Abstract
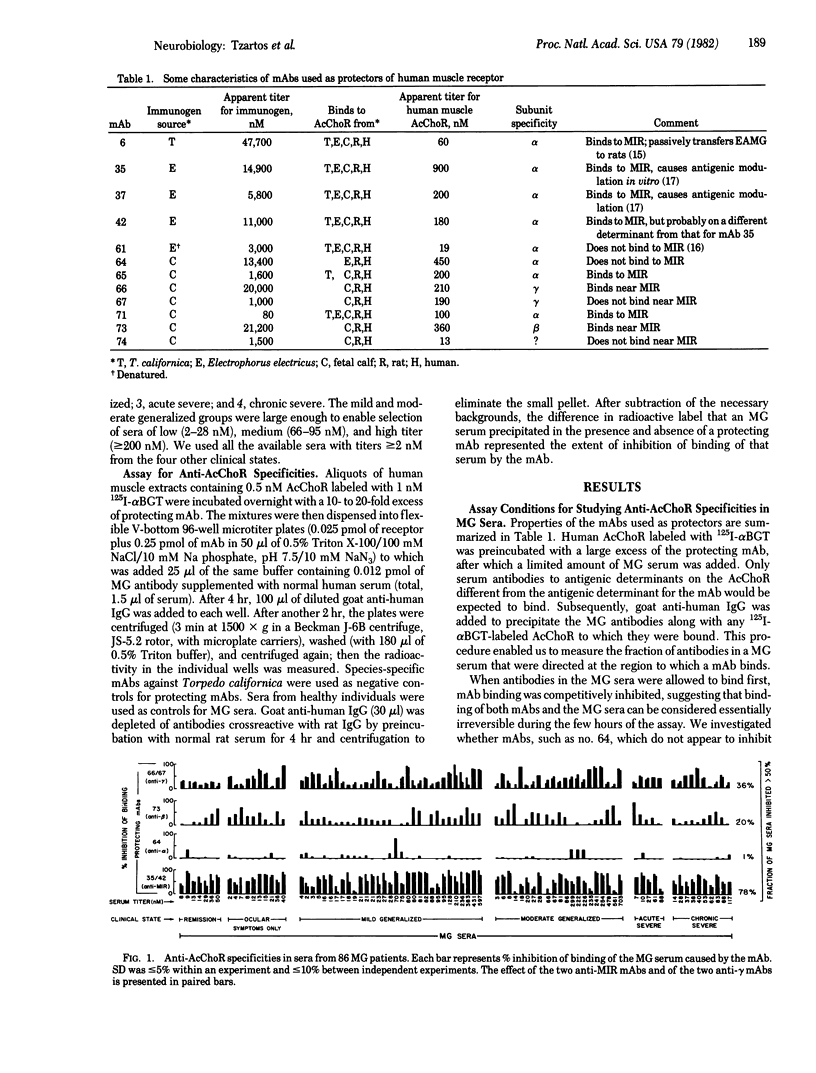
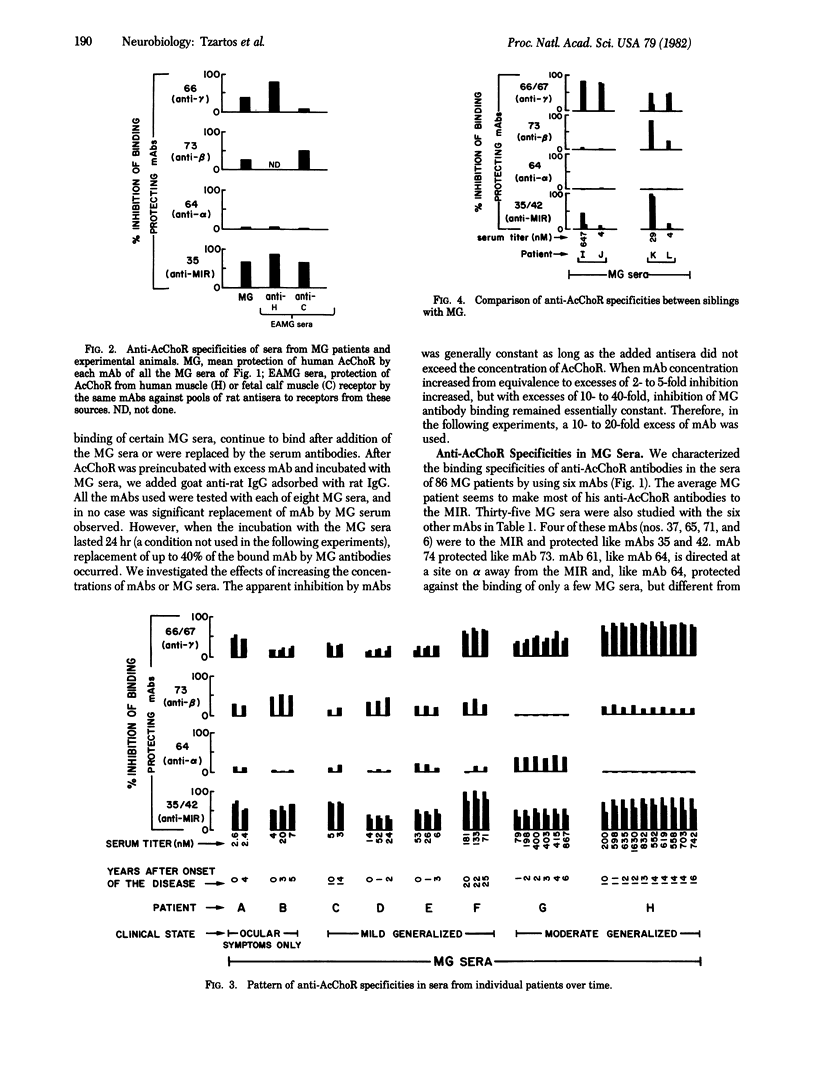
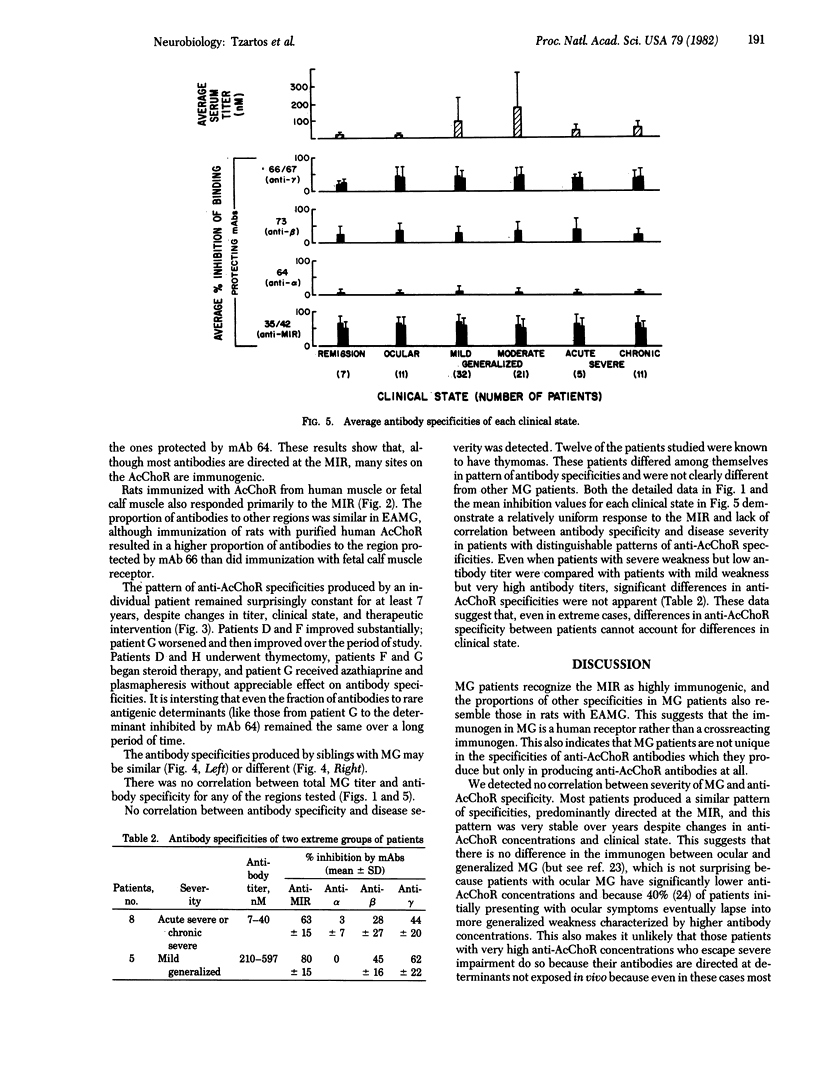
The pattern of antibody specificities in sera from patients with myasthenia gravis (MG) was determined by the ability of monoclonal antibodies against defined determinants on the acetylcholine receptor molecule to inhibit binding of the serum antibodies to receptor from human muscle. We found that MG patients produce fundamentally the same pattern of specificities as that produced by animals immunized with receptor purified from fish electric organs or mammalian muscle. Most of the antibodies are directed at the "main immunogenic region' which is located on the extracellular surface of the alpha subunit and is distinct from the acetylcholine binding site. Regions on the beta and gamma subunits near the main immunogenic region are also significantly immunogenic. In one patient the proportions of antibodies to various regions are constant over time despite changes in total antibody amount and clinical state. Between patients there is no obvious correlation between antibody specificities and clinical state. These data suggest that the autoimmune response in MG is stimulated by human receptor rather than a crossreacting (e.g., viral) antigen and that in both MG and experimental autoimmune MG the pattern of specificities produced is determined by the inherently immunogenic structural features of the receptor molecule. They also suggest that the wide differences in clinical state sometimes observed between patients with the same total concentration of antireceptor antibody are due primarily to differences in endogenous factors which affect the safety factor for neuromuscular transmission rather than to the presence of especially pathogenic antireceptor specificities.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Compston D. A., Vincent A., Newsom-Davis J., Batchelor J. R. Clinical, pathological, HLA antigen and immunological evidence for disease heterogeneity in myasthenia gravis. Brain. 1980 Sep;103(3):579–601. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.3.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. Monoclonal antibodies as probes of acetylcholine receptor structure. 2. Binding to native receptor. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2181–2191. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dau P. C., Lindstrom J. M., Cassel C. K., Denys E. H., Shev E. E., Spitler L. E. Plasmapheresis and immunosuppressive drug therapy in myasthenia gravis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 24;297(21):1134–1140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711242972102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Lambert E. H., Howard F. M. Immune complexes (IgG and C3) at the motor end-plate in myasthenia gravis: ultrastructural and light microscopic localization and electrophysiologic correlations. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 May;52(5):267–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Tsujihata M., Lambert E. H., Lindstrom J. M., Lennon V. A. Experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis: a sequential and quantitative study of the neuromuscular junction ultrastructure and electrophysiologic correlations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1976 Sep-Oct;35(5):569–587. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197609000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Drachman D. B., Satyamurti S. Neuromuscular junction in myasthenia gravis: decreased acetylcholine receptors. Science. 1973 Oct 19;182(4109):293–295. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4109.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez C. M., Richman D. P., Berman P. W., Burres S. A., Arnason B. G., Fitch F. W. Monoclonal antibodies against purified nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. Monoclonal antibodies as probes of acetylcholine receptor structure. 1. Peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2173–2180. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S., Bevan S., Kullberg R., Lindstrom J., Rice J. Modulation of acetylcholine receptor by antibody against the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3090–3094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R. W., Kato A. C., Rey M. J., Fulpius B. W. Monoclonal antibodies directed against the neurotransmitter binding site of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 20;120(1):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao I., Drachman D. B. Myasthenic immunoglobulin accelerates acetylcholine receptor degradation. Science. 1977 Apr 29;196(4289):527–529. doi: 10.1126/science.850793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. M., Einarson B. L., Lennon V. A., Seybold M. E. Pathological mechanisms in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. I. Immunogenicity of syngeneic muscle acetylcholine receptor and quantitative extraction of receptor and antibody-receptor complexes from muscles of rats with experimental automimmune myasthenia gravis. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):726–738. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. M., Lambert E. H. Content of acetylcholine receptor and antibodies bound to receptor in myasthenia gravis, experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis, and Eaton-Lambert syndrome. Neurology. 1978 Feb;28(2):130–138. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.2.