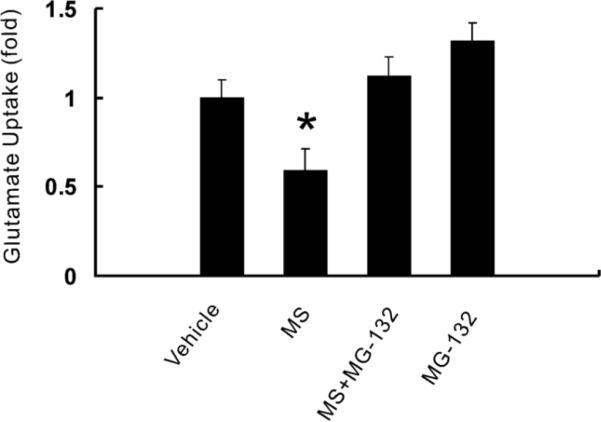
Fig. 4. The proteasome inhibitor MG-132 prevented the decrease of spinal glutamate uptake activity after chronic morphine exposure.
Rats (n=6) were administrated intrathecally (twice daily) with vehicle, morphine (MS, 15 nmol), morphine plus MG-132 (1, 2.5, 5 or 10 nmol) or MG132 (5 nmol) alone for seven consecutive days. Glutamate uptake activity within the spinal cord dorsal horn was examined using an in vitro glutamate uptake assay. Lane 1: vehicle, Lane 2: morphine (15 nmol), Lane 3: morphine (15 nmol) plus MG-132 (5 nmol), Lane 4: MG-132 (5 nmol) alone. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer test was used to analyze the data. * P< 0.05, as compared with each of the remaining groups. Results are the group mean (± SEM) obtained from the independent extract preparation from the same rats in each group.