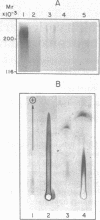
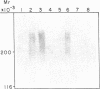
Abstract
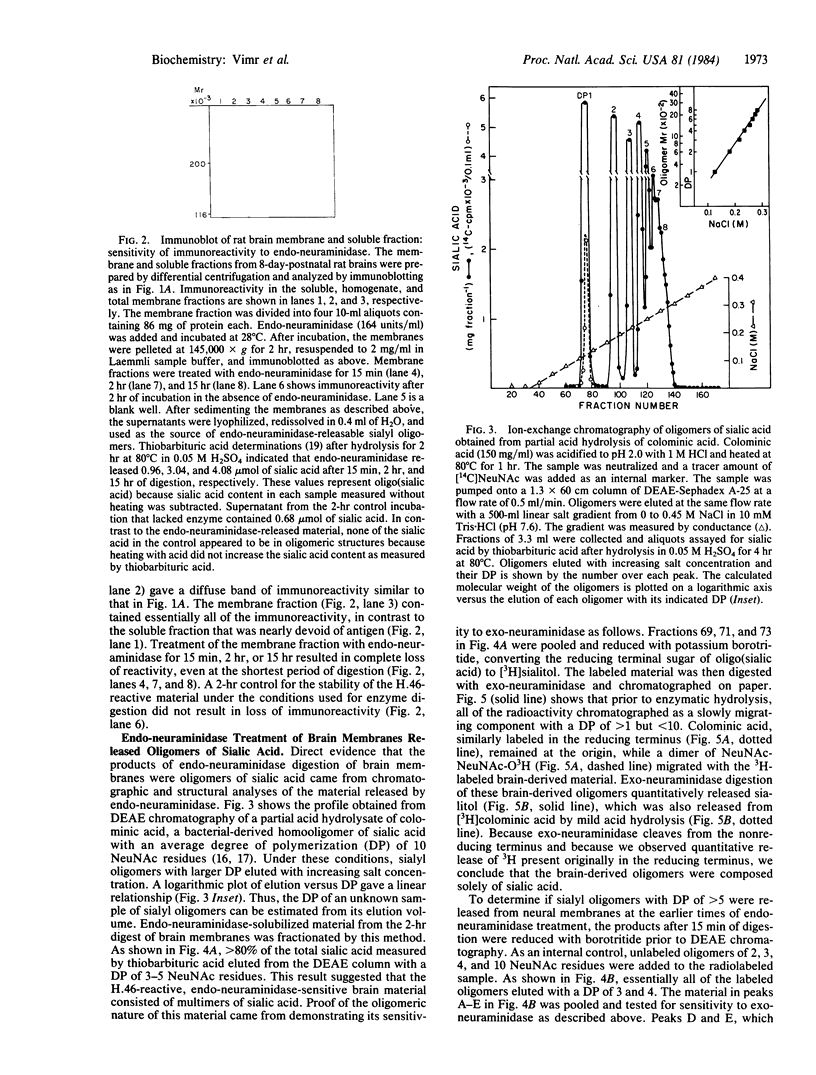
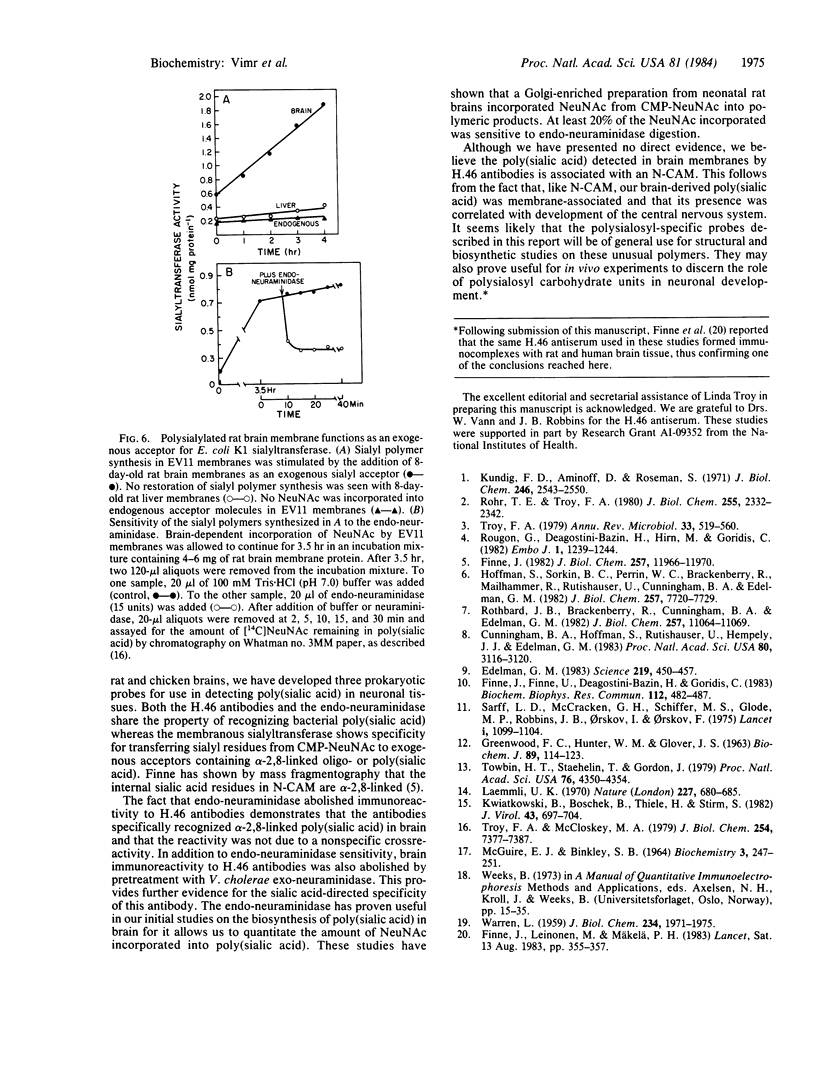
Three prokaryotic-derived probes to identify and study the temporal expression of polysialosyl units in neuronal tissue have been developed. A polyclonal antibody, a bacteriophage-derived endo-neuraminidase, and an Escherichia coli K1 sialyltransferase are all specific for either recognizing or synthesizing poly(sialic acid) containing alpha-2,8-ketosidic linkages. Polysialosyl immunoreactivity with apparent Mr values of 180,000-240,000 was specific for developing neuronal tissue; it was not detected in neonatal liver or kidney or in adult brain tissue. The developmentally regulated disappearance in poly(sialic acid) is consistent with the probes described here recognizing the polysialosyl carbohydrate units of a neuronal cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM). Treatment of brain extracts with a bacteriophage-derived endo-neuraminidase specific for alpha-2,8-linked polysialosyl units abolished the immunoreactivity. The material solubilized by endo-neuraminidase was isolated, reduced with borotritide, and shown to contain oligomers of sialic acid with three to six sialyl units. Treatment of the 3H-labeled oligosialic acid with exo-neuraminidase quantitatively converted the radioactivity to sialitol, establishing that the brain-derived oligomers were composed solely of sialic acid. A membranous sialytransferase from E. coli K1 that can transfer sialic acid to exogenous acceptors of oligo- or poly(sialic acid) also recognized rat brain membranes, further substantiating the presence of poly(sialic acid) in rat brain. This conclusion was confirmed by using a mutant of E. coli K1 that was defective in the synthesis of poly(sialic acid) and could only transfer sialic acid to exogenous acceptors of oligo- or poly(sialic acid). Sialyl polymer synthesis was restored in the mutant when brain membranes were added as exogenous acceptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cunningham B. A., Hoffman S., Rutishauser U., Hemperly J. J., Edelman G. M. Molecular topography of the neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM: surface orientation and location of sialic acid-rich and binding regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3116–3120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules. Science. 1983 Feb 4;219(4584):450–457. doi: 10.1126/science.6823544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Finne U., Deagostini-Bazin H., Goridis C. Occurrence of alpha 2-8 linked polysialosyl units in a neural cell adhesion molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 29;112(2):482–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91490-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Leinonen M., Mäkelä P. H. Antigenic similarities between brain components and bacteria causing meningitis. Implications for vaccine development and pathogenesis. Lancet. 