Abstract
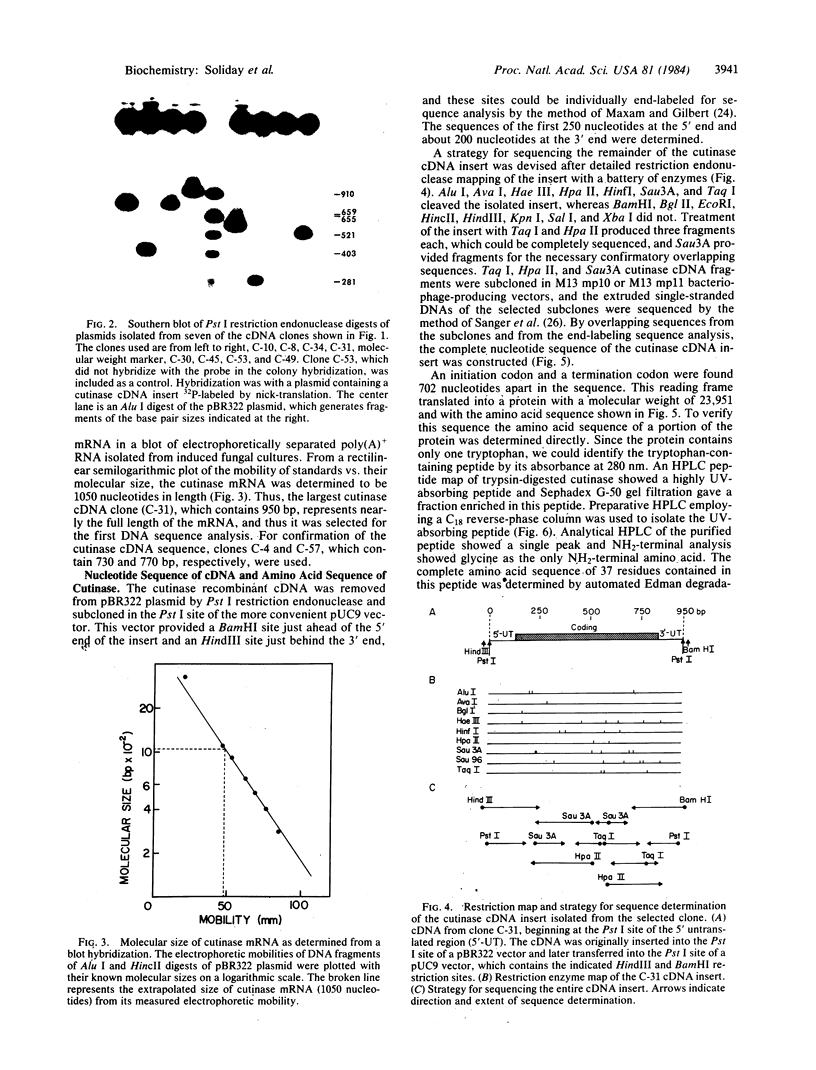
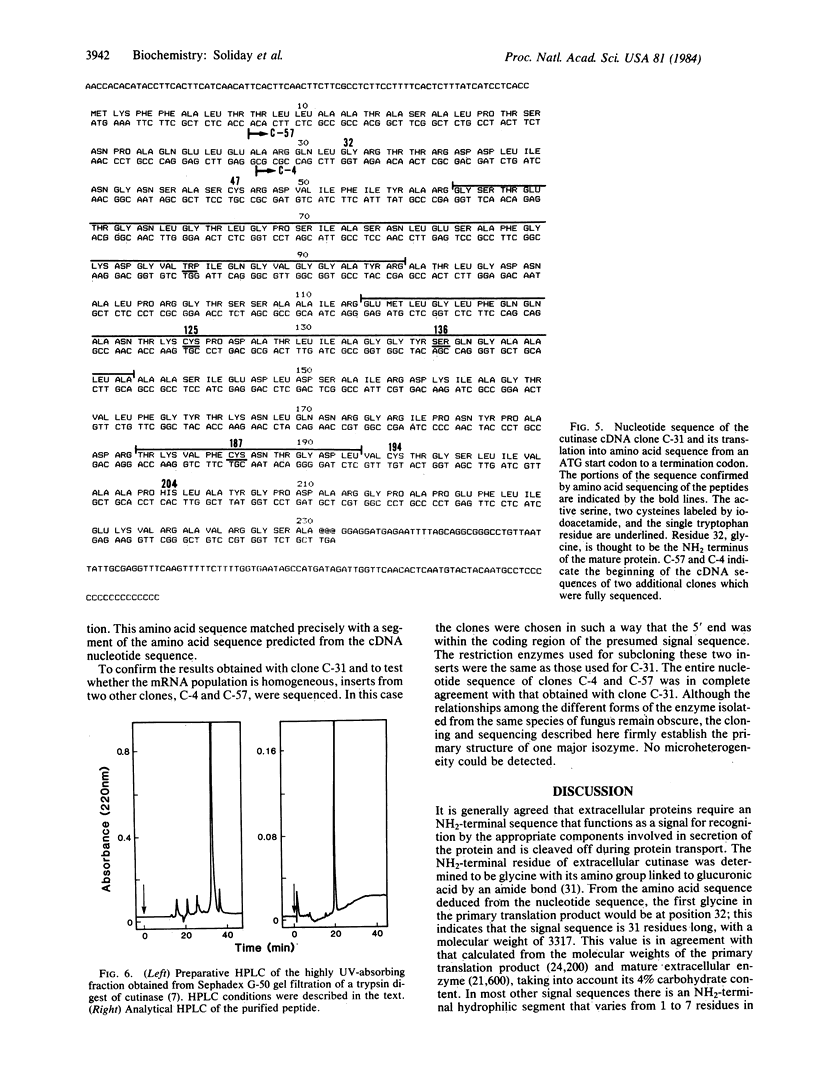
The primary structure of cutinase, an extracellular fungal enzyme involved in the penetration of plants by pathogenic fungi, has been determined from the nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA. Clones containing cDNA made from poly(A)+ RNA isolated from fungal cultures induced to synthesize cutinase were screened for their ability to hybridize with the [32P]cDNA for mRNA unique to the induced culture. The 75 cDNA clones thus identified were screened for the cutinase genetic code by hybrid-selected translation and examination of products with anti-cutinase IgG. This method yielded 15 clones containing cDNA for cutinase, and Southern blots showed that the size of the cDNA inserts ranged from 279 to 950 nucleotides. Blot analysis showed that cutinase mRNA contained 1050 nucleotides, indicating that the clone containing 950 nucleotides represented nearly the entire mRNA. This near-full-length cDNA and the restriction fragments subcloned from it were sequenced by a combination of the Maxam-Gilbert and the phage M13-dideoxy techniques. cDNAs from two other clones, containing the bulk of the coding region for cutinase, were also completely sequenced, and the results confirmed the sequence obtained with the first clone. A peptide isolated from a trypsin digest of cutinase was sequenced and the amino acid sequence as well as the initiation and termination codons were used to identify the coding region of the cDNA. The primary structure of the enzyme so far determined by amino acid sequencing (≈40% of the total) agreed completely with the nucleotide sequencing results. Thus, the complete primary structure of the mature enzyme and that of the signal peptide region were ascertained.
Keywords: cDNA cloning, nucleotide sequencing, amino acid sequencing, fungal cutinase
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell G. N., Wickens M. P., Payvar F., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of full length cDNAs from four partially purified oviduct mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2471–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouin J. Cloning of human mitochondrial DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 15;140(1):15–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Silhavy T. J. Molecular components of the signal sequence that function in the initiation of protein export. