Abstract
Guanine residues in nucleic acids can be modified by treatment with N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene and its 7-iodo derivative in an in vitro nonenzymatic reaction. The modified nucleic acids (ribo or deoxyribo, single or double stranded) are recognized by specific antibodies. They can be immunoprecipitated or used as probes in hybridization experiments and detected by immunochemical techniques.
Full text
PDF
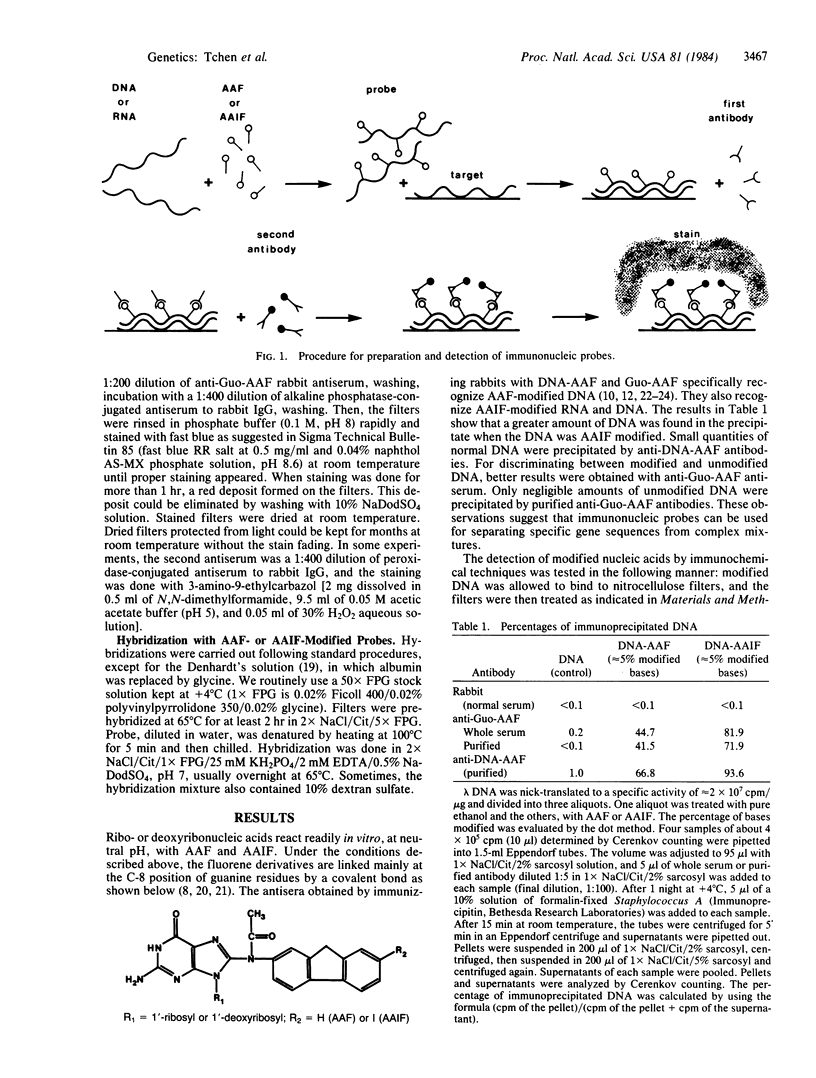
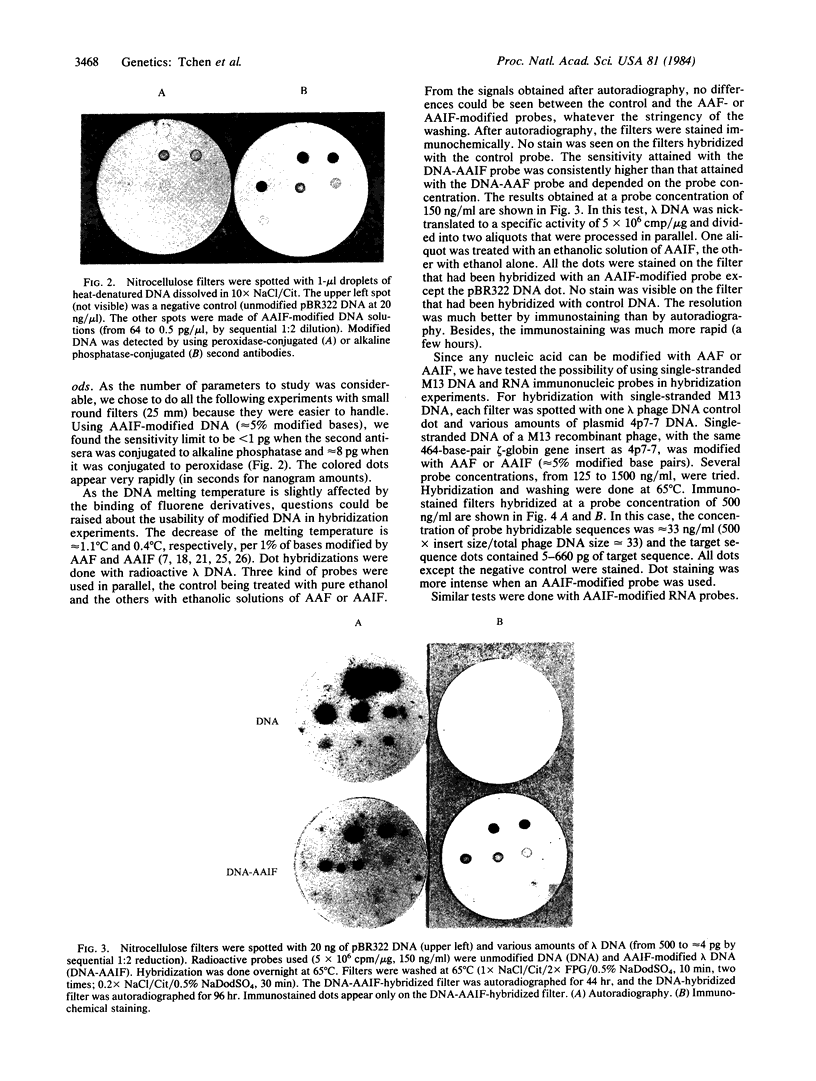
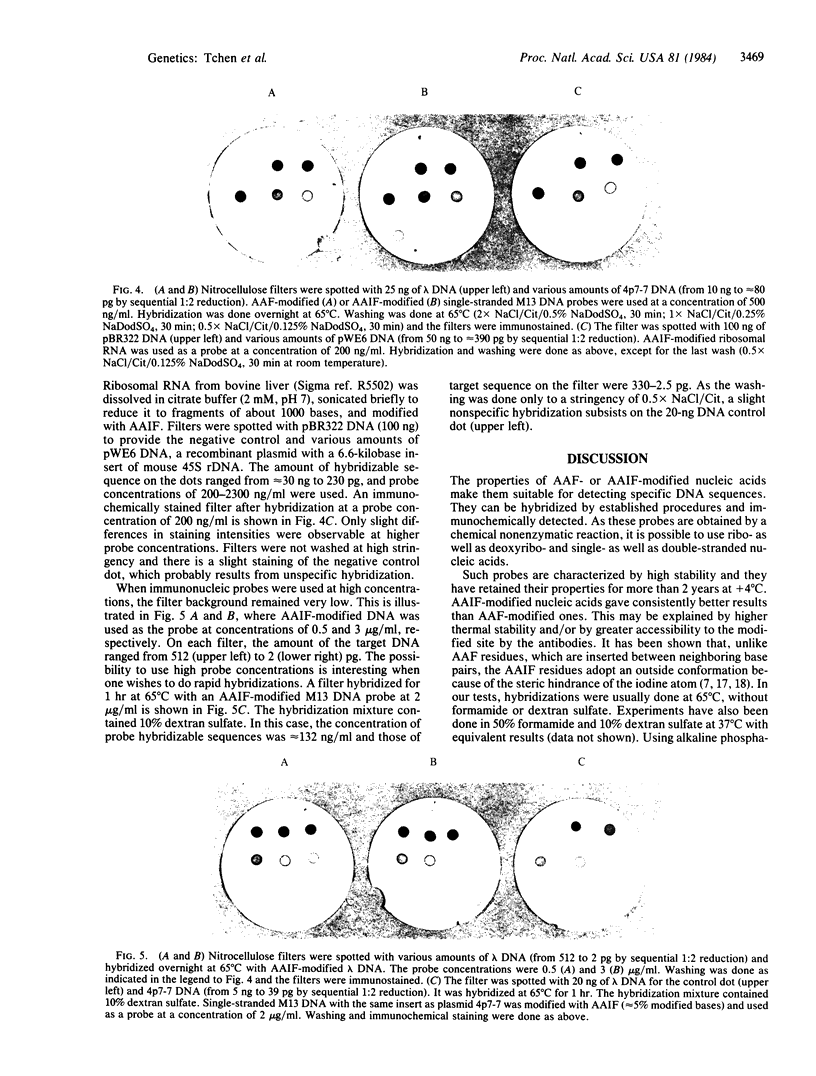

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asmussen M. A., Clegg M. T. Use of restriction fragment length polymorphisms for genetic counseling: population genetic considerations. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 May;34(3):369–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Solal M. M., Authier B., deRiel J. K., Murnane M. J., Forget B. G. Cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of human embryonic zeta-globin cDNA. DNA. 1982;1(4):355–363. doi: 10.1089/dna.1982.1.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escara J. F., Hutton J. R. Thermal stability and renaturation of DNA in dimethyl sulfoxide solutions: acceleration of the renaturation rate. Biopolymers. 1980 Jul;19(7):1315–1327. doi: 10.1002/bip.1980.360190708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R. P., Lefevre J. F., Pouyet J., Daune M. P. Comparative orientation of the fluorene residue in native DNA modified by N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene and two 7-halogeno derivatives. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3347–3351. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Daune M. Physical basis of chemical carcinogenesis by N-2-fluorenylacetamide derivatives and analogs. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 15;34(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80815-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Daune M. Physical studies on deoxyribonucleic acid after covalent binding of a carcinogen. