Abstract
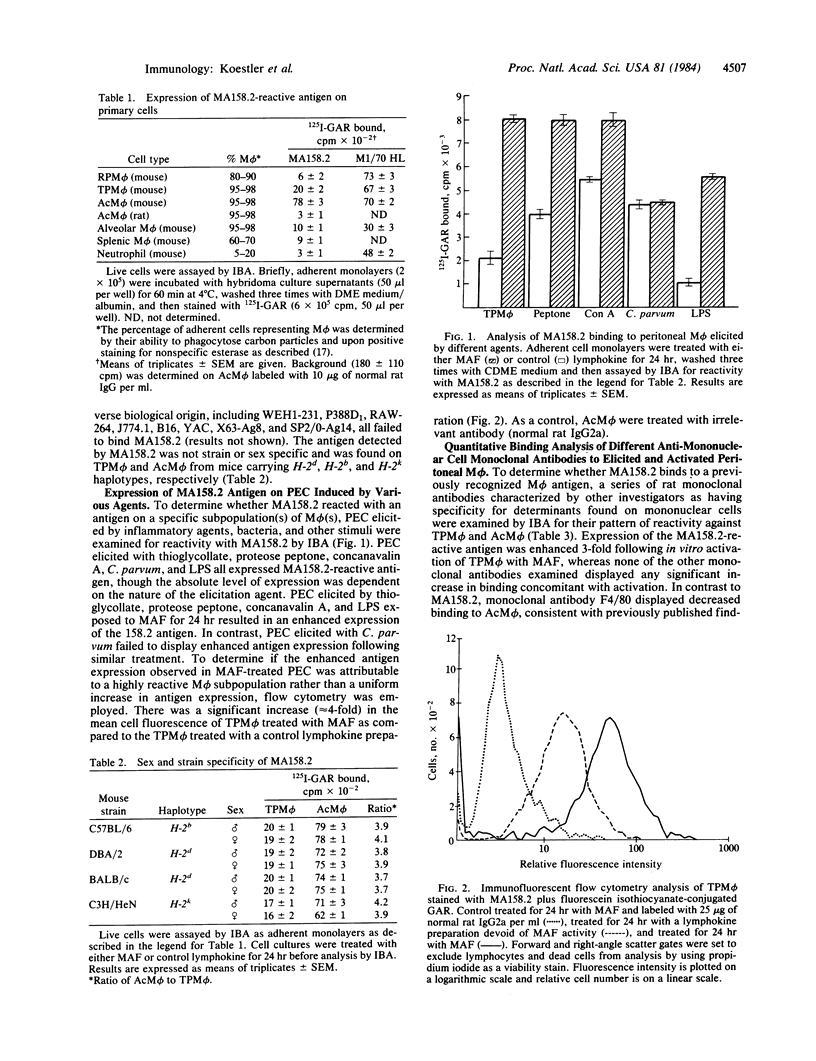
A hybridoma clone secreting a monoclonal antibody, designated MA158.2, that reacts with an antigen expressed on lymphokine-treated macrophages was produced by fusion of mouse myeloma cells with rat spleen cells immunized against C57BL/6 peritoneal macrophages rendered tumoricidal in vitro by incubation with the lymphokine macrophage-activating factor. The specificity of the antibody for activated macrophages and lack of reactivity with histologically diverse cell types was determined by radioimmune indirect binding and flow cytometry. MA158.2 antibody binds to mouse peritoneal macrophages elicited by nonspecific inflammatory agents and to tumoricidal macrophages elicited with Corynebacterium parvum. Resident peritoneal, splenic, and alveolar macrophages were only weakly positive. Several macrophage cell lines (P388D1, WEH1-231, J774, RAW 264.7), murine fibroblasts, and neutrophils did not bind detectable amounts of MA158.2. Radioimmune indirect binding analysis demonstrated that cell suspensions prepared from C57BL/6 mouse spleen, thymus, and lymph node as well as polymorphonuclear leukocytes, lymphocytes, and T- and B-cell murine lymphomas were MA158.2 negative. Expression of the reactive antigen on the macrophage cell surface was enhanced 3-fold following in vitro activation of elicited macrophages with macrophage-activating factor and the kinetics of activation to the tumoricidal state paralleled the increased expression of the antigen recognized by MA158.2. MA158.2 is a rat IgG2a antibody containing a single specific heavy and light chain that does not detect a polymorphic determinant. This monoclonal antibody will be a useful tool for monitoring the efficacy of agents in activating murine macrophages to the tumoricidal state and in analyzing the sequence of biochemical events that culminate in macrophage activation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austyn J. M., Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Oct;11(10):805–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya A., Dorf M. E., Springer T. A. A shared alloantigenic determinant on Ia antigens encoded by the I-A and I-E subregions: evidence for I region gene duplication. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2488–2495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cikes M., Friberg S., Jr, Klein G. Progressive loss of H-2 antigens with concomitant increase of cell-surface antigen(s) determined by Moloney leukemia virus in cultured murine lymphomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Feb;50(2):347–362. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.2.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A. Activation of mononuclear phagocytes: fact, fancy, and future. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon D., Martz E., Reynolds T., Kürzinger K., Springer T. A. Monoclonal antibody to a novel lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-1): mechanism of blockade of T lymphocyte-mediated killing and effects on other T and B lymphocyte functions. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):590–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Austyn J., Stahl P. D., Gordon S. Surface properties of bacillus Calmette-Guérin-activated mouse macrophages. Reduced expression of mannose-specific endocytosis, Fc receptors, and antigen F4/80 accompanies induction of Ia. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):60–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Darnell J. H., Budmen M. B. In vitro activation of mouse macrophages by rat lymphocyte mediators. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):666–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Raz A., Fogler W. E., Hoyer L. C., Poste G. The role of plasma membrane receptors and the kinetics of macrophage activation by lymphokines encapsulated in liposomes. Cancer Res. 1981 Feb;41(2):495–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Recognition and destruction of target cells by tumoricidal macrophages. Isr J Med Sci. 1978 Jan;14(1):177–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogler W. E., Talmadge J. E., Fidler I. J. The activation of tumoricidal properties in macrophages of endotoxin responder and nonresponder mice by liposome-encapsulated immunomodulators. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 Mar;33(3):165–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig R. G., Caltabiano L., Reid R., Jr, Feild J., Poste G. Heterogeneity of protein phosphorylation in metastatic variants of B16 melanoma. Cancer Res. 1983 Dec;43(12 Pt 1):6057–6065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Chapman H. A., Jr, Weinberg J. B. Macrophage tumor killing: influence of the local environment. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):279–282. doi: 10.1126/science.327547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. K., Springer T. A. Biosynthesis and assembly of the alpha and beta subunits of Mac-1, a macrophage glycoprotein associated with complement receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2766–2769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. K., Springer T. A. Mac-2, a novel 32,000 Mr mouse macrophage subpopulation-specific antigen defined by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1221–1228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. K., Springer T. A. Mac-2, a novel 32,000 Mr mouse macrophage subpopulation-specific antigen defined by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1221–1228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. K., Springer T. A. Tissue distribution, structural characterization, and biosynthesis of Mac-3, a macrophage surface glycoprotein exhibiting molecular weight heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):636–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. J., Marino P. A., Schreiber R. D., Adams D. O. Sequential activation of murine mononuclear phagocytes for tumor cytolysis: differential expression of markers by macrophages in the several stages of development. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):1038–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. L., Lazdins J. K. Biochemical criteria for activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):809–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. C., Berry D. Functional heterogeneity in macrophages activated by Corynebacterium parvum: characterization of subpopulations with different activities in promoting immune responses and suppressing tumor cell growth. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1530–1540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. A., Morahan P. S. Functional and biochemical heterogeneity among subpopulations of rat and mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1982 Aug;32(2):111–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Nogueira N., Juangbhanich C., Ellis J., Cohn Z. Activation of macrophages in vivo and in vitro. Correlation between hydrogen peroxide release and killing of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1056–1068. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The concept of the activated macrophage. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):806–809. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W. Activation of mouse macrophages for tumor cell killing. I. Quantitative analysis of interactions between lymphokine and lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1863–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W., Schreiber R. D., Altman A., Katz D. H. Macrophage activation: priming activity from a T-cell hybridoma is attributable to interferon-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3782–3786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Bucana C., Raz A., Bugelski P., Kirsh R., Fidler I. J. Analysis of the fate of systemically administered liposomes and implications for their use in drug delivery. Cancer Res. 1982 Apr;42(4):1412–1422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson T. A., Papadimitriou J. M., Walters M. N., Wolman M. Effects of exposure of murine peritoneal exudate and resident macrophages to high molecular levan: a morphological study. J Pathol. 1977 Nov;123(3):157–164. doi: 10.1002/path.1711230305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: development of macrophage cytotoxic activity requires completion of a sequence of short-lived intermediary reactions. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):2035–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz R. M., Chirigos M. A. Macrophage activation for nonspecific tumor cytotoxicity. Adv Pharmacol Chemother. 1980;17:157–193. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorg C. Heterogeneity of macrophages in response to lymphokines and other signals. Mol Immunol. 1982 Oct;19(10):1275–1278. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90293-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T., Galfré G., Secher D. S., Milstein C. Mac-1: a macrophage differentiation antigen identified by monoclonal antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Apr;9(4):301–306. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D., Lohmann-Matthes M. L. Functionally different subpopulations of mouse macrophages recognized by monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Feb;12(2):134–140. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniyama T., Tokunaga T. Monoclonal antibodies directed against mouse macrophages in different stages of activation for tumor cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):1032–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker S. B., Pierre R. V., Jordon R. E. Rapid identification of monocytes in a mixed mononuclear cell preparation. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):267–269. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against mouse macrophage and lymphocyte Fc receptors. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):580–596. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Kaplan G., Plutner H., Cohn Z. A. Fc-receptor variants of a mouse macrophage cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1400–1404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolman M., Eldar T. Different patterns of macrophage activation induced by various agents. Cell Mol Biol Incl Cyto Enzymol. 1981;27(5):543–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


