Abstract
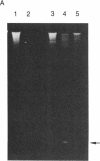
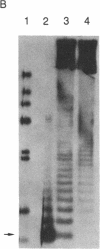
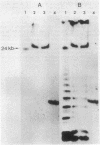
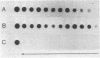
We have isolated genomic clones containing members of a tandemly repeated DNA family from Trypanosoma cruzi. This family, which contains a 195-base pair (bp) repeating unit, is the most abundant repetitive DNA in this organism. DNA sequencing analysis of three adjacent tandem repeats as well as two independent nonadjacent repeats showed relatively little sequence heterogeneity. Surprisingly, the three tandem elements contained a 585-bp open reading frame. However, blot hybridization of RNA from epimastigotes as well as blood-form trypomastigotes failed to show evidence for transcription of these sequences. Fractionation of whole T. cruzi DNA in sucrose gradients or in agarose gels followed by hybridization with appropriate radioactive probes showed that the size distribution of DNA bearing the 195-bp repetitive element is distinct from that of kinetoplast DNA as well as from that of DNA bearing tubulin genes. Hybridization of the 195-bp element probe with DNA from six different T. cruzi strains was positive; hybridization with DNA of other protozoa was negative with the single exception of Leptomonas collosoma , which displayed a weak cross-hybridization signal. Clones bearing this repetitive element are shown to be useful as probes for identification and counting of T. cruzi cells by dot-blot hybridization. The sensitivity of this assay permits detection of the DNA of 30 parasites in blood samples.
Full text
PDF
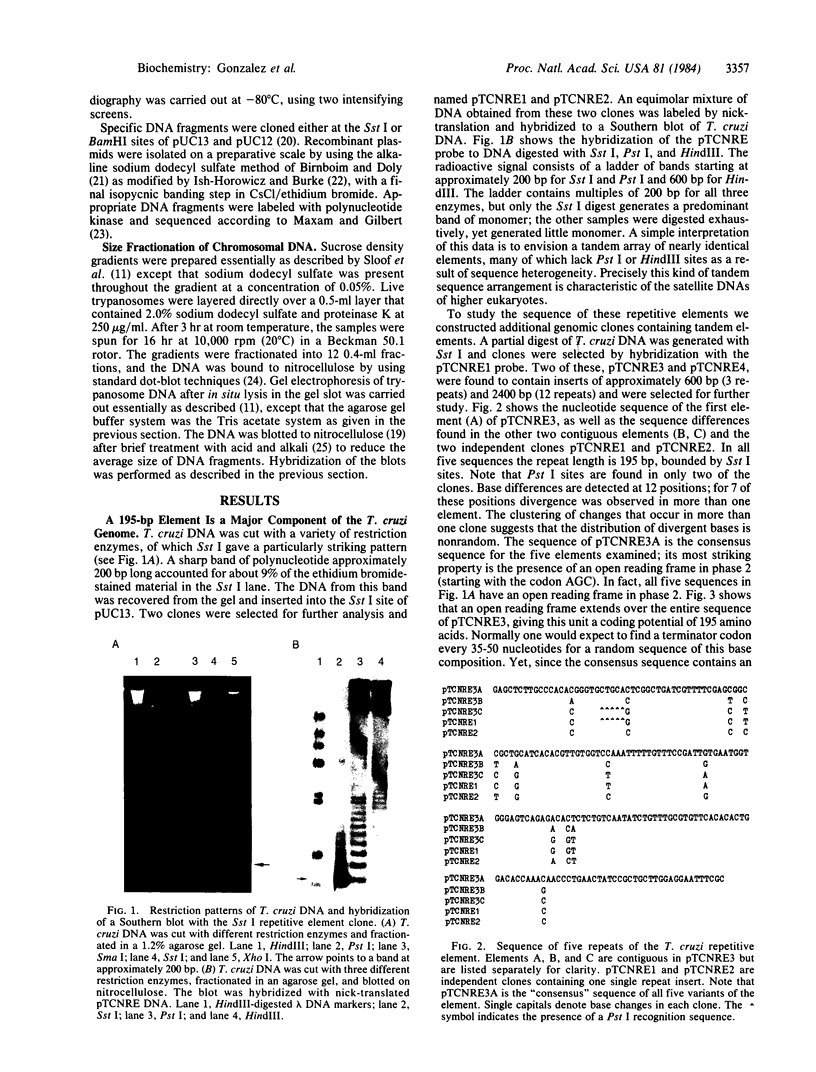
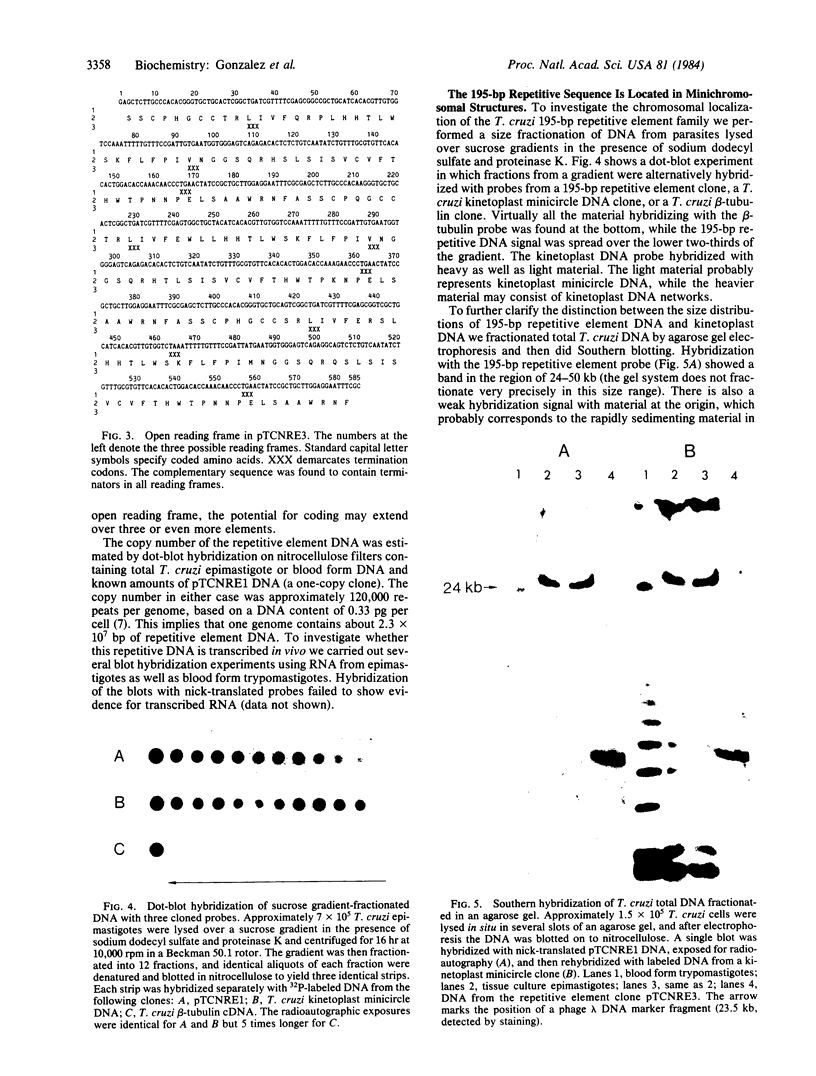


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro C., Craig S. P., Castañeda M. Genome organization and ploidy number in Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Dec 31;4(5-6):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz M. O., Barsacchi-Pilone G., Mahon K. A., Gall J. G. Transcripts from both strands of a satellite DNA occur on lampbrush chromosome loops of the newt Notophthalmus. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):649–659. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch A. C., Carrasco A. E., Goijman S. G., Sanchez D. O. Repetitive sequences scattered throughout the genome of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Jul;8(3):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch A. C., Hajduk S. L., Hoeijmakers J. H., Borst P., Brunel E., Davison J. The kinetoplast DNA of Trypanosoma equiperdum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 30;607(3):397–410. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Singer M. F. A monkey Alu sequence is flanked by 13-base pair direct repeats by an interrupted alpha-satellite DNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1497–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanar D. E., Levy L. S., Manning J. E. Complexity and content of the DNA and RNA in Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Sep;3(5):327–341. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langridge J., Langridge P., Bergquist P. L. Extraction of nucleic acids from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Apr;103(2):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel C., Chiari E., Camargo E. P., Mattei D. M., Romanha A. J., Simpson L. Strains and clones of Trypanosoma cruzi can be characterized by pattern of restriction endonuclease products of kinetoplast DNA minicircles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6810–6814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Bianco C., Cohn Z. Studies on the selective lysis and purification of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):224–229. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Cohn Z. A. Trypanosoma cruzi: in vitro induction of macrophage microbicidal activity. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):288–300. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Unkeless J., Cohn Z. Specific glycoprotein antigens on the surface of insect and mammalian stages of Trypanosoma cruzi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1259–1263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M. F. Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;76:67–112. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61789-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloof P., Bos J. L., Konings A. F., Menke H. H., Borst P., Gutteridge W. E., Leon W. Characterization of satellite DNA in Trypanosoma brucei and Trypanosoma cruzi. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloof P., Menke H. H., Caspers M. P., Borst P. Size fractionation of Trypanosoma brucei DNA: localization of the 177-bp repeat satellite DNA and a variant surface glycoprotein gene in a mini-chromosomal DNA fraction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):3889–3901. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.3889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson E. C., Erba H. P., Gall J. G. Histone gene clusters of the newt notophthalmus are separated by long tracts of satellite DNA. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):639–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tait A. Sexual processes in the kinetoplastida. Parasitology. 1983 Apr;86(Pt 4):29–57. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000050836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varley J. M., Macgregor H. C., Erba H. P. Satellite DNA is transcribed on lampbrush chromosomes. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):686–688. doi: 10.1038/283686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth D. F., Pratt D. M. Rapid identification of Leishmania species by specific hybridization of kinetoplast DNA in cutaneous lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6999–7003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]