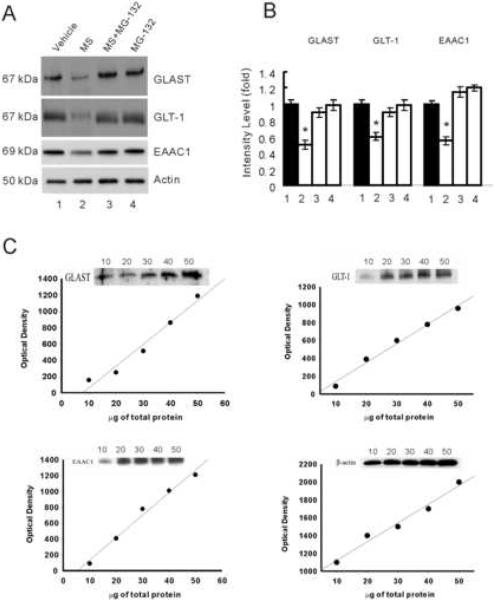
Fig. 3. The proteasome inhibitor MG-132 prevented spinal glutamate transporter downregulation.
Rats (n=6) were administrated intrathecally (twice daily) with vehicle, morphine (MS, 15 nmol), morphine plus MG-132 (1, 2.5, 5 or 10 nmol) or MG132 (5 nmol) alone for seven consecutive days. Independent samples from these rats were used for the Western blot assay. MG-132 effectively prevented morphine-induced downregulation of EAAC1, GLAST, and GLT-1. A, Western blotting of glutamate transporter EAAC1, GLAST, and GLT-1 within the spinal cord dorsal horn. B, Densitometric quantification of Western blotting results in A. The amount of glutamate transporter EAAC1, GLAST, and GLT-1 normalized to that of tubulin was plotted as fold change. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer test was used to analyze the data. * P< 0.05, as compared with vehicle, morphine plus MG-132, or MG-132 alone. Lane 1: vehicle, Lane 2: morphine (15 nmol), Lane 3: morphine (15 nmol) plus MG-132 (5 nmol), Lane 4: MG-132 (5 nmol) alone. Results are expressed as the group mean (± SEM) obtained from three independent extract preparations from the same rats in each group. Actin: loading control. C, A linear range of immunoreactivity for GLAST, GLT-1, EAAC1, and β-actin. Spinal cord dorsal horn samples containing 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 μg of protein were analyzed by Western blotting. Densitometric assessment of bands showed a linear response between 10 and 50 μg of total protein loading.