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. M., Seybold M. E., Lennon V. A., Whittingham S., Duane D. D. Antibody to acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis. Prevalence, clinical correlates, and diagnostic value. Neurology. 1976 Nov;26(11):1054–1059. doi: 10.1212/wnl.26.11.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Campbell M., Nave B. Specificities of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors. Muscle Nerve. 1978 Mar-Apr;1(2):140–145. doi: 10.1002/mus.880010206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Dau P. Biology of myasthenia gravis. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:337–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Einarson B. Antigenic modulation and receptor loss in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve. 1979 May-Jun;2(3):173–179. doi: 10.1002/mus.880020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Einarson B., Tzartos S. Production and assay of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1981;74(Pt 100):432–460. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)74031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D., Fuchs S. Monoclonal anti-acetylcholine-receptor antibodies directed against the cholinergic binding site. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 29;20(20):5920–5924. doi: 10.1021/bi00523a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsom-Davis J., Pinching A. J., Vincent A., Wilson S. G. Function of circulating antibody to acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis: investigation by plasma exchange. Neurology. 1978 Mar;28(3):266–272. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.3.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osserman K. E., Genkins G. Studies in myasthenia gravis: review of a twenty-year experience in over 1200 patients. Mt Sinai J Med. 1971 Nov-Dec;38(6):497–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahashi K., Engel A. G., Lambert E. H., Howard F. M., Jr Ultrastructural localization of the terminal and lytic ninth complement component (C9) at the motor end-plate in myasthenia gravis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1980 Mar;39(2):160–172. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198003000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Lindstrom J. M. Monoclonal antibodies used to probe acetylcholine receptor structure: localization of the main immunogenic region and detection of similarities between subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Rand D. E., Einarson B. L., Lindstrom J. M. Mapping of surface structures of electrophorus acetylcholine receptor using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8635–8645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



