Abstract
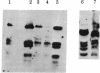
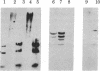
DNA-mediated gene transfer was used to investigate the mode of inheritance of 5-methylcytosine in mouse L cells. Unmethylated phi X174 replicative form DNA remains unmethylated after its introduction and integration into these cells. On the other hand, phi X174 replicative form DNA that was methylated in vitro at its C-C-G-G residues retains these methylations as shown by restriction enzyme analysis with Hpa II and Msp I to detect methylation at this specific site. Although these unselected methylated vectors are prone to lose 30-40% of their methyl moieties upon transfection, this demethylation appears to be random. Once established, the resulting methylation pattern is stable for at least 100 cell generations. In order to examine the specificity of methylation inheritance, fully hemimethylated duplex phi X174 DNA was synthesized in vitro from primed single-strand phi X174 DNA by using 5-methyl deoxycytidine 5'-triphosphate. This molecule was inserted into mouse L cells by cotransformation and subsequently was analyzed by a series of restriction enzymes. Only methylations located at C-G residues were conserved after many generations of cell growth. The results suggest that the inheritance of the cellular DNA methylation pattern is based on a C-G-specific methylase that operates on newly replicated hemimethylated DNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to study eukaryotic DNA methylation: II. The symmetry of methylated sites supports semi-conservative copying of the methylation pattern. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 5;118(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Solage A., Glaser G., Razin A. Direct detection of methylated cytosine in DNA by use of the restriction enzyme MspI. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(6):2125–2132. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Nature of Col E 1 plasmid replication in Escherichia coli in the presence of the chloramphenicol. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.667-676.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Mulder C., Fleckenstein B. Methylation of Herpesvirus saimiri DNA in lymphoid tumor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3839–3843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenbaum Y., Cedar H., Razin A. Restriction enzyme digestion of hemimethylated DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2509–2515. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenbaum Y., Naveh-Many T., Cedar H., Razin A. Sequence specificity of methylation in higher plant DNA. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):860–862. doi: 10.1038/292860a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenbaum Y., Stein R., Cedar H., Razin A. Methylation of CpG sequences in eukaryotic DNA. FEBS Lett. 1981 Feb 9;124(1):67–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R., Pugh J. E. DNA modification mechanisms and gene activity during development. Science. 1975 Jan 24;187(4173):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Chambon P. DNA methylation: organ specific variations in the methylation pattern within and around ovalbumin and other chicken genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2081–2103. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann M. B., Smith H. O. Specificity of Hpa II and Hae III DNA methylases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Dec;4(12):4211–4221. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.12.4211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Ginder G. D. Specific DNA methylation sites in the vicinity of the chicken beta-globin genes. Nature. 1979 Aug 2;280(5721):419–420. doi: 10.1038/280419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naveh-Many T., Cedar H. Active gene sequences are undermethylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4246–4250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack Y., Stein R., Razin A., Cedar H. Methylation of foreign DNA sequences in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6463–6467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quint A., Cedar H. In vitro methylation of DNA with Hpa II methylase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):633–646. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Friedman J. DNA methylation and its possible biological roles. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;25:33–52. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60482-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Hirose T., Itakura K., Riggs A. D. Efficient correction of a mutation by use of chemically synthesized DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4268–4270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Riggs A. D. DNA methylation and gene function. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):604–610. doi: 10.1126/science.6254144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Sedat J. W., Sinsheimer R. L. Structure of the DNA of bacteriophage phiX174. VII. Methylation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 28;53(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90298-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Urieli S., Pollack Y., Gruenbaum Y., Glaser G. Studies on the biological role of dna methylation; IV. Mode of methylation of DNA in E. coli cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1783–1792. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D. X inactivation, differentiation, and DNA methylation. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;14(1):9–25. doi: 10.1159/000130315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Friedmann T., Air G. M., Barrell B. G., Brown N. L., Fiddes J. C., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Slocombe P. M., Smith M. The nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phiX174. J Mol Biol. 1978 Oct 25;125(2):225–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90346-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneider T. W. The 5'-cytosine in CCGG1 is methylated in two eukaryotic DNAs and Msp I is sensitive to methylation at this site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3829–3840. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter D., Doerfler W. Methylation of integrated adenovirus type 12 DNA sequences in transformed cells is inversely correlated with viral gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):253–256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation at a CCGG sequence in the large intron of the rabbit beta-globin gene: tissue-specific variations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4631–4634. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.12.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Levy D., Perucho M. The somatic replication of DNA methylation. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90498-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ploeg L. H., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation in the human gamma delta beta-globin locus in erythroid and nonerythroid tissues. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):947–958. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ploeg L. H., Groffen J., Flavell R. A. A novel type of secondary modification of two CCGG residues in the human gamma delta beta-globin gene locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4563–4574. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]