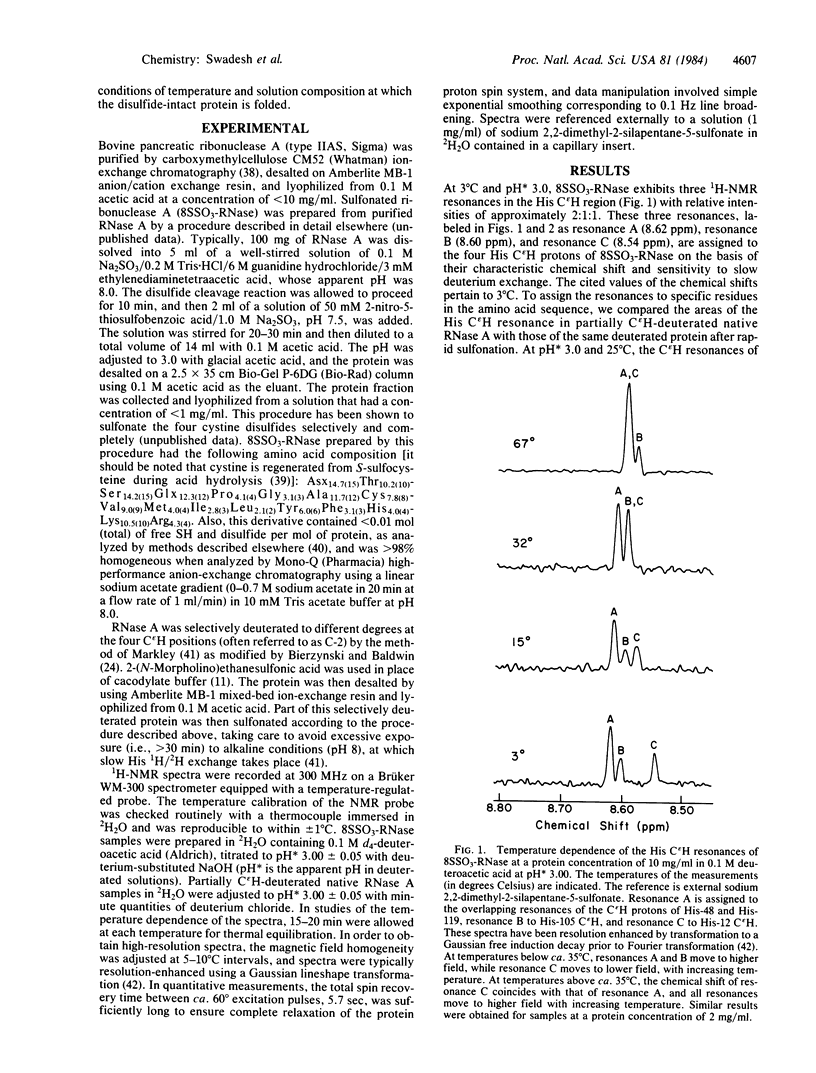
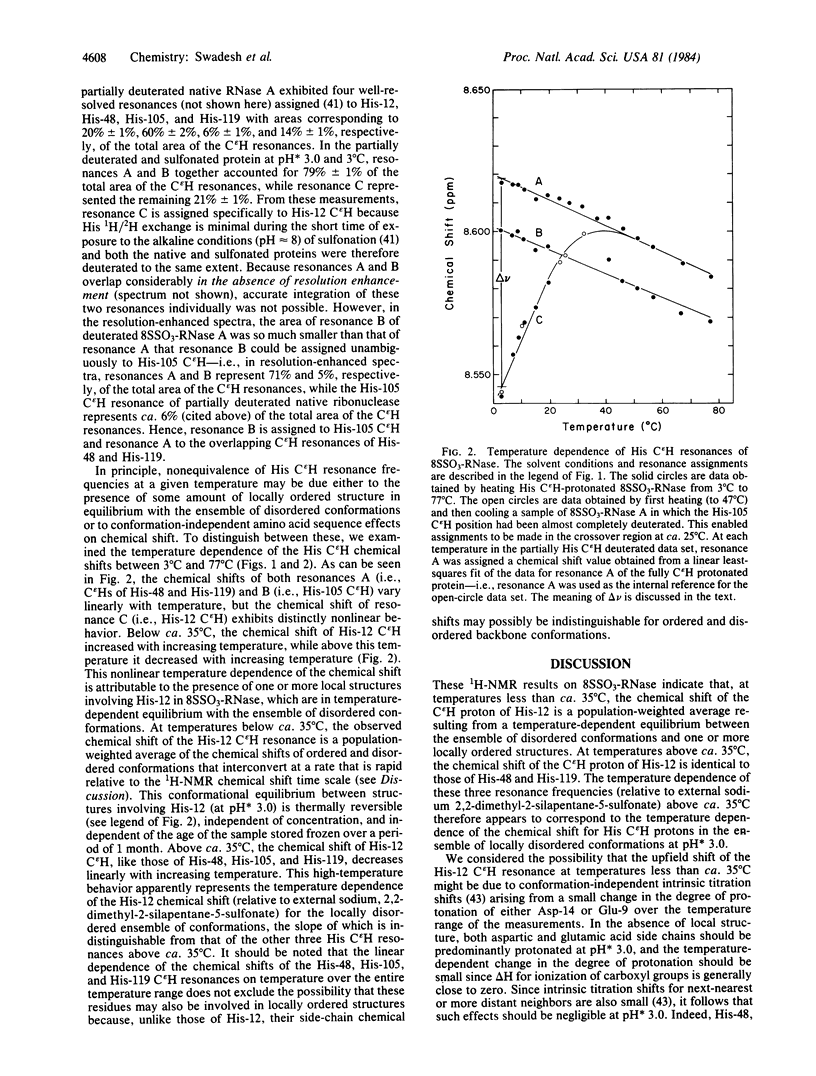
Abstract
The C epsilon H proton resonance of His-12 of reduced cysteine S-sulfonated bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A exhibits a nonlinear temperature dependence of the chemical shift in its 1H-NMR spectrum at an apparent pH of 3.0. At temperatures below ca. 35 degrees C, the temperature dependence of the chemical shift of the His-12 C epsilon H resonance is opposite in sign to those of His-48, His-105, and His-119. At temperatures above ca. 35 degrees C, the temperature dependence of the chemical shift of the His-12 C epsilon H resonance is similar to those of the other three His C epsilon H resonances. These data indicate the existence of an equilibrium between locally ordered and locally disordered environments of His-12 in the sulfonated protein at temperatures below ca. 35 degrees C. The ordered and disordered conformations interconvert at a rate that is fast relative to the 1H-NMR chemical shift time scale--i.e., the locally ordered structure has a lifetime of much less than 7 msec. These results demonstrate that short- and medium-range interactions can define short-lived local structures under conditions of temperature and solution composition at which the native protein structure is stable. Furthermore, they demonstrate the utility of reduced derivatives of disulfide-containing proteins as model systems for the identification of local structures that may play a role as early-forming chain-folding initiation structures.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAILEY J. L., COLE R. D. Studies on the reaction of sulfite with proteins. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jul;234(7):1733–1739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz F. W., Roberts G. C. Nucler magnetic resonance studies of the unfolding of pancreatic ribonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):345–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90385-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierzynski A., Baldwin R. L. Local secondary structure in ribonuclease A denatured by guanidine . HCl near 1 degree C. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 25;162(1):173–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierzynski A., Kim P. S., Baldwin R. L. A salt bridge stabilizes the helix formed by isolated C-peptide of RNase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2470–2474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Klee W. A. Helix-coil transition of the isolated amino terminus of ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1971 Feb 2;10(3):470–476. doi: 10.1021/bi00779a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Scheraga H. A. A hypothesis for the pathway of the thermally-induced unfolding of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. J Theor Biol. 1975 Sep;53(2):403–420. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(75)80012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavez L. G., Jr, Scheraga H. A. Folding of ribonuclease, S-protein, and des(121-124)-ribonuclease during glutathione oxidation of the reduced proteins. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):996–1004. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavez L. G., Jr, Scheraga H. A. Intrinsic stabilities of portions of the ribonuclease molecule. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):1005–1012. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. C., Lord R. C. Laser Raman spectroscopic studies of the thermal unfolding of ribonuclease A. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1889–1897. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton J. B., Konishi Y., Scheraga H. A. Folding of ribonuclease A from a partially disordered conformation. Kinetic study under folding conditions. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 12;21(21):5155–5163. doi: 10.1021/bi00264a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galat A., Creighton T. E., Lord R. C., Blout E. R. Circular dichroism, Raman spectroscopy, and gel filtration of trapped folding intermediates of ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 3;20(3):594–601. doi: 10.1021/bi00506a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABER E., ANFINSEN C. B. Regeneration of enzyme activity by air oxidation of reduced subtilisin-modified ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:422–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howarth O. W. The thermal unfolding of ribonuclease A. A 13C NMR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 25;576(1):163–175. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90495-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato I., Anfinsen C. B. On the stabilization of ribonuclease S-protein by ribonuclease S-peptide. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1004–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim P. S., Baldwin R. L. Structural intermediates trapped during the folding of ribonuclease A by amide proton exchange. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):6124–6129. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim P. S., Bierzynski A., Baldwin R. L. A competing salt-bridge suppresses helix formation by the isolated C-peptide carboxylate of ribonuclease A. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 25;162(1):187–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi Y., Ooi T., Scheraga H. A. Regeneration of RNase A from the reduced protein: models of regeneration pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5734–5738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotelchuck D., Scheraga H. A. The influence of short-range interactions on protein conformation. I. Side chain-backbone interactions within a single peptide unit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1163–1170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotelchuck D., Scheraga H. A. The influence of short-range interactions on protein onformation. II. A model for predicting the alpha-helical regions of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jan;62(1):14–21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima K., Baldwin R. L. Nature and locations of the most slowly exchanging peptide NH protons in residues 1 to 19 of ribonuclease S. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):281–297. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima K., Kim P. S., Baldwin R. L. Strategy for trapping intermediates in the folding of ribonuclease and for using 1H-nmr to determine their structures. Biopolymers. 1983 Jan;22(1):59–67. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhardt A. M., Baldwin R. L. Recombination of S-peptide with S-protein during folding of ribonuclease S. I. Folding pathways of the slow-folding and fast-folding classes of unfolded S-protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 25;135(1):231–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90349-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhardt A. M. Secondary structure in ribonuclease. I. Equilibrium folding transitions seen by amide circular dichroism. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 15;157(2):331–355. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. N., Brandts J. F. Mechanism for the unfolding and refolding of ribonuclease A. Kinetic studies utilizing spectroscopic methods. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 1;22(3):564–573. doi: 10.1021/bi00272a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markley J. L. Correlation proton magnetic resonance studies at 250 MHz of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. I. Reinvestigation of the histidine peak assignments. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 12;14(16):3546–3554. doi: 10.1021/bi00687a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews C. R., Westmoreland D. G. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of residual structure in thermally unfolded ribonuclease A. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 7;14(20):4532–4538. doi: 10.1021/bi00691a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Némethy G., Scheraga H. A. A possible folding pathway of bovine pancreatic RNase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6050–6054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rico M., Nieto J. L., Santoro J., Bermejo F. J., Herranz J., Gallego E. Low-temperature 1H-NMR evidence of the folding of isolated ribonuclease S-peptide. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 17;162(2):314–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80779-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. C., Benz F. W. Proton Fourier transform NMR studies of the unfolding of ribonuclease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Dec 31;222:130–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb15257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer S. W. Mechanism of glutathione regeneration of reduced pancreatic ribonuclease a. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1975;7(2):179–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1975.tb02430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid F. X., Baldwin R. L. Detection of an early intermediate in the folding of ribonuclease A by protection of amide protons against exchange. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 25;135(1):199–215. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90347-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. N., Kotelchuck D., Taylor G. T., Scheraga H. A. Nuclearmagnetic resonance study of the N-terminal fragment of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jun;150(2):757–766. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimson E. R., Montelione G. T., Meinwald Y. C., Rudolph R. K., Scheraga H. A. Equilibrium ratios of cis- and trans-proline conformers in fragments of ribonuclease A from nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of adjacent tyrosine ring resonances. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 12;21(21):5252–5262. doi: 10.1021/bi00264a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABORSKY G. Chromatography of ribonuclease on carboxymethyl cellulose columns. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2652–2656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Kontani T., Yoneda M., Ooi T. A circular dichroic spectral study on disulfide-reduced pancreatic ribonuclease A and its renaturation to the active enzyme. J Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(4):1127–1133. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Scheraga H. A. Hypothesis about the mechanism of protein folding. Macromolecules. 1977 Mar-Apr;10(2):291–304. doi: 10.1021/ma60056a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thannhauser T. W., Konishi Y., Scheraga H. A. Sensitive quantitative analysis of disulfide bonds in polypeptides and proteins. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90786-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y., Baldwin R. L., Elson E. L. Properties of the refolding and unfolding reactions of ribonuclease A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1809–1812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetlaufer D. B. Nucleation, rapid folding, and globular intrachain regions in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):697–701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodawer A., Bott R., Sjölin L. The refined crystal structure of ribonuclease A at 2.0 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1325–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