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 4;11(14):2659–2666. doi: 10.1021/bi00764a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guigues M., Leng M. Reactivity of antibodies to guanosine modified by the carcinogen N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):733–744. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan Y. W., Dozy A. M. Antenatal diagnosis of sickle-cell anaemia by D.N.A. analysis of amniotic-fluid cells. Lancet. 1978 Oct 28;2(8096):910–912. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91629-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuler A. M., Michelson A. M. The reaction of the carcinogen N-acetoxy-2-acetyl-aminofluorene with DNA and other polynucleotides and its stereochemical implications. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 25;232(3):436–450. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90598-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriek E. Carcinogenesis by aromatic amines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 9;355(2):177–203. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(74)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriek E., Miller J. A., Juhl U., Miller E. C. 8-(N-2-fluorenylacetamido)guanosine, an arylamidation reaction product of guanosine and the carcinogen N-acetoxy-N-2-fluorenylacetamide in neutral solution. Biochemistry. 1967 Jan;6(1):177–182. doi: 10.1021/bi00853a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary J. J., Brigati D. J., Ward D. C. Rapid and sensitive colorimetric method for visualizing biotin-labeled DNA probes hybridized to DNA or RNA immobilized on nitrocellulose: Bio-blots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefèvre J. F., Fuchs R. P., Daune M. P. Comparative studies on the 7-iodo and 7-fluoro derivatives of N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene: binding sites on DNA and conformational change of modified deoxytrinucleotides. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2561–2567. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng M., Sage E., Fuchs R. P., Duane M. P. Antibodies to DNA modified by the carcinogen N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80755-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michot B., Bachellerie J. P., Raynal F. Sequence and secondary structure of mouse 28S rRNA 5'terminal domain. Organisation of the 5.8S-28S rRNA complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5273–5283. