Abstract
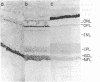
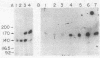
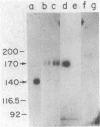
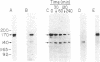
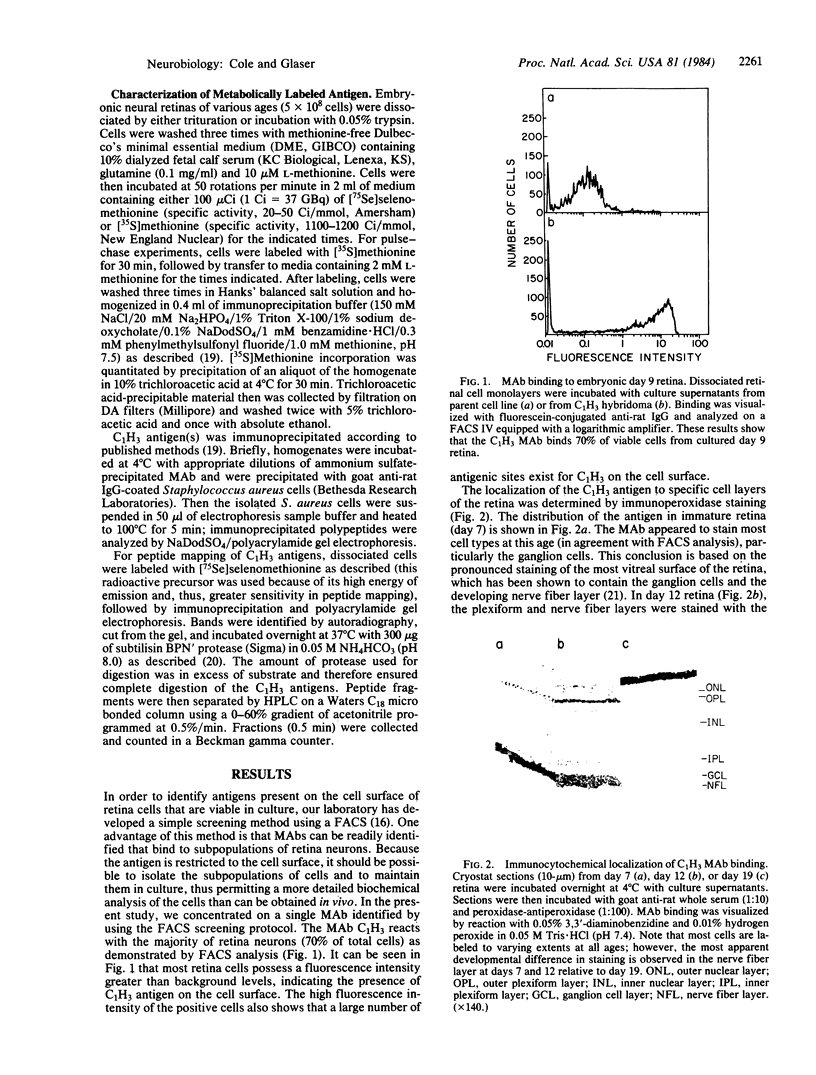
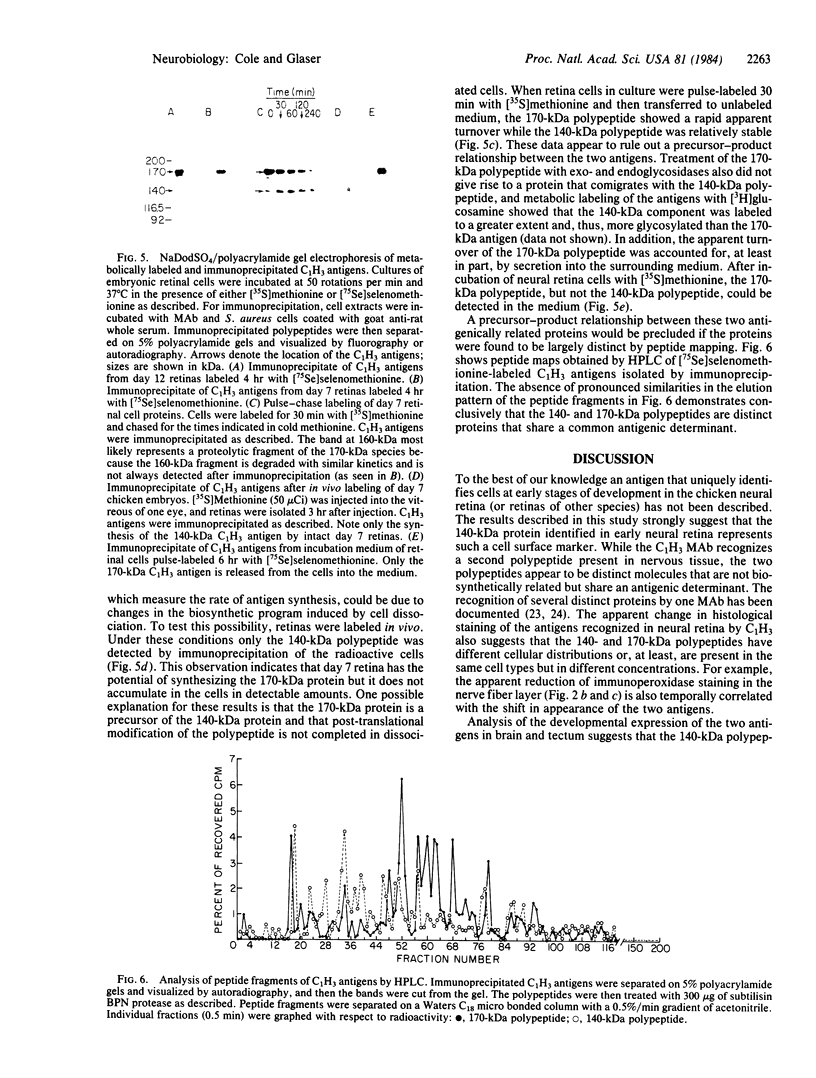
A fluorescence-activated cell sorter screening method has been used to identify hybridomas that secrete monoclonal antibodies that can bind to viable subpopulations of embryonic chicken neural retina cells. One monoclonal antibody, C1H3, recognizes two nervous tissue-specific polypeptides that exhibit distinct developmental patterns. The monoclonal antibody reacts with a 140-kilodalton (kDa) polypeptide that is present at early stages of development (day 7) but is detected by immunoblotting in only negligible amounts at later times (day 17). In contrast, a 170-kDa polypeptide is first detectable by immunoblotting at day 10 and is the predominant C1H3 antigen at day 17. Analysis of proteolytic fragments of the two proteins indicates that the polypeptides are distinct molecules that share a common antigenetic determinant. Both polypeptides are neural-specific; the 140-kDa polypeptide appears to be retina-specific, while the 170-kDa polypeptide is also present in other areas of the nervous system. Metabolic labeling of retina cells in situ at early embryonic stages reveals only the synthesis of the 140-kDa polypeptide. When such cells are dissociated and labeled in vitro, they synthesize primarily the 170-kDa polypeptide. Thus, the differential rate of synthesis of these two polypeptides is controlled by environmental factors that possibly include cell-cell contacts or an unknown systemic factor. The 140-kDa polypeptide is a unique marker for early neural retina cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnstable C. J. Monoclonal antibodies which recognize different cell types in the rat retina. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):231–235. doi: 10.1038/286231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., Selvendran S. Y. A neuronal cell-surface antigen is found in the CNS but not in peripheral neurones. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):421–423. doi: 10.1038/291421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derby M. A., Dyer S. A., Glaser L. Monoclonal antibodies against a differentiated retinal cell population. Brain Res. 1983 Apr;283(2-3):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer S. A., Derby M. A., Cole G. J., Glaser L. Identification of sub-populations of chick neural retinal cells by monoclonal antibodies: a fluorescence activated cell sorter screening technique. Brain Res. 1983 Aug;285(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Walsh F. S., Nirenberg M. Monoclonal antibody to a plasma membrane antigen of neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson J. A., Beverley P. C., Coakham H. B., Harper E. I. Monoclonal antibodies against human T lymphocytes label Purkinje neurones of many species. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):375–377. doi: 10.1038/298375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Matus A. Monoclonal antibodies identify novel neural antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2410–2414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirn M., Pierres M., Deagostini-Bazin H., Hirsch M., Goridis C. Monoclonal antibody against cell surface glycoprotein of neurons. Brain Res. 1981 Jun 15;214(2):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. R., Langley O. K., Ghandour M. S., Hirn M., Gombos G., Goridis C. A monoclonal antibody recognizing subpopulations of neurones in mouse brain. J Neuroimmunol. 