Abstract
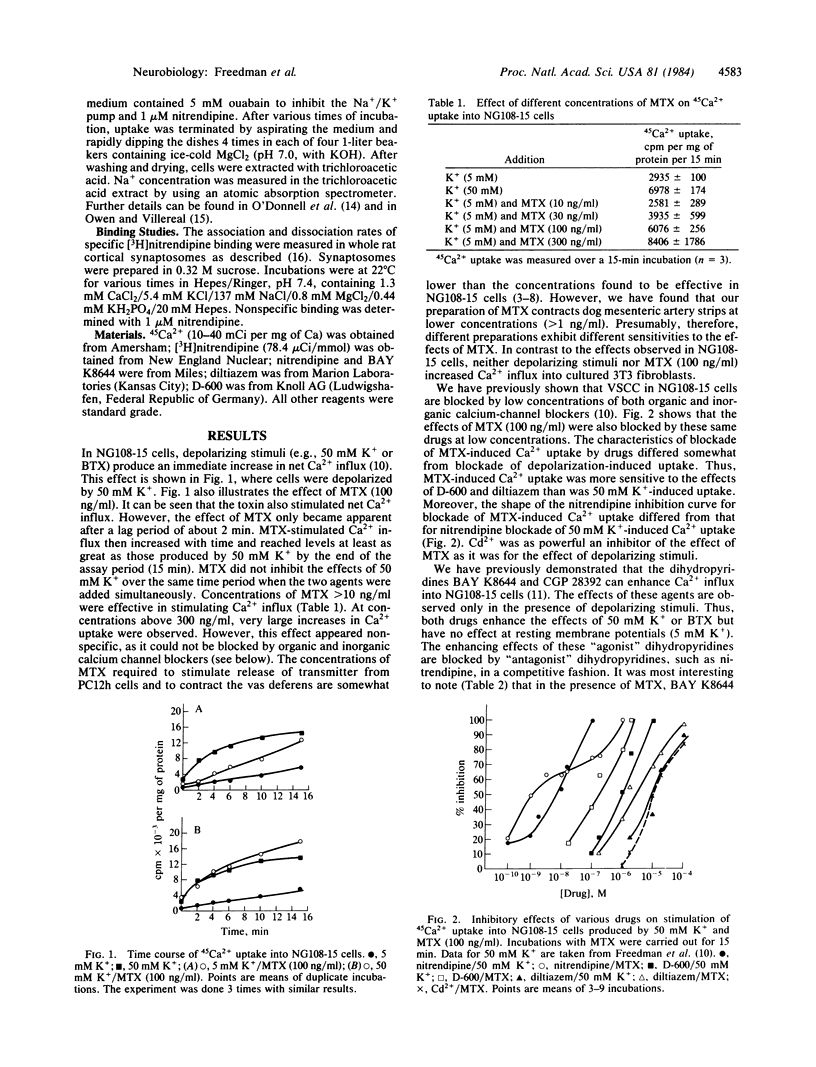
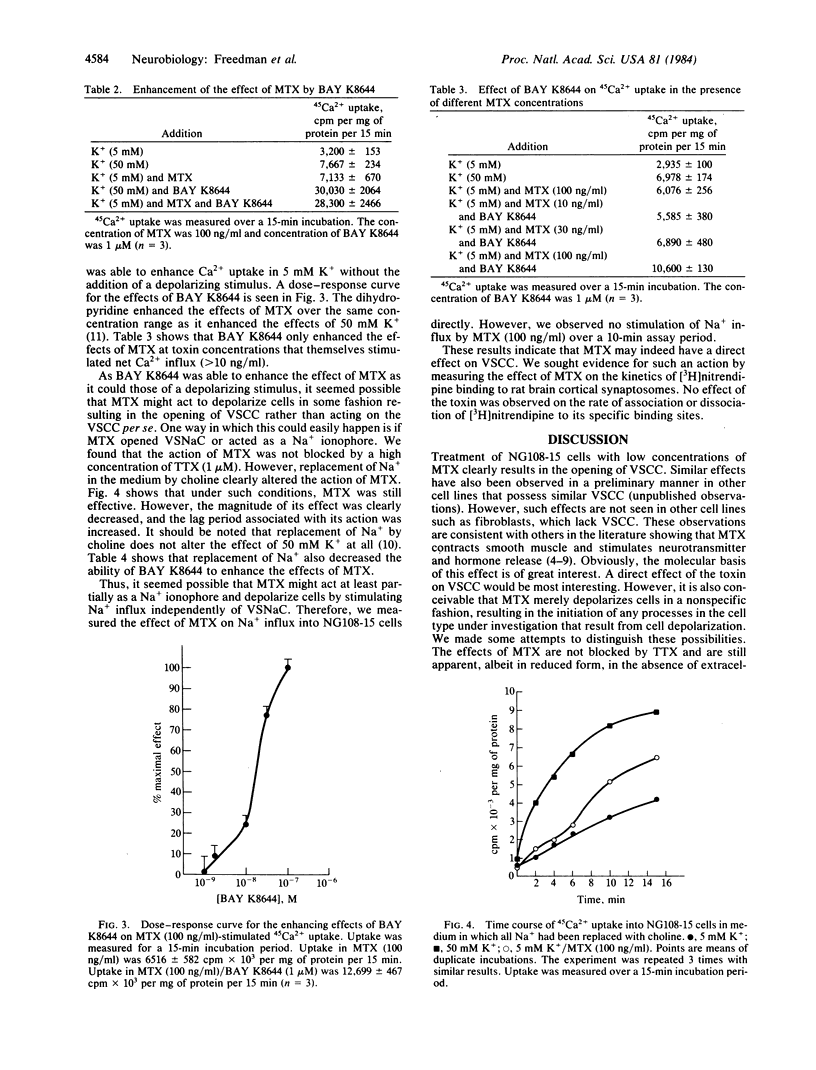
The dinoflagellate toxin maitotoxin (MTX) stimulated 45Ca2+ uptake in cultured NG108-15 neuroblastoma X glioma cells. Depolarizing stimuli (e.g., 50 mM K+) produced an immediate stimulation in Ca2+ uptake, whereas that produced by MTX occurred only after a lag period of about 2 min. MTX did not stimulate Ca2+ uptake into fibroblasts. Both 50 mM K+- and MTX-stimulated Ca2+ uptake was blocked by organic calcium channel antagonists (nitrendipine, D-600, diltiazem) at very low concentrations. Cd2+ was also a potent blocker. The novel dihydropyridine BAY K8644 enhanced Ca2+ uptake in the presence of 50 mM K+ but had no effect in 5 mM Ca2+. However, in the presence of MTX, BAY K8644 stimulated Ca2+ uptake in 5 mM K+. The effects of MTX were not blocked by tetrodotoxin but were decreased in Na+-free medium. MTX did not stimulate Na+ uptake into NG108-15 cells and did not alter [3H]nitrendipine binding to rat brain cortical synaptosomes. It is concluded that MTX may alter the voltage dependence of calcium-channel activation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A. Synaptic inhibition of the M-current: slow excitatory post-synaptic potential mechanism in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:263–272. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Wallach D. F. Preparation and properties of plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum fragments from isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):334–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Neurotoxins that act on voltage-sensitive sodium channels in excitable membranes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:15–43. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.000311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Hildebrandt J., Iyengar R., Birnbaumer L., Sekura R. D., Manclark C. R. Pertussis toxin substrate, the putative Ni component of adenylyl cyclases, is an alpha beta heterodimer regulated by guanine nucleotide and magnesium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4276–4280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. J., Murphy K. M., Snyder S. H. [3H]nitrendipine-labeled calcium channels discriminate inorganic calcium agonists and antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3656–3660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara J. T., Akau C. K., Yasumoto T. Effects of ciguatoxin and maitotoxin on the isolated guinea pig atria. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;25(1):177–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T. Modulation of nerve membrane sodium channels by chemicals. J Physiol (Paris) 1981 May;77(9):1093–1101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell M. E., Cragoe E., Jr, Villereal M. L. Inhibition of Na+ influx and DNA synthesis in human fibroblasts and neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells by amiloride analogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Aug;226(2):368–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Kajiwara A., Yasumoto T. Excitatory effect of the most potent marine toxin, maitotoxin, on the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Oct;227(1):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. Contractile response of the rabbit aorta to maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:711–721. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen N. E., Villereal M. L. Evidence for a role of calmodulin in serum stimulation of Na+ influx in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3537–3541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quandt F. N., Narahashi T. Modification of single Na+ channels by batrachotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6732–6736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. Maitotoxin, a Ca2+ channel activator candidate. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7287–7289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Tatsumi M., Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. Ca2+ channel activating function of maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin known, in clonal rat pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10944–10949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. A., Moss J., Vaughan M. Effects of GTP on choleragen-catalyzed ADP ribosylation of membrane and soluble proteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3959–3963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



