Abstract
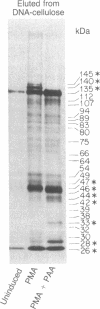
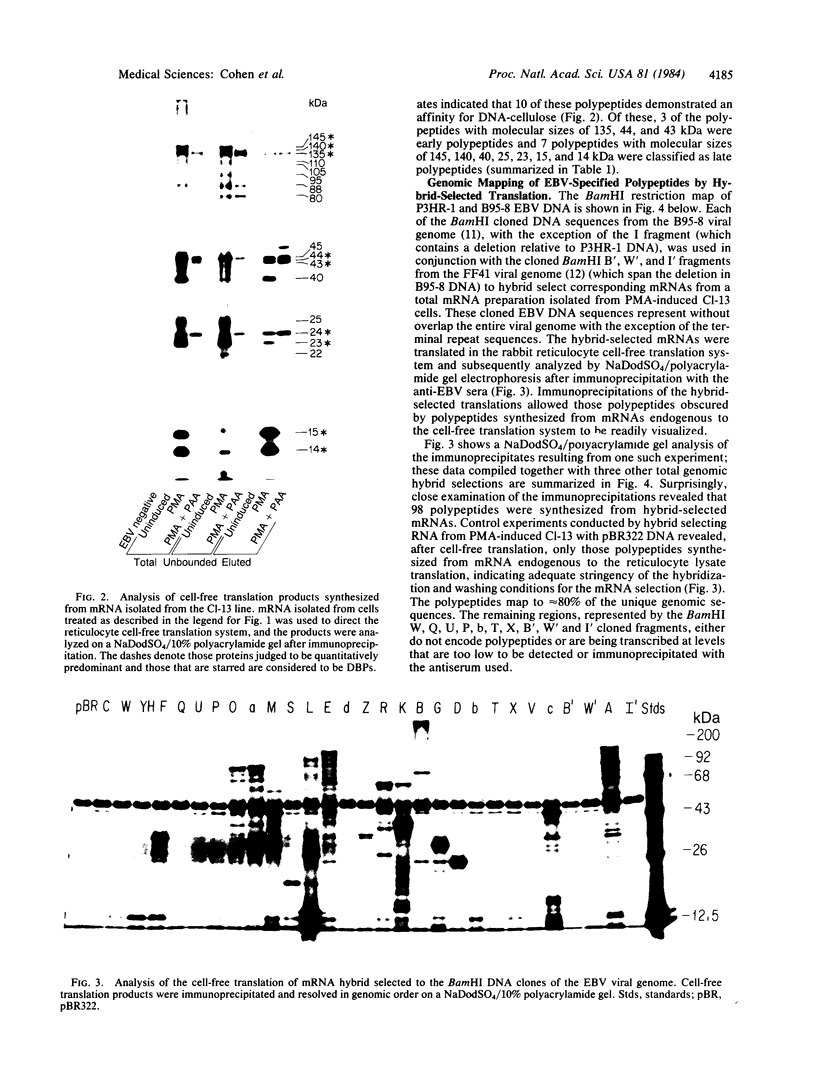
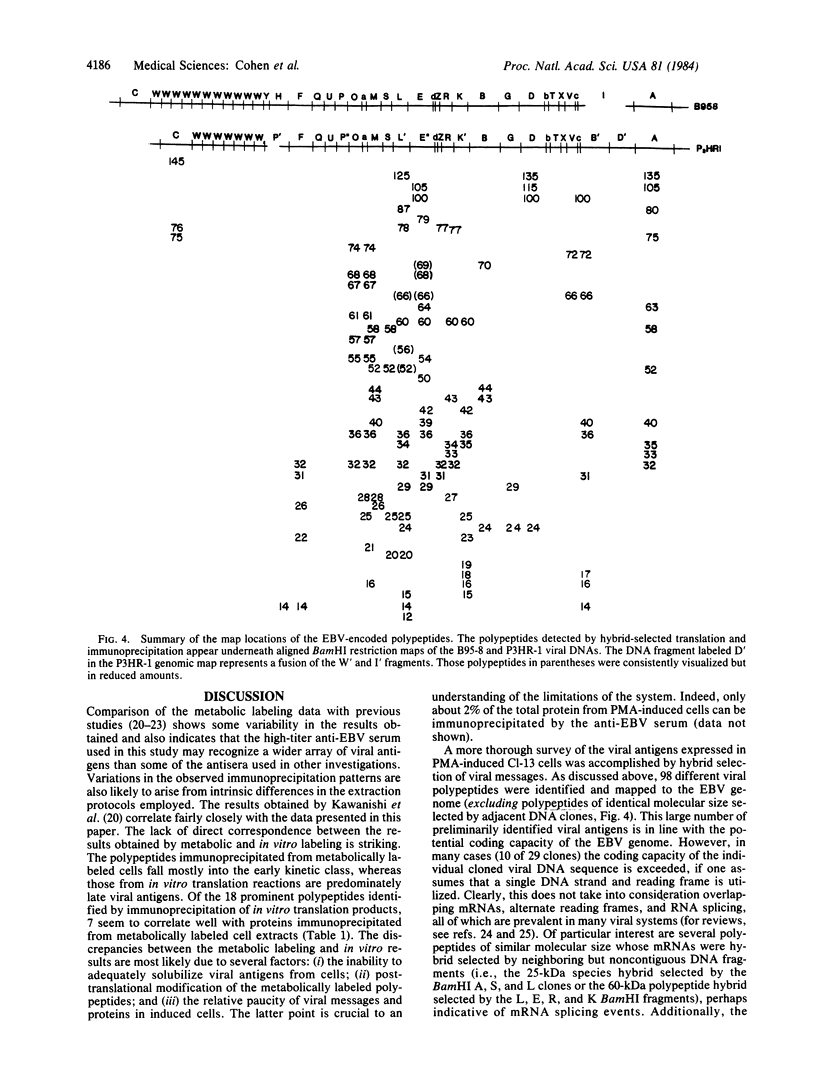
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-specified polypeptides induced upon viral replication in the P3HR-1 cell line have been examined by immunoprecipitation with a high-titer human anti-EBV serum. Twenty-five predominant polypeptides were identified in cell extracts, whereas 18 polypeptides were precipitated from cell-free translation reactions directed by total mRNA. Hybrid selection of mRNA to the BamHI DNA clones of the EBV genome and immunoprecipitation of the corresponding cell-free translation products revealed 98 EBV-specified polypeptides and their coding location along the viral genome. In addition, the viral polypeptides that bind reversibly to DNA-cellulose have been characterized and the deduced map locations of this functional group of EBV-specified polypeptides is presented.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bankier A. T., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Barrell B. G. Sequence analysis of the 17,166 base-pair EcoRI fragment C of B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Jul;1(1):21–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett T., Pachl C., Gergen J. P., Wensink P. C. The isolation and characterization of Drosophila yolk protein genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90436-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss G. J., Marsden H. S., Hay J. Herpes simplex virus proteins: DNA-binding proteins in infected cells and in the virus structure. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):124–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M., Moore C., Sharp P. A. Spliced segments at the 5' terminus of adenovirus 2 late mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3171–3175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Roberts J. M., Lewis J. B., Broker T. R. A map of cytoplasmic RNA transcripts from lytic adenovirus type 2, determined by electron microscopy of RNA:DNA hybrids. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):819–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer K., Bodemer M., Summers W. C. Characterization of the mRNA for herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase by cell-free synthesis of active enzyme. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2333–2344. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson C. M., Cohen L. K., Henle W., Strominger J. L. An unusually high-titer human anti-Epstein Barr virus (EBV) serum and its use in the study of EBV-specific proteins synthesized in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):919–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feighny R. J., Henry B. E., 2nd, Pagano J. S. Epstein-Barr virus polypeptides: effect of inhibition of viral DNA replication on their synthesis. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):61–71. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.61-71.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D. K., Miller G., Gradoville L., Heston L., Westrate M. W., Maris W., Wright J., Brandsma J., Summers W. C. Genome of a mononucleosis Epstein-Barr virus contains DNA fragments previously regarded to be unique to Burkitt's lymphoma isolates. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossberger D., Clough W. Incorporation into DNA of the base analog 2-aminopurine by the Epstein-Barr virus-induced DNA polymerase in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7271–7275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Immunofluorescence in cells derived from Burkitt's lymphoma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1248–1256. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1248-1256.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston L., Rabson M., Brown N., Miller G. New Epstein-Barr virus variants from cellular subclones of P3J-HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):160–163. doi: 10.1038/295160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Ball L. A. Cell-free synthesis of enzymatically active vaccinia virus thymidine kinase. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):594–601. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel M., Kieff E. Mapping of polypeptides encoded by the Epstein-Barr virus genome in productive infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5698–5702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallin B., Luka J., Klein G. Immunochemical characterization of Epstein-Barr virus-associated early and late antigens in n-butyrate-treated P3HR-1 cells. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):710–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.710-716.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanishi M., Sugawara K., Ito Y. Epstein-Barr virus-induced polypeptides: a comparative study with superinfected Raji, IUdR-Treated, and N-butyrate-treated P3HR-1 cells. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):72–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90472-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieff E., Dambaugh T., Heller M., King W., Cheung A., van Santen V., Hummel M., Beisel C., Fennewald S., Hennessy K. The biology and chemistry of Epstein-Barr virus. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):506–517. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Kallin B., Klein G. Induction of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) cycle in latently infected cells by n-butyrate. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):228–231. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Lantzsch N., Yamamoto N., zur Hausen H. Analysis of early and late Epstein-Barr virus associated polypeptides by immunoprecipitation. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):378–387. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. The pathway of eukaryotic mRNA formation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:441–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyormoi O., Thorley-Lawson D. A., Elkington J., Strominger J. L. Differential effect of phosphonoacetic acid on the expression of Epstein-Barr viral antigens and virus production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1745–1748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B. M., Roberts B. E., Kuff E. L. Structural gene identification and mapping by DNA-mRNA hybrid-arrested cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4370–4374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L. DNA-binding proteins induced by herpes simplex virus type 2 in HEp-2 cells. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):717–731. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.717-731.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubal J., Kallin B., Luka J., Klein G. Early DNA-binding polypeptides of Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Strominger J. L. Cloning and mapping of BamHi endonuclease fragments of DNA from the transforming B95-8 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3860–3864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara K., Kawanishi M., Ito Y. Epstein-barr virus-related DNA-binding proteins induced by n-butyrate in P3HR-1 cells. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):354–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. C., Klein G. Inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus DNA synthesis and late gene expression by phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):151–155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.151-155.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel R., Miller G. Major EB virus-specific cytoplasmic transcripts in a cellular clone of the HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma line during latency and after induction of viral replicative cycle by phorbol esters. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):287–298. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90202-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B. Transcription and RNA processing by the DNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):491–499. doi: 10.1038/287491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Bornkamm G. W., Schmidt R., Hecker E. Tumor initiators and promoters in the induction of Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):782–785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]