Abstract
The principal curarimimetic toxin of Naja naja siamensis derivatized with biotinyl groups binds specifically both to acetylcholine receptor, isolated from Torpedo californica electric tissue, and to avidin. Isolated complexes of receptor monomer or dimer, biotinyl-toxin, and avidin were negatively stained and examined in the scanning transmission electron microscope. We measured the angle made by the radius of each avidin bound at the periphery of a monomeric unit in dimer to the axis connecting the centers of the monomers, starting at the crosslink between the monomers. We infer from the distribution of these angles that one toxin binding site is located in the range of 45 degrees to 85 degrees and another at about 100 degrees further from the crosslink between the monomers. Because it is known that there are two toxin binding sites per monomer, associated with the two alpha chains, the bound avidins presumably point to portions of the alpha chains, indicating their positions relative to that portion of the delta chain located at the crosslink between monomers in dimer.
Full text
PDF
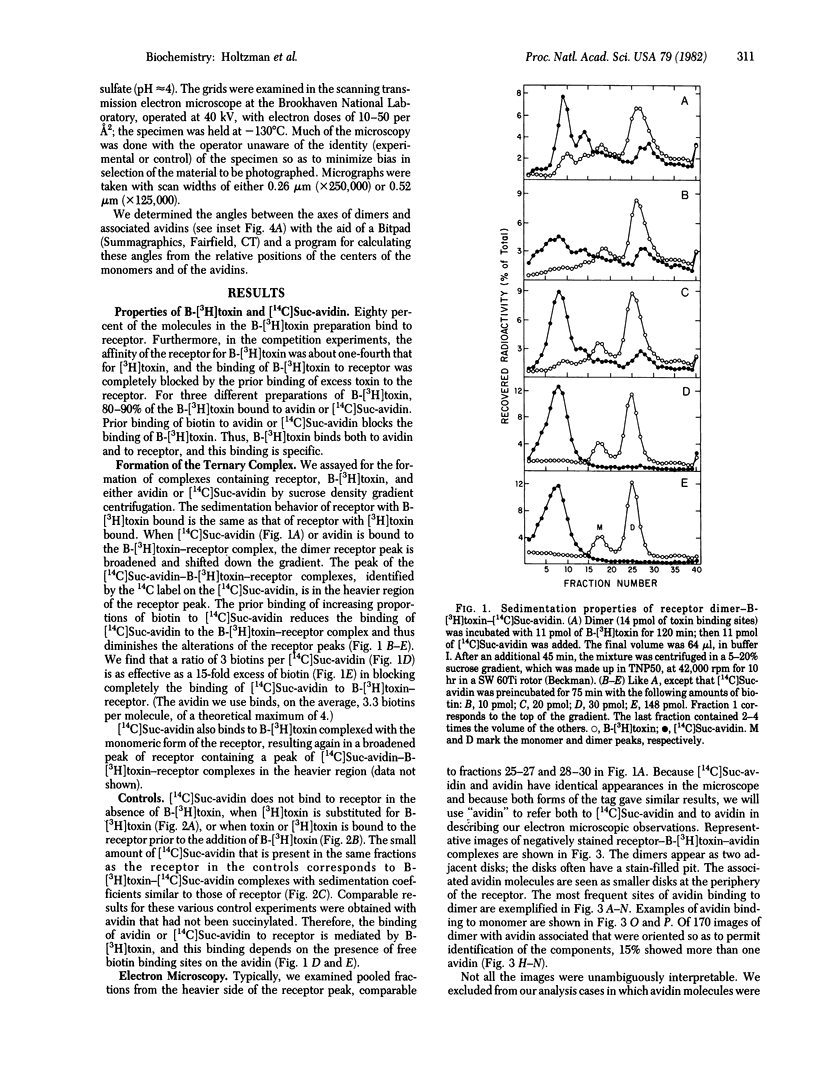
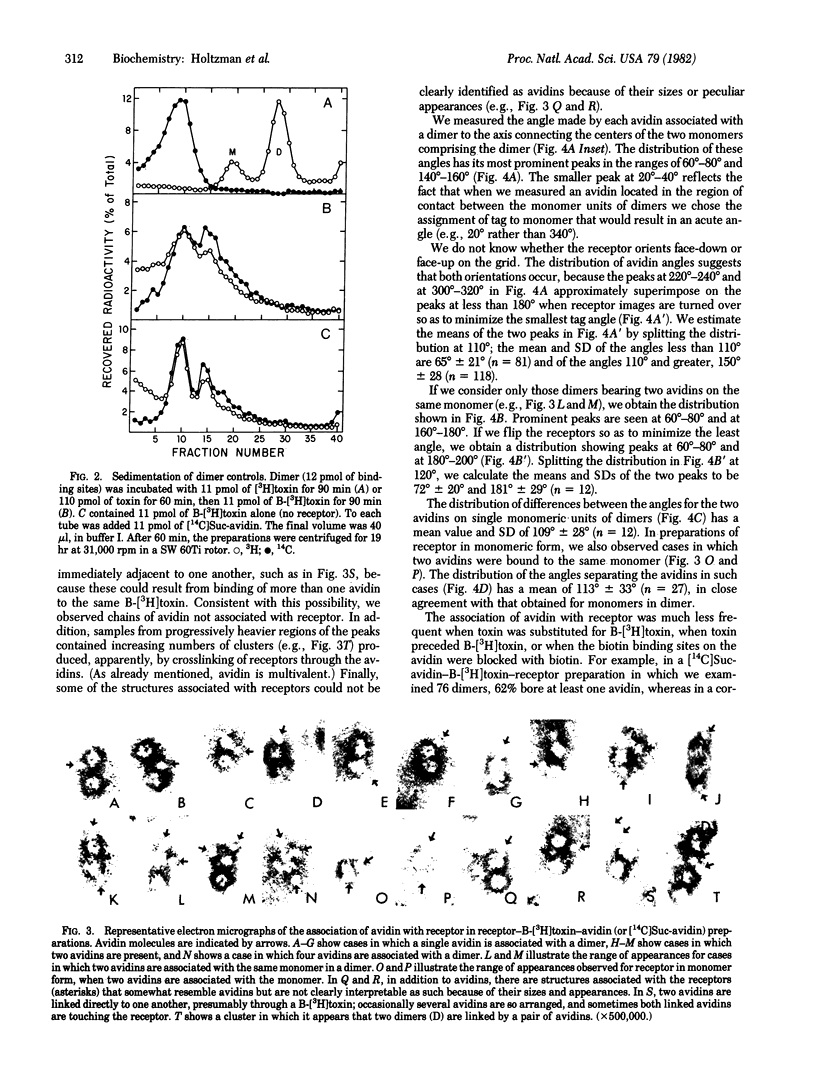


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod D. Crosslinkage and visualization of acetylcholine receptors on myotubes with biotinylated alpha-bungarotoxin and fluorescent avidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4823–4827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Skutelsky E., Wilchek M. The avidin-biotin complex in affinity cytochemistry. Methods Enzymol. 1979;62:308–315. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)62235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartaud J., Benedetti E. L., Cohen J. B., Meunier J. C., Changeux J. P. Presence of a lattice structure in membrane fragments rich in nicotinic receptor protein from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 15;33(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartaud J., Popot J. L., Changeux J. P. Light and heavy forms of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo marmorata electric organ: morphological identification using reconstituted vesicles. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 1;121(2):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80374-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Bock E. Molecular forms of acetylcholine receptor. Effects of calcium ions and a sulfhydryl reagent on the occurrence of oligomers. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 4;16(20):4513–4520. doi: 10.1021/bi00639a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle V. N., Karlin A. Affinity labeling of one of two alpha-neurotoxin binding sites in acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2039–2045. