Abstract
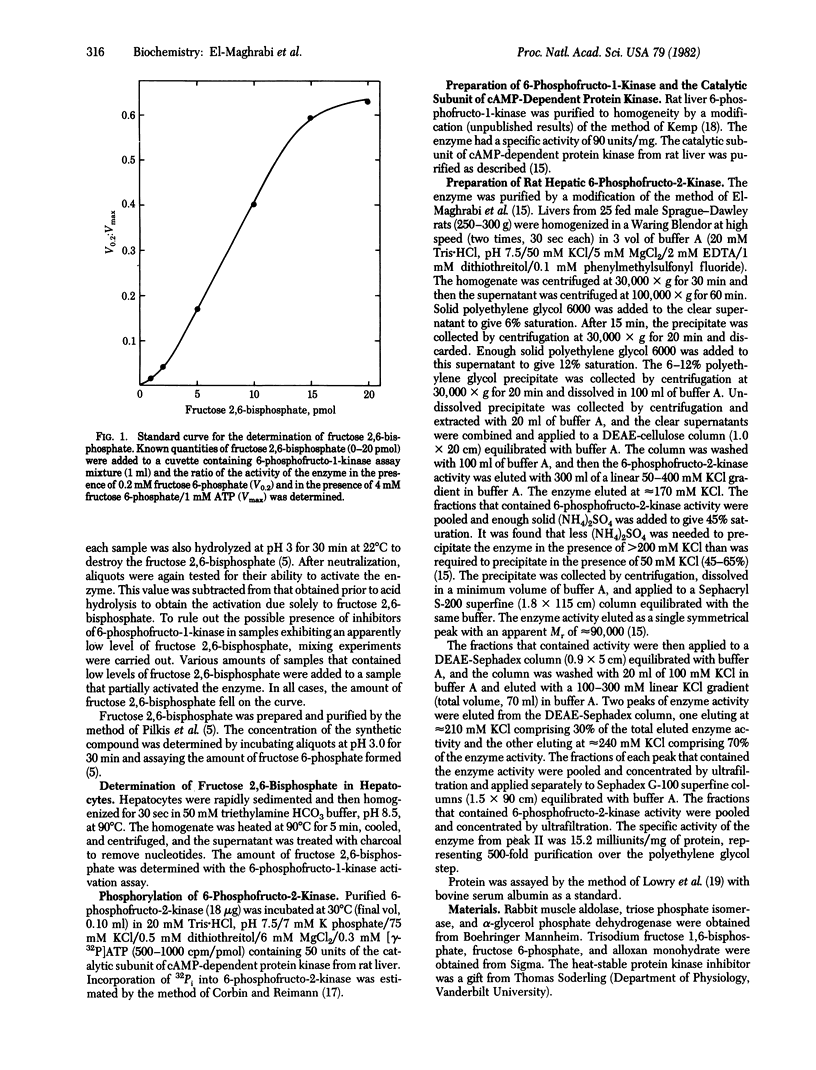
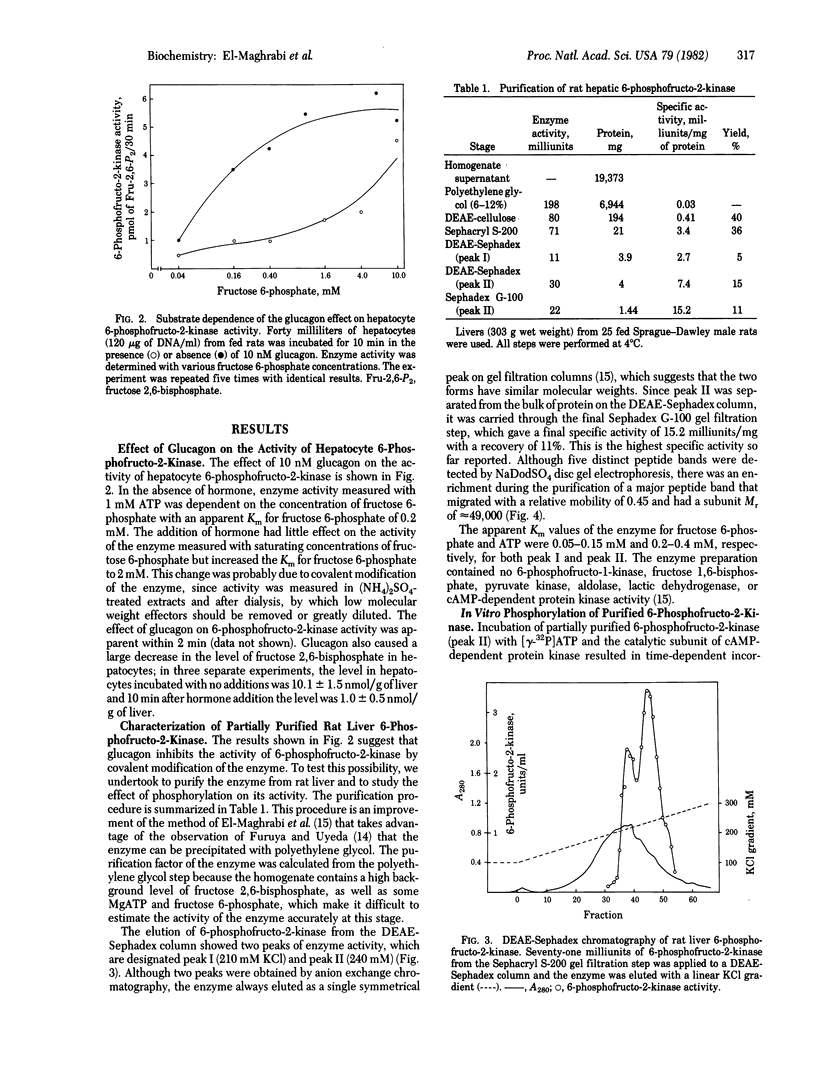
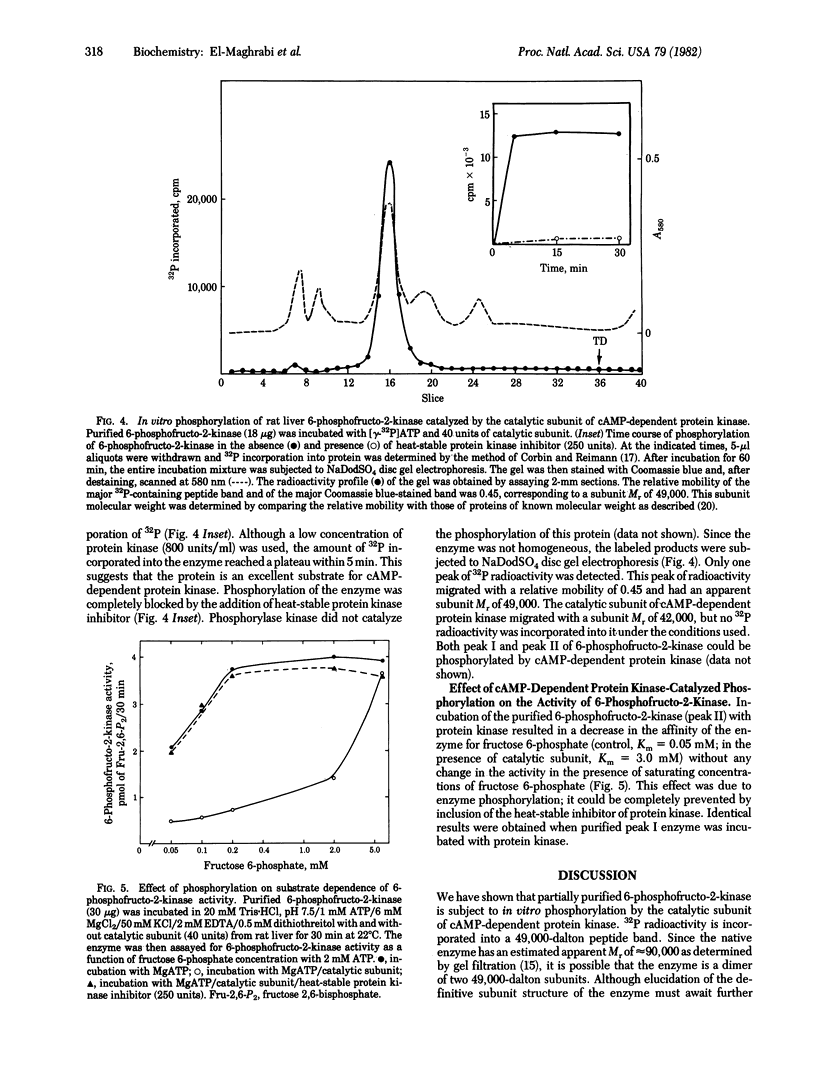
Addition of glucagon to isolated rat hepatocytes resulted in inhibition of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (ATP:D-fructose-6-phosphate-2-phosphotransferase) activity in extracts of the cells and in a decrease in the intracellular level of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. The effect on 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase was characterized by a decrease in the affinity of the enzyme for fructose 6-phosphate. To investigate the mechanism of action of glucagon, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase from rat liver was partially purified by polyethylene glycol precipitation, DEAE-cellulose chromatography, (NH4)2SO4 fractionation, Sephacryl S-200 gel filtration, DEAE-Sephadex chromatography, and Sephadex G-100 gel filtration. Incubation of the purified enzyme with the catalytic subunit of the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from rat liver and [gamma-32P]ATP resulted in 32P incorporation into a protein with a subunit Mr of 49,000 as determined by NaDodSO4 disc gel electrophoresis. Associated with this phosphorylation was an inhibition of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase activity that was also characterized by a decrease in the affinity of the enzyme for fructose-6-phosphate. Both the phosphorylation and the inhibition of the purified 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase were blocked by addition of the heat-stable protein kinase inhibitor. It is concluded that the glucagon-induced decrease in fructose 2,6-bisphosphate levels observed in isolated hepatocytes is due, at least in part, to cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation and inhibition of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Claus T. H., Schlumpf J. R., el-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis J., Pilkis S. J. Mechanism of action of glucagon on hepatocyte phosphofructokinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6501–6505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claus T. H., Schlumpf J., Maghrabi M. R., McGrane M., Pilkis S. J. Glucagon stimulation of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase phosphorylation in rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):716–723. