;27:1–51. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60596-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Manganiello V. C., Vaughan M. Hydrolysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide by choleragen and its A protomer: possible role in the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4424–4427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Stanley S. J. Amino acid-specific ADP-ribosylation. Identification of an arginine-dependent ADP-ribosyltransferase in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7830–7833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Ueda K., Yoshihara K., Yamamura H., Takeda M., Hayaishi O. Enzymic adenosine diphosphoribosylation of nuclear proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:781–786. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolde S., Hilz H. Extracellular NAD as a cytostatic agent. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Apr;353(4):505–513. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.1.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer N. J., Bodley J. W. Diphtheria toxin. Site and configuration of ADP-ribosylation of diphthamide in elongation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8579–8581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purnell M. R., Stone P. R., Whish W. J. ADP-ribosylation of nuclear proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Apr;8(2):215–227. doi: 10.1042/bst0080215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römer V., Lambrecht J., Kittler M., Hilz H. Identity of nuclear NAD nucleosidase with a polyADP-ribose forming enzyme in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1968 Jan;349(1):109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sies H., Graf P., Estrela J. M. Hepatic calcium efflux during cytochrome P-450-dependent drug oxidations at the endoplasmic reticulum in intact liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3358–3362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbanowski J. C., Cohenford M. A., Dain J. A. Nonenzymatic galactosylation of human serum albumin. In vitro preparation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):111–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wielckens K., George E., Pless T., Hilz H. Stimulation of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation during Ehrlich ascites tumor cell "starvation" and suppression of concomitant DNA fragmentation by benzamide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4098–4104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wielckens K., Schmidt A., George E., Bredehorst R., Hilz H. DNA fragmentation and NAD depletion. Their relation to the turnover of endogenous mono(ADP-ribosyl) and poly(ADP-ribosyl) proteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12872–12877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



