Abstract
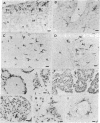
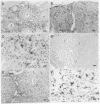
Macrophages of endocrine organs have been identified by immunohistochemical localization of the macrophage-specific antigen F4/80. F4/80+ cells line vascular sinuses and capillaries in anterior and posterior pituitary, adrenal cortex, corpus luteum, parathyroid, pineal gland, and islets of Langerhans. In testis approximately 20% of interstitial cells are F4/80+. F4/80+ cells infiltrate corpus luteum in increased numbers during luteolysis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austyn J. M., Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Oct;11(10):805–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULMER D. THE HISTOCHEMISTRY OF OVARIAN MACROPHAGES IN THE RAT. J Anat. 1964 Jul;98:313–319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergh A. Paracrine regulation of Leydig cells by the seminiferous tubules. Int J Androl. 1983 Feb;6(1):57–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.1983.tb00323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Bonney R. J. Secretory products of mononuclear phagocytes: a brief review. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Jul;26(1):37–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland J., Setton C., Silverstein E. Angiotensin converting enzyme: induction by steroids in rabbit alveolar macrophages in culture. Science. 1977 Jul 1;197(4298):64–65. doi: 10.1126/science.194311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch S., Austyn J. M., Gordon S. Expression of the macrophage-specific antigen F4/80 during differentiation of mouse bone marrow cells in culture. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):713–725. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume D. A., Gordon S. Mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80. Identification of resident macrophages in renal medullary and cortical interstitium and the juxtaglomerular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1704–1709. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume D. A., Perry V. H., Gordon S. Immunohistochemical localization of a macrophage-specific antigen in developing mouse retina: phagocytosis of dying neurons and differentiation of microglial cells to form a regular array in the plexiform layers. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):253–257. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume D. A., Robinson A. P., MacPherson G. G., Gordon S. The mononuclear phagocyte system of the mouse defined by immunohistochemical localization of antigen F4/80. Relationship between macrophages, Langerhans cells, reticular cells, and dendritic cells in lymphoid and hematopoietic organs. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1522–1536. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K. L., Laychock S. G. Prostaglandin synthesis and metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets of the rat. Prostaglandins. 1981 May;21(5):759–769. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(81)90233-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch T. M., Friedman A. C., Vogel R. L., Flickinger G. L. Macrophages in corpora lutea of mice: characterization and effects on steroid secretion. Biol Reprod. 1981 Oct;25(3):629–638. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod25.3.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt W. W., Basom C. R., Bagwell J. N., Blaha G. C. Structure and function of the hamster corpus luteum during the estrous cycle. Am J Anat. 1973 Feb;136(2):235–249. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001360209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milewich L., Chen G. T., Lyons C., Tucker T. F., Uhr J. W., MacDonald P. C. Metabolism of androstenedione by guinea-pig peritoneal macrophages: synthesis of testosterone and 5 alpha-reduced metabolites. J Steroid Biochem. 1982 Jul;17(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(82)90592-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. C., Bowman B. M., Rowland H. G. Structure, cytochemistry, endocytic activity, and immunoglobulin (Fc) receptors of rat testicular interstitial-tissue macrophages. Am J Anat. 1983 Sep;168(1):1–13. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001680102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda S. R., Negro-Vilar A., McCann S. M. Role of prostaglandins in the control of pituitary hormone secretion. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981;74:229–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L. Macro- and micro-domains in the endocrine pancreas. Diabetes. 1982 Jun;31(6 Pt 1):538–565. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.6.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paavola L. G. The corpus luteum of the guinea pig. Fine structure at the time of maximum progesterone secretion and during regression. Am J Anat. 1977 Dec;150(4):565–603. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001500406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paavola L. G. The corpus luteum of the guinea pig. IV. Fine structure of macrophages during pregnancy and postpartum luteolysis, and the phagocytosis of luteal cells. Am J Anat. 1979 Mar;154(3):337–364. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001540304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H., Nathan P., Srivastava L. S., Hess E. V. Release of estradiol from fetal bovine serum by rat thymus, spleen, kidney, lung and lung macrophage cultures. Endocrinology. 1982 Jun;110(6):2213–2215. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-6-2213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldhuis J. D. Interactions among endocrine control systems in the regulation of ovarian function. Clin Biochem. 1981 Oct;14(5):252–257. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(81)90976-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]