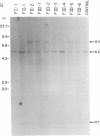
Abstract
The developmental loss of neurons in sympathetic, sensory, and some parasympathetic ganglia in familial dysautonomia suggests an inherited defect in the action of beta-nerve growth factor (beta-NGF). The role of this growth factor in dysautonomia has been difficult to resolve as there is no known source of authentic human beta-NGF. The availability of a cloned DNA probe for the human beta-NGF gene has allowed identification of some copies of the gene (alleles) in six affected families. Alleles differ in the length of restriction endonuclease fragments that hybridize to DNA probes for the gene. In two families, affected children did not inherit the same two alleles at the beta-NGF locus. Since this disease is transmitted in an autosomal recessive manner, affected children must share the same alleles at the locus causing the disease. This analysis excludes the beta-NGF gene region as the cause of this neurologic disease but does not eliminate other genes involved in beta-NGF action, such as those coding for processing enzymes, receptors, or other subunits of the NGF complex.
Full text
PDF
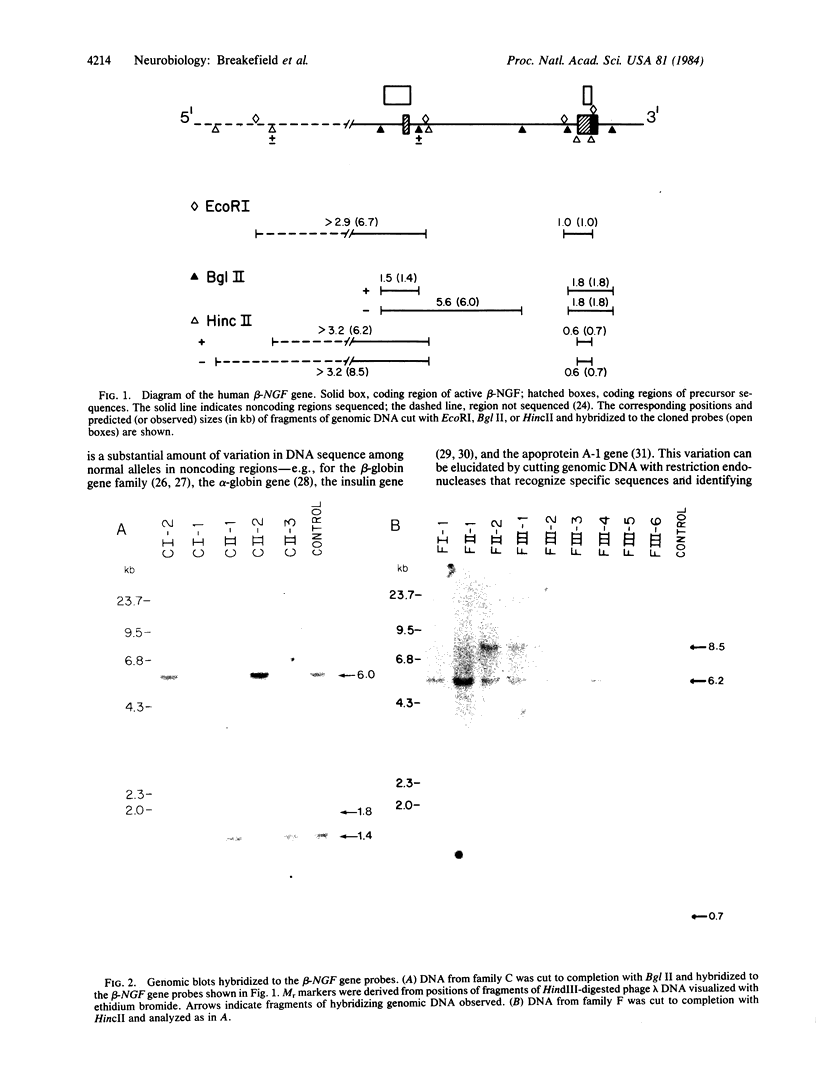
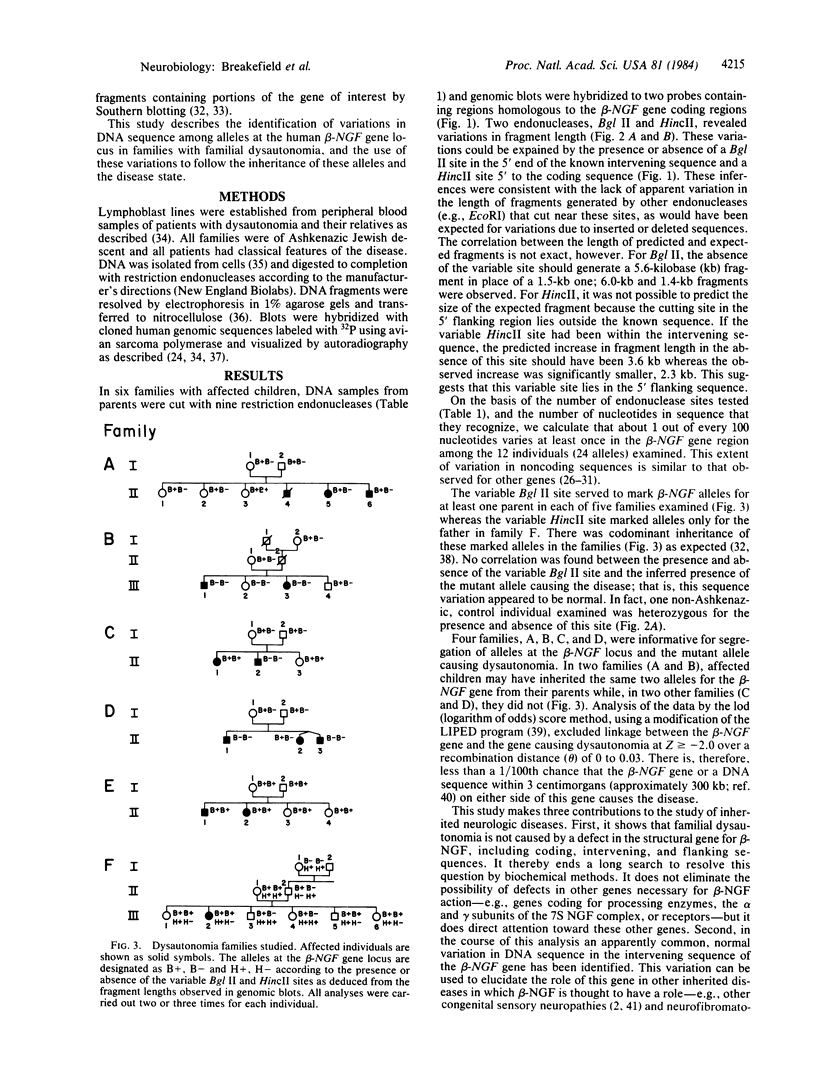

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloe L., Cozzari C., Calissano P., Levi-Montalcini R. Somatic and behavioral postnatal effects of fetal injections of nerve growth factor antibodies in the rat. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):413–415. doi: 10.1038/291413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barde Y. A., Edgar D., Thoenen H. New neurotrophic factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:601–612. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. Insulin and somatemedin MSA promote nerve growth factor-independent neurite formation by cultured chick dorsal root ganglionic sensory neurons. J Neurosci Res. 1982;8(2-3):225–231. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490080212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A. Nerve growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:191–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Gilliam T. C., Williamson R. Cystic fibrosis is not caused by a defect in the gene coding for human complement C3. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Sep;1(2):185–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebendal T. Stage-dependent stimulation of neurite outgrowth exerted by nerve growth factor and chick heart in cultured embryonic ganglia. Dev Biol. 1979 Oct;72(2):276–290. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge R. Central neurofibromatosis with bilateral acoustic neuroma. Adv Neurol. 1981;29:57–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant R. N., Todaro G. J. Increased serum levels of nerve growth factor in von Recklinghausen's disease. Arch Neurol. 1981 Jul;38(7):401–405. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510070035003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., de Martinville B., Coussens L., Ullrich A. The human gene for the beta subunit of nerve growth factor is located on the proximal short arm of chromosome 1. Science. 1983 Dec 16;222(4629):1248–1251. doi: 10.1126/science.6648531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin P. D., Johnson E. M., Jr Effects of exposure to nerve growth factor antibodies on the developing nervous system of the rat: an experimental autoimmune approach. Dev Biol. 1980 Dec;80(2):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Shooter E. M. The nerve growth factor: biochemistry, synthesis, and mechanism of action. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1980;3:353–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper G. P., Thoenen H. Nerve growth factor: biological significance, measurement, and distribution. J Neurochem. 1980 Jan;34(1):5–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb04615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Goodbourn S. E., Wainscoat J. S., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J. Highly variable regions of DNA flank the human alpha globin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4213–4224. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J. DNA sequence variants in the G gamma-, A gamma-, delta- and beta-globin genes of man. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer N., Lembeck F., Goedert M., Otten U. Effects of antibodies against nerve growth factor on the postnatal development of substance P-containing sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Mar 17;29(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Server A. C., Ishii D. N., Riopelle R. J., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor (third of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1211–1218. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses S. W., Rotem Y., Jagoda N., Talmor N., Eichhorn F., Levin S. A clinical, genetic and biochemical study of familial dysautonomia in Israel. Isr J Med Sci. 1967 May-Jun;3(3):358–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E., Goff S. C., Boehm C. D., Sexton J. P., Waber P. G., Giardina P. J. Linkage of beta-thalassaemia mutations and beta-globin gene polymorphisms with DNA polymorphisms in human beta-globin gene cluster. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):627–631. doi: 10.1038/296627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. A computer program for linkage analysis of general human pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Sep;28(5):528–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J., Axelrod F., Dancis J. Trophic functions of the neuron. V. Familial dysautonomis. Current concepts of dysautonomia: neuropathological defects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Mar 22;228(0):288–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb20517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J., Johnson E. M., Brandeis L. Effects of antibodies to nerve growth factor on intrauterine development of derivatives of cranial neural crest and placode in the guinea pig. Dev Biol. 1983 Mar;96(1):32–36. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90308-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J., Pytel B. A., Grover-Johnson N., Axelrod F., Dancis J. Quantitative studies of dorsal root ganglia and neuropathologic observations on spinal cords in familial dysautonomia. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Jan;35(1):77–92. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J., Pytel B. A. Quantitative studies of sympathetic ganglia and spinal cord intermedio-lateral gray columns in familial dysautonomia. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Nov;39(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J., Pytel B. Quantitative studies of ciliary and sphenopalatine ganglia in familial dysautonomia. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Nov;39(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. A., 3rd, Parks J. S., Hjelle B. L., Herd J. E., Plotnick L. P., Migeon C. J., Seeburg P. H. Genetic analysis of familial isolated growth hormone deficiency type I. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):489–495. doi: 10.1172/JCI110640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees A., Shoulders C. C., Stocks J., Galton D. J., Baralle F. E. DNA polymorphism adjacent to human apoprotein A-1 gene: relation to hypertriglyceridaemia. Lancet. 1983 Feb 26;1(8322):444–446. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91440-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi V. M. Von Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 31;305(27):1617–1627. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112313052704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. N. Recombinant DNA and neurologic disease: the coming of a new age. Neurology. 1983 May;33(5):622–625. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.5.622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roses A. D., Pericak-Vance M. A., Yamaoka L. H., Stubblefield E., Stajich J., Vance J. M., Roses M. J., Carter D. B. Recombinant DNA strategies in genetic neurological diseases. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Jun;6(5):339–355. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. P., Breakefield X. O. Altered nerve growth factor in fibroblasts from patients with familial dysautonomia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1154–1158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Selby M., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Bell G. I., Rutter W. J. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the precursor of mouse nerve growth factor. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):538–540. doi: 10.1038/302538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siggers D. C., Rogers J. G., Boyer S. H., Margolet L., Dorkin H., Banerjee S. P., Shooter E. M. Increased nerve-growth-factor beta-chain cross-reacting material in familial dysautonomia. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 16;295(12):629–634. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609162951201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaper S. D., Varon S. Three independent biological assays for nerve growth factor: no measurable activity in human sera. Exp Neurol. 1982 Jun;76(3):655–665. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(82)90132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:152–176. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Dull T. J., Gray A., Philips J. A., 3rd, Peter S. Variation in the sequence and modification state of the human insulin gene flanking regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2225–2240. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Berman C., Dull T. J. Human beta-nerve growth factor gene sequence highly homologous to that of mouse. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):821–825. doi: 10.1038/303821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinores S., Guroff G. Nerve growth factor: mechanism of action. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1980;9:223–257. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.09.060180.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., White R. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6754–6758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martinville B., Wyman A. R., White R., Francke U. Assignment of first random restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) locus ((D14S1) to a region of human chromosome 14. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):216–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]