1983 Jun;4(3):175–186. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(83)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockfield S., McKay R. D. A surface antigen expressed by a subset of neurons in the vertebrate central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5758–5761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen O. S., Delouvée A., Thiery J. P., Edelman G. M. The nervous system specific protein D2 is involved in adhesion among neurites from cultured rat ganglia. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80756-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. J. Ganglion cell formation in the chick neural retina. Brain Res. 1973 Dec 7;63:285–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley O. K., Ghandour M. S., Gombos G., Hirn M., Goridis C. Monoclonal antibodies as neural cell surface markers. Neurochem Res. 1982 Mar;7(3):349–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00965646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon V., Gottlieb D. I. Monoclonal antibodies selective for the inner portion of the chick retina. J Neurosci. 1982 May;2(5):531–535. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-05-00531.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R. D., Hockfield S. J. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish antigenically discrete neuronal types in the vertebrate central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6747–6751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Caldwell K. L., Gordon J. I., Glaser L. Regulation of creatine phosphokinase expression during differentiation of BC3H1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2644–2652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager G. Morphogenesis and physiogenesis of the retino-tectal connection in the chicken. I. The retinal ganglion cells and their axons. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Feb 17;192(1108):331–352. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., LaCorbiere M., Klier F. G., Birdwell C. A role for adherons in neural retina cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;96(4):990–998. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.4.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer I., Schachner M. Monoclonal antibodies (O1 to O4) to oligodendrocyte cell surfaces: an immunocytological study in the central nervous system. Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 30;83(2):311–327. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90477-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W. R., Barondes S. H. Monoclonal antibodies block cell-cell adhesion in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4698–4701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Brackenbury R., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. II. Purification and characterization of a cell adhesion molecule from neural retina. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6841–6845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulliamy T., Rattray S., Mirsky R. Cell-surface antigen distinguishes sensory and autonomic peripheral neurones from central neurones. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):418–420. doi: 10.1038/291418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]