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn F. M., Titus G., Montibeller J. A., Hofmann K. Hormone-receptor studies with avidin and biotinylinsulin-avidin complexes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5742–5746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:85–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton S. L., McLaughlin M., Karlin A. Disulfide bond cross-linked dimer in acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 7;79(3):692–699. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann T., Changeux J. P. Structural and functional properties of the acetylcholine receptor protein in its purified and membrane-bound states. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:317–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Salpeter S. R. Organization of acetylcholine receptors in quick-frozen, deep-etched, and rotary-replicated Torpedo postsynaptic membrane. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jul;82(1):150–173. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.1.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F., Layer P., Kiefer H. R., Bandini G. Photoaffinity labeling and quaternary structure of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2624–2628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Holtzman E., Valderrama R., Damle V., Hsu K., Reyes F. Binding of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors in Electrophorus and Torpedo electroplax membranes. J Cell Biol. 1978 Mar;76(3):577–592. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Weill C. L., McNamee M. G., Valderrama R. Facets of the structures of acetylcholine receptors from Electrophorus and Torpedo. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:203–210. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson E., Eaker D., Ponterius G. Modification of amino groups in Naja naja neurotoxins and the preparation of radioactive derivatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90275-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klymkowsky M. W., Stroud R. M. Immunospecific identification and three-dimensional structure of a membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 5;128(3):319–334. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Gullick W., Conti-Tronconi B., Ellisman M. Proteolytic nicking of the acetylcholine receptor. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4791–4795. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Merlie J., Yogeeswaran G. Biochemical properties of acteylcholine receptor subunits from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4465–4470. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson N. M., Hall Z. W. In situ labeling of Torpedo and rat muscle acetylcholine receptor by a photoaffinity derivative of alpha-bungarotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1698–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel E., Potter L. T. Ultrastructure of isolated membranes of Torpedo electric tissue. Brain Res. 1973 Jul 27;57(2):508–517. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K., Vandlen R., Bode J., Duguid J., Raftery M. A. Characterization of acetylcholine receptor-rich and acetylcholinesterase-rich membrane particles from Torpedo californica electroplax. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Mar;167(1):138–144. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90449-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Karlin A. Molecular weight in detergent solution of acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1978 May 30;17(11):2035–2038. doi: 10.1021/bi00604a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluth J. Synaptic membrane structure in Torpedo electric organ. J Neurocytol. 1975 Dec;4(6):697–712. doi: 10.1007/BF01181631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Isla B. A., Hucho F. Acetylcholine receptor: SH group reactivity as indicator of conformational changes and functional states. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):65–69. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsetlin V. I., Karlsson E., Arseniev A. S., Utkin Y. N., Surin A. M., Pashkov V. S., Pluzhnikov K. A., Ivanov V. T., Bystrov V. F., Ovchinnikov Y. A. EPR and fluorescence study of interaction of Naja naja oxiana neurotoxin II and its derivatives with acetylcholine receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata. FEBS Lett. 1979 Oct 1;106(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80692-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walkinshaw M. D., Saenger W., Maelicke A. Three-dimensional structure of the "long" neurotoxin from cobra venom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2400–2404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland G., Taylor P. Ligand specificity of state transitions in the cholinergic receptor: behavior of agonists and antagonists. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Mar;15(2):197–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise D. S., Karlin A., Schoenborn B. P. An analysis by low-angle neutron scattering of the structure of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica in detergent solution. Biophys J. 1979 Dec;28(3):473–496. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85194-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise D. S., Schoenborn B. P., Karlin A. Structure of acetylcholine receptor dimer determined by neutron scattering and electron microscopy. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):4124–4126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzemann V., Raftery M. A. Affinity directed crosslinking of acetylcholine receptor polypeptide components in post-synaptic membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 29;85(2):623–631. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91208-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



