Abstract
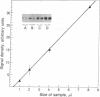
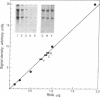
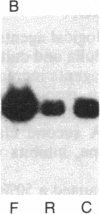
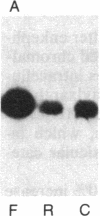
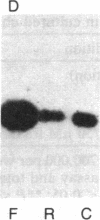
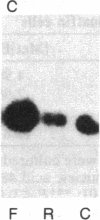
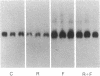
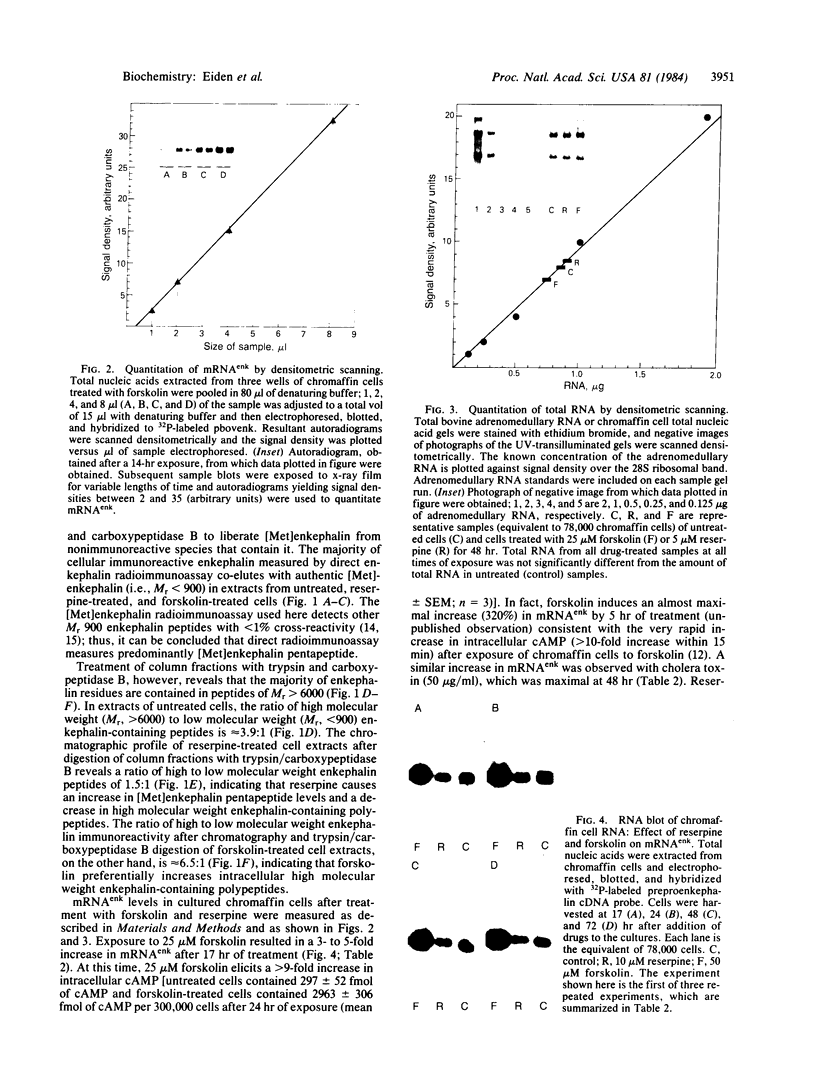
Exposure of bovine chromaffin cells in primary culture to 5 microM reserpine or 25 microM forskolin results in an increase in enkephalin peptide levels within 24-48 hr; 25 microM forskolin (or cholera toxin at 50 micrograms/ml) causes a 1.5- to 2-fold increase in enkephalin peptide levels, which is maximal after 48 hr of exposure and is totally blocked by addition of cycloheximide (0.5 microgram/ml). Reserpine (5 microM) elicits a 1.5- to 2-fold increase in enkephalin peptide levels within 24 hr, which is only partially blocked by cycloheximide. Chromatographic analysis of cellular extracts shows that forskolin increases levels of both [Met]enkephalin pentapeptide and high molecular weight enkephalin-containing peptides, while reserpine causes an increase in [Met]enkephalin pentapeptide and a concomitant decrease in high molecular weight enkephalin-containing peptides, suggesting enhanced conversion of enkephalin precursor(s) to the mature polypeptide hormone. Measurement of preproenkephalin messenger RNA (mRNAenk) by RNA blot hybridization with a cDNA probe for mRNAenk reveals that forskolin and cholera toxin cause a relatively rapid (less than 17 hr) 3- to 5-fold increase in mRNAenk, while exposure to reserpine elicits a gradual decrease in enkephalin mRNA (a 50%-80% decline) beginning within 24 hr and continuing over a 72-hr period. These results suggest that forskolin and reserpine differentially regulate enkephalin biosynthesis in cultured chromaffin cells, the former by increasing, presumably via a cAMP-dependent mechanism, cellular mRNA coding for preproenkephalin and the latter by a post-translational increase in proenkephalin processing.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cascio S. M., Wassarman P. M. Program of early development in the mammal: post-transcriptional control of a class of proteins synthesized by mouse oocytes and early embryos. Dev Biol. 1982 Feb;89(2):397–408. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90328-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Seeburg P. H., Adelman J., Eiden L., Herbert E. Primary structure of the human Met- and Leu-enkephalin precursor and its mRNA. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):663–666. doi: 10.1038/295663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandekar S., Sabol S. L. Cell-free translation and partial characterization of mRNA coding for enkephalin-precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1017–1021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E., Eskay R. L., Scott J., Pollard H., Hotchkiss A. J. Primary cultures of bovine chromaffin cells synthesize and secrete vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP). Life Sci. 1983 Aug 22;33(8):687–693. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90772-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E., Hotchkiss A. J. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate regulates vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and enkephalin biosynthesis in cultured bovine chromaffin cells. Neuropeptides. 1983 Dec;4(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(83)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker L. D., Snyder S. H. Purification and characterization of enkephalin convertase, an enkephalin-synthesizing carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10950–10955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Seeburg P., Hoffman B. J., Gage L. P., Udenfriend S. Molecular cloning establishes proenkephalin as precursor of enkephalin-containing peptides. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):206–208. doi: 10.1038/295206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Kurosawa A., Costa E. Association between the increase of cAMP content and the trans-synaptic induction of tyrosine hydroxylase in rat adrenal medulla. Studies with dexamethasone and reserpine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;295(2):135–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00499445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook V. Y., Eiden L. E., Brownstein M. J. A carboxypeptidase processing enzyme for enkephalin precursors. Nature. 