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):689–696. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flurkey W. H., Kolattukudy P. E. In vitro translation of cutinase mRNA: evidence for a precursor form of an extracellular fungal enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Nov;212(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köller W., Kolattukudy P. E. Mechanism of action of cutinase: chemical modification of the catalytic triad characteristic for serine hydrolases. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3083–3090. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. S., Kolattukudy P. E. Induction of a biopolyester hydrolase (cutinase) by low levels of cutin monomers in Fusarium solani f.sp. pisi. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):942–951. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.942-951.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. S., Kolattukudy P. E. Structural studies on cutinase, a glycoprotein containing novel amino acids and glucuronic acid amide at the N terminus. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):341–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K., Dudock B. Characterization of a highly efficient protein synthesizing system derived from commercial wheat germ. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1385–1397. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Tocci M. J., Monahan J. J. On the cloning of eukaryotic total poly(A)-RNA populations in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7665–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Wu R. Terminal transferase-catalyzed addition of nucleotides to the 3' termini of DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):43–62. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soliday C. L., Kolattukudy P. E. Primary structure of the active site region of fungal cutinase, an enzyme involved in phytopathogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 12;114(3):1017–1022. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90663-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. P., Buell G. N., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of double-stranded DNA complementary to lysozyme, ovomucoid, and ovalbumin mRNAs. Optimization for full length second strand synthesis by Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2483–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):17–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]