Abstract
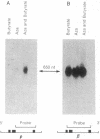
Adult White Leghorn chickens were rendered anemic by injection with 1-acetyl-2-phenylhydrazine and then treated with parenteral 5-azacytidine, and levels of embryonic globin RNA in circulating reticulocytes were measured. A very small but detectable amount of correctly initiated embryonic p-type globin RNA was detected in reticulocytes from birds treated with 5-azacytidine, while none was detected in reticulocytes from those receiving only phenylhydrazine or phenylhydrazine plus 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (cytosine arabinonucleoside). An attempt to increase embryonic globin RNA induction by treatment with parenteral sodium butyrate after 7 days of 5-azacytidine administration resulted in a 5- to 10-fold increase in the level of embryonic globin RNA. However, sodium butyrate did not induce embryonic gene expression when given alone or after treatment with cytosine arabinonucleoside. Sodium butyrate treatment also caused a DNase I-hypersensitive site to be exposed at the 5' end of the rho-globin gene only after 5-azacytidine induced demethylation of several CpG sites in and around the gene. The implications of this model of gene activation in vivo are discussed in the context of multistep gene regulation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. C., Jokinen M., Gahmberg C. G. Induction of erythroid differentiation in the human leukaemia cell line K562. Nature. 1979 Mar 22;278(5702):364–365. doi: 10.1038/278364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Doederlein G., Freudenstein C., Graf T. Erythroblast cell lines transformed by a temperature-sensitive mutant of avian erythroblastosis virus: a model system to study erythroid differentiation in vitro. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1982;1:195–207. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. L., Ingram V. M. Structural studies on chick embryonic hemoglobins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3960–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Hurst J., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation and the regulation of globin gene expression. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candido E. P., Reeves R., Davie J. R. Sodium butyrate inhibits histone deacetylation in cultured cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charache S., Dover G., Smith K., Talbot C. C., Jr, Moyer M., Boyer S. Treatment of sickle cell anemia with 5-azacytidine results in increased fetal hemoglobin production and is associated with nonrandom hypomethylation of DNA around the gamma-delta-beta-globin gene complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4842–4846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compere S. J., Palmiter R. D. DNA methylation controls the inducibility of the mouse metallothionein-I gene lymphoid cells. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covault J., Chalkley R. The identification of distinct populations of acetylated histone. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9110–9116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSimone J., Heller P., Hall L., Zwiers D. 5-Azacytidine stimulates fetal hemoglobin synthesis in anemic baboons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4428–4431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation--a regulatory signal in eukaryotic gene expression. J Gen Virol. 1981 Nov;57(Pt 1):1–20. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D. Analysis of the adult chicken beta-globin gene. Nucleotide sequence of the locus, microheterogeneity at the 5'-end of beta-globin mRNA, and aberrant nuclear RNA species. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3983–3990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan M., Sugarman B. J., Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D. Chromosomal arrangement of the chicken beta-type globin genes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):669–677. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G., McGhee J. Methylation and gene control. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):602–603. doi: 10.1038/296602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradin A., Manley J. L., Prives C. L. Methylation of simian virus 40 Hpa II site affects late, but not early, viral gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5142–5146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginder G. D., Wood W. I., Felsenfeld G. Isolation and characterization of recombinant clones containing the chicken adult beta-globin gene. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8099–8102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation of cloned human beta-globin genes by viral immediate-early gene products. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Eisenman R., Weintraub H. Chromatin structure of endogenous retroviral genes and activation by an inhibitor of DNA methylation. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):311–317. doi: 10.1038/292311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Propagation of globin DNAase I-hypersensitive sites in absence of factors required for induction: a possible mechanism for determination. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., Taylor S. M. Cellular differentiation, cytidine analogs and DNA methylation. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruh J. Effects of sodium butyrate, a new pharmacological agent, on cells in culture. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Feb 5;42(2):65–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00222695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Leder P. Butyric acid, a potent inducer of erythroid differentiation in cultured erythroleukemic cells. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Wilson B. Enhanced phosphorylation of high-mobility-group proteins in nuclease-sensitive mononucleosomes from butyrate-treated HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2189–2193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley T. J., DeSimone J., Anagnou N. P., Keller G. H., Humphries R. K., Turner P. H., Young N. S., Keller P., Nienhuis A. W. 5-azacytidine selectively increases gamma-globin synthesis in a patient with beta+ thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 9;307(24):1469–1475. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212093072401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Chambon P. DNA methylation: organ specific variations in the methylation pattern within and around ovalbumin and other chicken genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2081–2103. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Ginder G. D. Specific DNA methylation sites in the vicinity of the chicken beta-globin genes. Nature. 1979 Aug 2;280(5721):419–420. doi: 10.1038/280419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Riggs A. D. DNA methylation and gene function. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):604–610. doi: 10.1126/science.6254144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs M. G., Whittaker R. G., Neumann J. R., Ingram V. M. n-Butyrate causes histone modification in HeLa and Friend erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):462–464. doi: 10.1038/268462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Chalkley R. The effect of sodium butyrate on histone modification. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C. K., Maniatis T. Tissue-specific DNA methylation in a cluster of rabbit beta-like globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6634–6638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Razin A., Cedar H. In vitro methylation of the hamster adenine phosphoribosyltransferase gene inhibits its expression in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3418–3422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Kressmann A., Cedar H., Maechler M., Doerfler W. Expression of a cloned adenovirus gene is inhibited by in vitro methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1073–1077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Beug H., Groudine M., Graf T. Temperature-sensitive changes in the structure of globin chromatin in lines of red cell precursors transformed by ts-AEV. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):931–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Larsen A., Groudine M. Alpha-Globin-gene switching during the development of chicken embryos: expression and chromosome structure. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Bingham P. M., Livak K. J., Holmgren R., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: I. Evidence for higher order domains of defined DNA sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ploeg L. H., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation in the human gamma delta beta-globin locus in erythroid and nonerythroid tissues. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):947–958. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]