1982 Jan 28;295(5847):341–342. doi: 10.1038/295341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Kaumeyer J. F., Young E. M., Raff R. A. A test for masked message: the template activity of messenger ribonucleoprotein particles isolated from sea urchine eggs. Dev Biol. 1978 Apr;63(2):279–298. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Scarpa A. Protonmotive force and catecholamine transport in isolated chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3750–3760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoth J., Handloser K., Njus D. Electrogenic epinephrine transport in chromaffin granule ghosts. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 24;19(13):2938–2942. doi: 10.1021/bi00554a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumakura K., Guidotti A., Costa E. Primary cultures of chromaffin cells: molecular mechanisms for the induction of tyrosine hydroxylase mediated by 8-Br-cyclic AMP. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(3):865–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. V., Stern A. S. Biosynthesis of the enkephalins and enkephalin-containing polypeptides. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:353–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G., Dean D. M., Whelan L. G., Udenfriend S., Rossier J. Co-release of enkephalin and catecholamines from cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):317–319. doi: 10.1038/289317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch G. H., Rosenfeld M. G. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulation and chromatin-associated protein phosphorylation by cyclic AMP. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.6293056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Hirose T., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for bovine adrenal preproenkephalin. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):202–206. doi: 10.1038/295202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J., Dean D. M., Livett B. G., Udenfriend S. Enkephalin congeners and precursors are synthesized and released by primary cultures of adrenal chromaffin cells. Life Sci. 1981 Feb 16;28(7):781–789. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., Moen R. C., Davidson J. M., Byers P. H., Bornstein P., Palmiter R. D. Correlation of procollagen mRNA levels in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts with different rates of procollagen synthesis. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1581–1590. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Daly J. W. Forskolin: a unique diterpene activator of cyclic AMP-generating systems. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;7(4):201–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stine S. M., Yang H. Y., Costa E. Release of enkephalin-like immunoreactive material from isolated bovine chromaffin cells. Neuropharmacology. 1980 Jul;19(7):683–685. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(80)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Kilpatrick D. L. Biochemistry of the enkephalins and enkephalin-containing peptides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):309–323. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungar A., Phillips J. H. Regulation of the adrenal medulla. Physiol Rev. 1983 Jul;63(3):787–843. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.3.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viveros O. H., Arqueros L., Connett R. J., Kirshner N. Mechanism of secretion from the adrenal medulla. IV. The fate of the storage vesicles following insulin and reserpine administration. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;5(1):69–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viveros O. H., Arqueros L., Kirshner N. Mechanism of secretion from the adrenal medulla. VI. Effect of reserpine on the dopamine -hydroxylase and catecholamine content and on the buoyant density of adrenal storage vesicles. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Jul;7(4):434–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. P., Chang K. J., Viveros O. H. Opioid peptide synthesis in bovine and human adrenal chromaffin cells. Peptides. 1981;2 (Suppl 1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(81)90060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. P., Chang K. J., Viveros O. H. Synthesis of enkephalins by adrenal medullary chromaffin cells: reserpine increases incorporation of radiolabeled amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4364–4368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]