Abstract
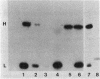
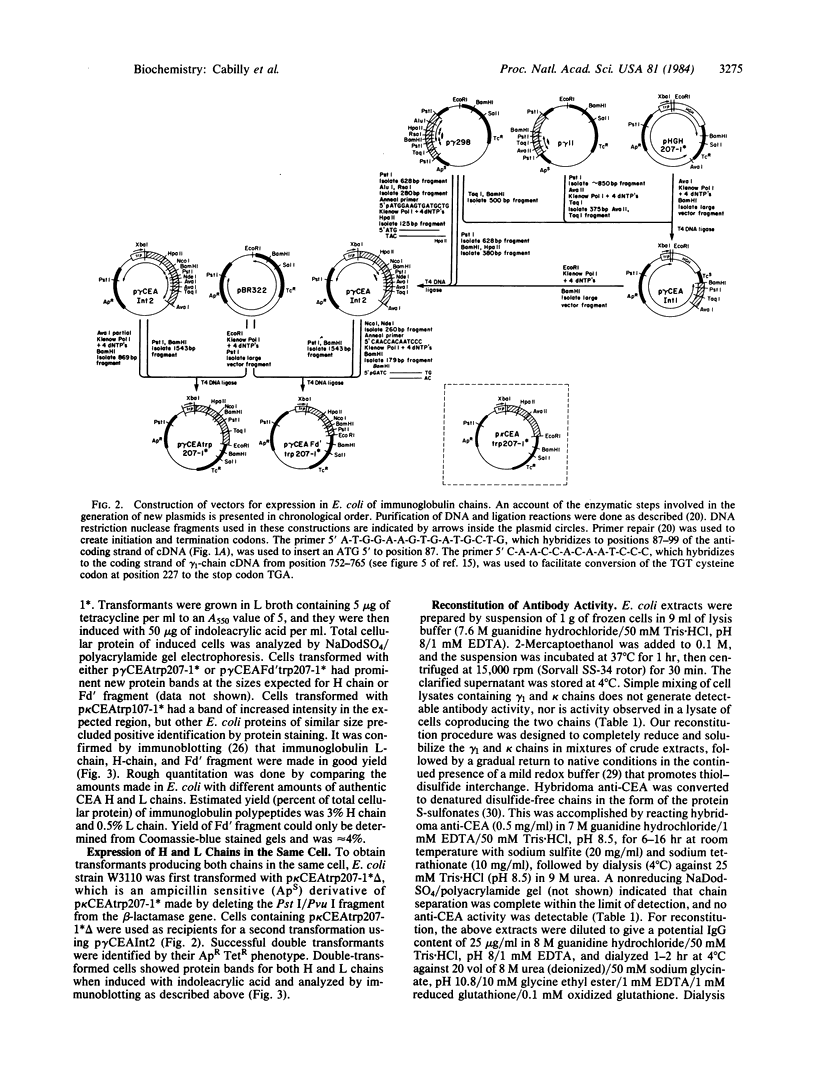
Plasmids have been constructed that direct the synthesis in Escherichia coli of heavy chains and/or light chains of an anti-carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) antibody. Another plasmid was constructed for expression of a truncated form of heavy chain (Fd' fragment) in E. coli. Functional CEA-binding activity was obtained by in vitro reconstitution in E. coli extracts of heavy chain or Fd' fragment mixed with extracts containing light chain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Accolla R. S., Carrel S., Mach J. P. Monoclonal antibodies specific for carcinoembryonic antigen and produced by two hybrid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):563–566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Erlich H. A., Schimke R. T., Cohen S. N. Phenotypic expression in E. coli of a DNA sequence coding for mouse dihydrofolate reductase. Nature. 1978 Oct 19;275(5681):617–624. doi: 10.1038/275617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer H. A., Comstock L. J., Hui A., Wong E., Vasser M. A hybrid promoter and portable Shine-Dalgarno regions of Escherichia coli. Biochem Soc Symp. 1983;48:233–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. H., Sela M. Recovery of specific activity upon reoxidation of completely reduced polyalanyl rabbit antibody. J Biol Chem. 1966 Nov 25;241(22):5225–5232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLD P., FREEDMAN S. O. DEMONSTRATION OF TUMOR-SPECIFIC ANTIGENS IN HUMAN COLONIC CARCINOMATA BY IMMUNOLOGICAL TOLERANCE AND ABSORPTION TECHNIQUES. J Exp Med. 1965 Mar 1;121:439–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.3.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Heyneker H. L., Hozumi T., Arentzen R., Itakura K., Yansura D. G., Ross M. J., Miozzari G., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. Direct expression in Escherichia coli of a DNA sequence coding for human growth hormone. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):544–548. doi: 10.1038/281544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Shepard H. M., Yelverton E., Leung D., Crea R., Sloma A., Pestka S. Synthesis of human fibroblast interferon by E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4057–4074. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Yelverton E., Ullrich A., Heyneker H. L., Miozzari G., Holmes W., Seeburg P. H., Dull T., May L., Stebbing N. Human leukocyte interferon produced by E. coli is biologically active. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):411–416. doi: 10.1038/287411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABER E. RECOVERY OF ANTIGENIC SPECIFICITY AFTER DENATURATION AND COMPLETE REDUCTION OF DISULFIDES IN A PAPAIN FRAGMENT OF ANTIBODY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1099–1106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn P. H., Gait M. J., Milstein C. Complete sequence of an immunoglobulin mRNA using specific priming and the dideoxynucleotide method of RNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4485–4494. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedin A., Hammarström S., Larsson A. Specificities and binding properties of eight monoclonal antibodies against carcinoembryonic antigen. Mol Immunol. 1982 Dec;19(12):1641–1648. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90275-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Obata M., Yamawaki-Katoaka Y., Kataoka T., Kawakami T., Takahashi N., Mano Y. Cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of mouse immunoglobulin gamma 1 chain gene. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):559–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupchik H. Z., Zurawski V. R., Jr, Hurrell J. G., Zamcheck N., Black P. H. Monoclonal antibodies to carcinoembryonic antigen produced by somatic cell fusion. Cancer Res. 1981 Sep;41(9 Pt 1):3306–3310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch K. R., Pennica D., Ennis H. L., Cohen P. S. Separation and purification of the mRNAs for vesicular stomatitis virus NS and M proteins. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90543-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matteucci M. D., Heyneker H. L. Targeted random mutagenesis: the use of ambiguously synthesized oligonucleotides to mutagenize sequences immediately 5' of an ATG initiation codon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3113–3121. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi A., Hawley R. G., Shulman M. J., Hozumi N. Transfer of a cloned immunoglobulin light-chain gene to mutant hybridoma cells restores specific antibody production. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):340–342. doi: 10.1038/302340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Morrison S. L., Herzenberg L. A., Berg P. Immunoglobulin gene expression in transformed lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):825–829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollitt S., Zalkin H. Role of primary structure and disulfide bond formation in beta-lactamase secretion. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.27-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primus F. J., Newell K. D., Blue A., Goldenberg D. M. Immunological heterogeneity of carcinoembryonic antigen: antigenic determinants on carcinoembryonic antigen distinguished by monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 1983 Feb;43(2):686–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice D., Baltimore D. Regulated expression of an immunoglobulin kappa gene introduced into a mouse lymphoid cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7862–7865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena V. P., Wetlaufer D. B. Formation of three-dimensional structure in proteins. I. Rapid nonenzymic reactivation of reduced lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 8;9(25):5015–5023. doi: 10.1021/bi00827a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard H. M., Yelverton E., Goeddel D. V. Increased synthesis in E. coli of fibroblast and leukocyte interferons through alterations in ribosome binding sites. DNA. 1982;1(2):125–131. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1982.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E. Sequence determinations of proteins and peptides at the nanomole and subnanomole level with a modified spinning cup sequenator. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):31–48. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J. DNA sequence analysis by primed synthesis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):560–580. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wabl M., Steinberg C. A theory of allelic and isotypic exclusion for immunoglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6976–6978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagener C., Clark B. R., Rickard K. J., Shively J. E. Monoclonal antibodies for carcinoembryonic antigen and related antigens as a model system: determination of affinities and specificities of monoclonal antibodies by using biotin-labeled antibodies and avidin as precipitating agent in a solution phase immunoassay. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2302–2307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagener C., Yang Y. H., Crawford F. G., Shively J. E. Monoclonal antibodies for carcinoembryonic antigen and related antigens as a model system: a systematic approach for the determination of epitope specificities of monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2308–2315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. P., Buell G. N., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of double-stranded DNA complementary to lysozyme, ovomucoid, and ovalbumin mRNAs. Optimization for full length second strand synthesis by Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2483–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]