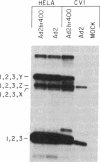
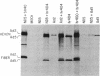
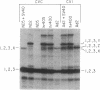
Abstract
Messenger RNA encoding the fiber protein of the human adenovirus serotype 2 (Ad2) capsid is inefficiently translated in abortively infected African green monkey kidney cells. The amount of fiber mRNA present in the cytoplasm of abortively infected monkey cells is less than that in productively infected cells by a factor of 5-10 but synthesis of the fiber polypeptide is reduced by a factor of more than 100. Evidence from a variety of experiments indicates that the defect does not lie in the translational apparatus of the monkey cell but may best be explained by differences in the fiber messages made in abortively versus productively infected cells. Here we report that fiber mRNA isolated from abortively infected monkey cells is processed differently than that made in productively infected cells. Primer extension analysis of the 5' ends of fiber messages from several different productive and abortive infections shows a direct correlation between synthesis of the fiber polypeptide in vivo and the presence of the "x" and/or "y" ancillary leaders on messages encoding the fiber polypeptide. Of all the mRNAs encoded by the major late transcriptional unit of Ad2 only the fiber message can contain the x and y leaders, and the fiber protein is the only late Ad2 protein reported to be glycosylated. We speculate that these leader sequences play a role in the synthesis of this glycoprotein, as well as that of the Ad2 19-kilodalton glycoprotein encoded by early region 3, whose mRNA also contains the x and y leaders.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akusjärvi G., Pettersson U. Sequence analysis of adenovirus DNA: complete nucleotide sequence of the spliced 5' noncoding region of adenovirus 2 hexon messenger RNA. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):841–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W., Hardy M. M., Dunn J. J., Klessig D. F. Independent, spontaneous mutants of adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrid Ad2+ND3 that grow efficiently in monkey cells possess indentical mutations in the adenovirus type 2 DNA-binding protein gene. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):31–39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.31-39.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W. Spontaneous mutants of the adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrid, Ad2+ND3, that grow efficiently in monkey cells. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90670-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Klessig D. F. Posttranscriptional block to synthesis of a human adenovirus capsid protein in abortively infected monkey cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):31–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Klessig D. F. Synthesis of human adenovirus early RNA species is similar in productive and abortive infections of monkey and human cells. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):748–754. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.748-754.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babich A., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr, Weinberger C. Effect of adenovirus on metabolism of specific host mRNAs: transport control and specific translational discrimination. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1212–1221. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R. The spliced structures of adenovirus 2 fiber message and the other late mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):497–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey G., Lewis J. B., Grodzicker T., Bothwell A. Characterization of a fused protein specified by the adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrid Ad2+ND1 dp2. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):201–217. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.201-217.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Sharp P. A. Adenovirus transcription. V. Quantitation of viral RNA sequences in adenovirus 2-infected and transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):749–774. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. P., Lyons M. J., Ginsberg H. S. Biochemical consequences of type 2 adenovirus and Simian virus 40 double infections of African green monkey kidney cells. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):586–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.586-597.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F., Wills N., Lewis J. B., Grodzicker T. Identification of amber and ochre mutants of the human virus Ad2+ND1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4567–4571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Piatak M., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Determination of RNA sequences by primer directed synthesis and sequencing of their cDNA transcripts. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):580–595. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Nakajima K., Oda K., Shimojo H. Complementation of translational defect for growth of human adenovirus type 2 in Simian cells by a Simian virus 40-induced factor. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 5;81(2):207–223. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérissé J., Courtois G., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the EcoRI D fragment of adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2173–2192. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérissé J., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the EcoRI E fragment of adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1229–1240. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi M., Maizel J. V., Jr The polypeptides of adenovirus. VI. Early and late glycopolypeptides. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):345–361. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Lewis A. M., Jr Use of nondefective adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrids for mapping the simian virus 40 genome. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):643–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.643-652.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Anderson C. W. Block to multiplication of adenovirus serotype 2 in monkey cells. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1650–1668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1650-1668.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Chow L. T. Incomplete splicing and deficient accumulation of the fiber messenger RNA in monkey cells infected by human adenovirus type 2. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 15;139(2):221–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F., Grodzicker T. Mutations that allow human Ad2 and Ad5 to express late genes in monkey cells map in the viral gene encoding the 72K DNA binding protein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):957–966. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90335-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klessig D. F. Isolation of a variant of human adenovirus serotype 2 that multiplies efficiently on monkey cells. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1243–1246. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1243-1246.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., van Schaik F. M., Sussenbach J. S. Structure and organization of the gene coding for the DNA binding protein of adenovirus type 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4439–4457. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Levin M. J., Wiese W. H., Crumpacker C. S., Henry P. H. A nondefective (competent) adenovirus-SV40 hybrid isolated from the AD.2-SV40 hybrid population. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1128–1135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Levine A. S., Crumpacker C. S., Levin M. J., Samaha R. J., Henry P. H. Studies of nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. V. Isolation of additional hybrids which differ in their simian virus 40-specific biological properties. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):655–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.655-664.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the "docking protein'. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):647–650. doi: 10.1038/297647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Steps in the processing of Ad2 mRNA: poly(A)+ nuclear sequences are conserved and poly(A) addition precedes splicing. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Jansson M., Philipson L. Synthesis and genomic site for an adenovirus type 2 early glycoprotein. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 5;136(4):375–394. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Philipson L., Höglund S. Structural proteins of adenoviruses. II. Purification and characterization of the adenovirus type 2 fiber antigen. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):204–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90261-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Klessig D. F. Normal translation of human adenovirus mRNA in cell-free lysates prepared from abortively as well as productively infected monkey cells. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):426–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.426-430.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABSON A. S., O'CONOR G. T., BEREZESKY I. K., PAUL F. J. ENHANCEMENT OF ADENOVIRUS GROWTH IN AFRICAN GREEN MONKEY KIDNEY CELL CULTURES BY SV40. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 May;116:187–190. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich P. R., Baum S. G., Rose J. A., Rowe W. P., Weissman S. M. Nucleic acid homology studies of adenovirus type 7-SV40 interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):336–341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Klessig D. F. The function(s) provided by the adenovirus-specified, DNA-binding protein required for viral late gene expression is independent of the role of the protein in viral DNA replication. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):35–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.35-49.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Weinberger C., Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA is required for efficient translation of viral mRNAs at late times after infection. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C., Tjian R., Hu S. L., Grodzicker T. Translational control of SV40 T antigen expressed from the adenovirus late promoter. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):455–464. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90427-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén M., Svensson C., Josephson S., Aleström P., Chattapadhyaya J. B., Pettersson U., Philipson L. Leader arrangement in the adenovirus fiber mRNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):249–254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine R. C., Pereira H. G. Antigens and structure of the adenovirus. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen A., Aleström P., Persson H., Katze M. G., Pettersson U. An adenovirus agnogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2539–2548. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum III. Signal recognition protein (SRP) causes signal sequence-dependent and site-specific arrest of chain elongation that is released by microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):557–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain S., Sambrook J., Roberts R. J., Keller W., Fried M., Dunn A. R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the leader segments in a cloned copy of adenovirus 2 fiber mRNA. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):851–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorn G. A., Anderson C. W. Adenovirus type 2 expresses fiber in monkey-human hybrids and reconstructed cells. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):759–769. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.759-769.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]