Abstract
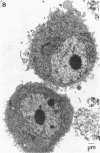
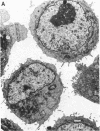
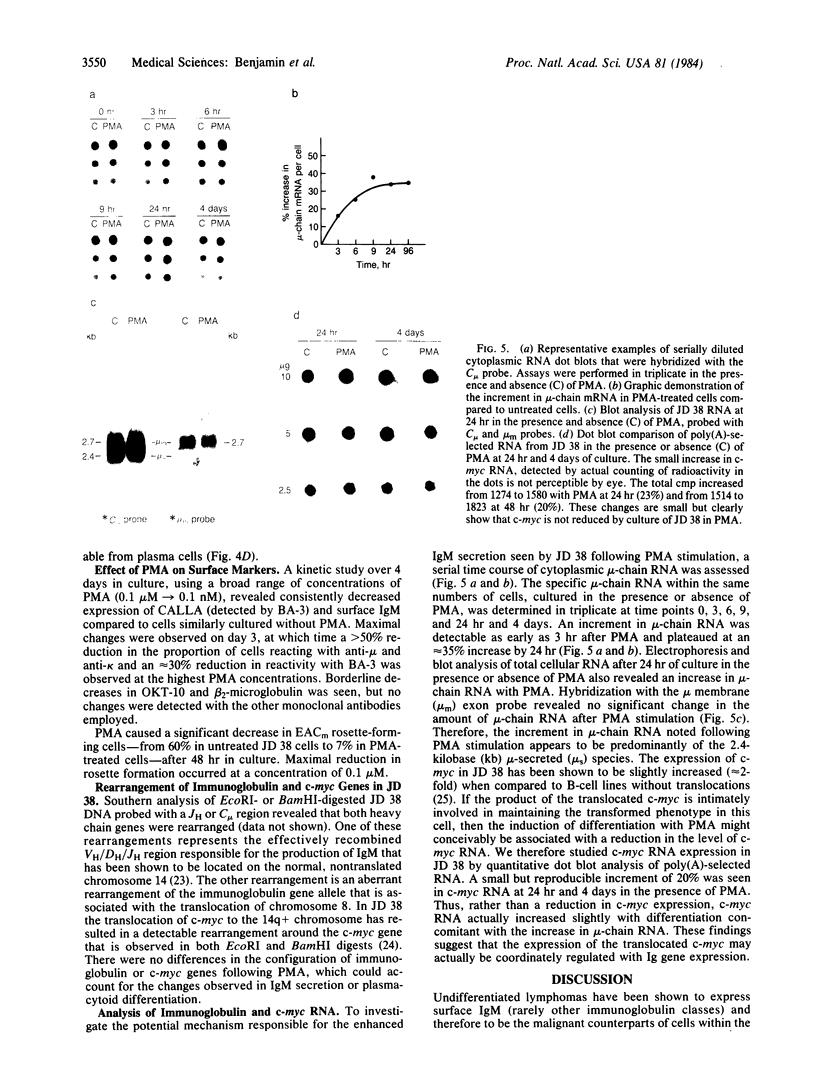
At nanomolar concentrations, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate induced differentiation in a human Epstein-Barr virus-negative B-cell line, JD 38, derived from an undifferentiated lymphoma and containing an 8;14 translocation. The changes induced by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate were consistent with differentiation towards plasma cells and included (i) a marked increase (30-fold) in IgM secretion; (ii) a decrease in the nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio associated with the development of a single prominent nucleolus instead of multiple nucleoli; (iii) the development of parallel arrays of rough endoplasmic reticulum, eccentric nuclei, and marginated heterochromatin; (iv) a reduction in the expression of surface markers, including common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen, IgM, and C3 receptors. Essentially all cells showed plasmacytoid differentiation, although the degree varied. Rare cells (less than 1%) appeared to be terminally differentiated into plasma cells. The increase in secreted IgM was preceded by a small increase in mu-chain RNA, with an increase in the ratio of secreted to membrane form. A small increase in c-myc RNA was also detected with differentiation. This might reflect coordinate regulation of the transcription of immunoglobulin and the translocated c-myc gene. Thus, the maturational arrest of this lymphoma cell line can be overcome with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, indicating that translocation of the c-myc gene does not permanently block the capacity for differentiation. Further, this gene continues to be expressed to at least the same level during cell maturation. Similar ultrastructural changes were induced by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate in four of seven additional lines studied.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin D., Magrath I. T., Douglass E. C., Corash L. M. Derivation of lymphoma cell lines from microscopically normal bone marrow in patients with undifferentiated lymphomas: evidence of occult bone marrow involvement. Blood. 1983 May;61(5):1017–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin D., Magrath I. T., Freeman C. B. Use of fluoresceinated complement-coated bacteria and sheep erythrocyte-antibody-complement complexes for identification of complement receptors on lymphoid cell lines: differences in binding characteristics between cell lines of normal and malignant origin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Nov;71(5):897–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin D., Magrath I. T., Maguire R., Janus C., Todd H. D., Parsons R. G. Immunoglobulin secretion by cell lines derived from African and American undifferentiated lymphomas of Burkitt's and non-Burkitt's type. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1336–1342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheim A., Berger R., Lenoir G. Cytogenetic studies on African Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines: t(8;14), t(2;8) and t(8;22) translocations. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1981 Jun;3(4):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(81)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman T. R., Selonick S. E., Collins S. J. Induction of differentiation of the human promyelocytic leukemia cell line (HL-60) by retinoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C. Terminal differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and other polar compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2458–2462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossman J., Neckers L. M., Arnold A., Korsmeyer S. J. Induction of differentiation in a case of common acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1982 Nov 11;307(20):1251–1254. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198211113072006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Bregni M., Erikson J., Patterson D., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M. Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7824–7827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Martinotti S., Gallo R. C., Erikson J., Croce C. M. Translocation and rearrangements of the c-myc oncogene locus in human undifferentiated B-cell lymphomas. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):963–967. doi: 10.1126/science.6401867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass E. C., Magrath I. T., Lee E. C., Whang-Peng J. Cytogenetic studies in non-African Burkitt lymphoma. Blood. 1980 Jan;55(1):148–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halper J. P., Tolidjian B., Knowles D. M., 2nd Acid alpha-naphthyl acetate esterase (ANAE) in human b cells: correlation of expression with stages of B-cell differentiation. Cell Immunol. 1982 Sep 15;72(2):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90485-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. The role of gene dosage and genetic transpositions in carcinogenesis. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):313–318. doi: 10.1038/294313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Bar-Eli M., Territo M. Phorbol diester-induced macrophage differentiation of leukemic blasts from patients with human myelogenous leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1101–1108. doi: 10.1172/JCI109939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer S. J., Arnold A., Bakhshi A., Ravetch J. V., Siebenlist U., Hieter P. A., Sharrow S. O., LeBien T. W., Kersey J. H., Poplack D. G. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangement and cell surface antigen expression in acute lymphocytic leukemias of T cell and B cell precursor origins. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):301–313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau B., Jäger G., Thiel E., Pachmann K., Rodt H., Huhn D., Thierfelder S., Dörmer P. Phenotypic changes in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells of the common type in diffusion chambers. Leuk Res. 1980;4(6):561–569. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(80)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magrath I. T. Lymphocyte differentiation: an essential basis for the comprehension of lymphoid neoplasia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Sep;67(3):501–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire R. T., Robins T. S., Thorgeirsson S. S., Heilman C. A. Expression of cellular myc and mos genes in undifferentiated B cell lymphomas of Burkitt and non-Burkitt types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1947–1950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., ar-Rushdi A., Erikson J., Watt R., Rovera G., Croce C. M. Differential expression of the normal and of the translocated human c-myc oncogenes in B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4822–4826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Babonits M., Wiener F., Spira J., Klein G., Potter M. Nonrandom chromosome changes involving the Ig gene-carrying chromosomes 12 and 6 in pristane-induced mouse plasmacytomas. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1001–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90212-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura J., Gelfand E. W., Letarte M. Heterogeneity of the response of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to phorbol ester. Blood. 1982 Nov;60(5):1082–1088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Siebenlist U., Korsmeyer S., Waldmann T., Leder P. Structure of the human immunoglobulin mu locus: characterization of embryonic and rearranged J and D genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):583–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90400-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L. Control of normal cell differentiation and the phenotypic reversion of malignancy in myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):535–539. doi: 10.1038/274535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroff R. W., Foon K. A., Billing R. J., Fahey J. L. Immunologic classification of lymphocytic leukemias based on monoclonal antibody-defined cell surface antigens. Blood. 1982 Feb;59(2):207–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Kirsch I., Morton C., Lenoir G., Swan D., Tronick S., Aaronson S., Leder P. Translocation of the c-myc gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7837–7841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin E. H., Wong-Staal F., Gelmann E. P., Dalla-Favera R., Papas T. S., Lautenberger J. A., Eva A., Reddy E. P., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Expression of cellular homologues of retroviral onc genes in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2490–2494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]