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80234-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claus T. H., Schlumpf J., Pilkis J., Johnson R. A., Pilkis S. J. Evidence for a new activator of rat liver phosphofructokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jan 30;98(2):359–366. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90848-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Reimann E. M. Assay of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:287–290. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunaway G. A., Jr, Weber G. Rat liver phosphofructokinase isozymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jun;162(2):620–628. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90224-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Maghrabi M. R., Claus T. H., Pilkis J., Pilkis S. J. Partial purification of a rat liver enzyme that catalyzes the formation of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Aug 14;101(3):1071–1077. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91858-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya E., Uyeda K. A novel enzyme catalyzes the synthesis of activation factor from ATP and D-fructose-6-P. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7109–7112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya E., Uyeda K. An activation factor of liver phosphofructokinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5861–5864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp R. G. Phosphofructokinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:71–77. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mörikofer-Zwez S., Stoecklin F. B., Walter P. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase in rat liver cytosol: activation after glucagon treatment in vivo and inhibition by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jul 16;101(1):104–111. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., El-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis J., Claus T. H., Cumming D. A. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. A new activator of phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3171–3174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., El-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis J., Claus T. Inhibition of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3619–3622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. S., Furuya E., Uyeda K. Regulation of fructose 2,6-P2 concentration in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun;100(4):1673–1679. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90711-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. S., Uyeda K. Changes in the concentration of activation factor for phosphofructokinase in hepatocytes in response to glucose and glucagon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Dec 31;97(4):1535–1540. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Inhibition of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by fructose 2,6-biphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2861–2863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Phosphofructokinase 2: the enzyme that forms fructose 2,6-bisphosphate from fructose 6-phosphate and ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Aug 14;101(3):1078–1084. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91859-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Synthesis of a stimulator of phosphofructokinase, most likely fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, from phosphoric acid and fructose 6-phosphoric acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 31;96(4):1524–1531. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91347-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, the probably structure of the glucose- and glucagon-sensitive stimulator of phosphofructokinase. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):897–901. doi: 10.1042/bj1920897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