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michot B., Bachellerie J. P., Raynal F. Structure of mouse rRNA precursors. Complete sequence and potential folding of the spacer regions between 18S and 28S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3375–3391. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. C., Juhl U., Miller J. A. Nucleic acid guanine: reaction with the carcinogen N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene. Science. 1966 Sep 2;153(3740):1125–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3740.1125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M. Polynucleotide-histone H1 complexes as probes for blot hybridization. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):817–822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage E., Fuchs R. P., Leng M. Reactivity of the antibodies to DNA modified by the carcinogen N-acetoxy-N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1328–1332. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage E., Leng M. Conformation of poly(dG-dC) . poly(dG-dC) modified by the carcinogens N-acetoxy-N-acetyl-2-aminofluorene and N-hydroxy-N-2-aminofluorene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4597–4601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spodheim-Maurizot M., Saint-Ruf G., Leng M. Conformational changes induced in DNA by in vitro reaction with N-hydroxy-N-2-aminofluorene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1683–1694. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troll W., Rinde E., Day P. Effect on N-7 and C-8 substitution of guanine in DNA on Tm, buoyant density and RNA polymerase priming. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;174(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Murcia G., Lang M. C., Freund A. M., Fuchs R. P., Duane M. P., Sage E., Leng M. Electron microscopic visualization of N-acetoxy-N-2-acetylaminofluorene binding sites in ColE1 DNA by means of specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6076–6080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