1983 Aug 13;2(8346):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J. Occurrence of unique polysialosyl carbohydrate units in glycoproteins of developing brain. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11966–11970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Sorkin B. C., White P. C., Brackenbury R., Mailhammer R., Rutishauser U., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Chemical characterization of a neural cell adhesion molecule purified from embryonic brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7720–7729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig J. D., Aminoff D., Roseman S. The sialic acids. XII. Synthesis of colominic acid by a sialyltransferase from Escherichia coli K-235. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2543–2550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski B., Boschek B., Thiele H., Stirm S. Endo-N-acetylneuraminidase associated with bacteriophage particles. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):697–704. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.697-704.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGUIRE E. J., BINKLEY S. B. THE STRUCTURE AND CHEMISTRY OF COLOMINIC ACID. Biochemistry. 1964 Feb;3:247–251. doi: 10.1021/bi00890a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohr T. E., Troy F. A. Structure and biosynthesis of surface polymers containing polysialic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2332–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Brackenbury R., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Differences in the carbohydrate structures of neural cell-adhesion molecules from adult and embryonic chicken brains. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11064–11069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougon G., Deagostini-Bazin H., Hirn M., Goridis C. Tissue- and developmental stage-specific forms of a neural cell surface antigen linked to differences in glycosylation of a common polypeptide. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1239–1244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00019.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarff L. D., McCracken G. H., Schiffer M. S., Glode M. P., Robbins J. B., Orskov I., Orskov F. Epidemiology of Escherichia coli K1 in healthy and diseased newborns. Lancet. 1975 May 17;1(7916):1099–1104. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., 2nd The chemistry and biosynthesis of selected bacterial capsular polymers. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:519–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troy F. A., McCloskey M. A. Role of a membranous sialyltransferase complex in the synthesis of surface polymers containing polysialic acid in Escherichia coli. Temperature-induced alteration in the assembly process. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7377–7387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]