Abstract
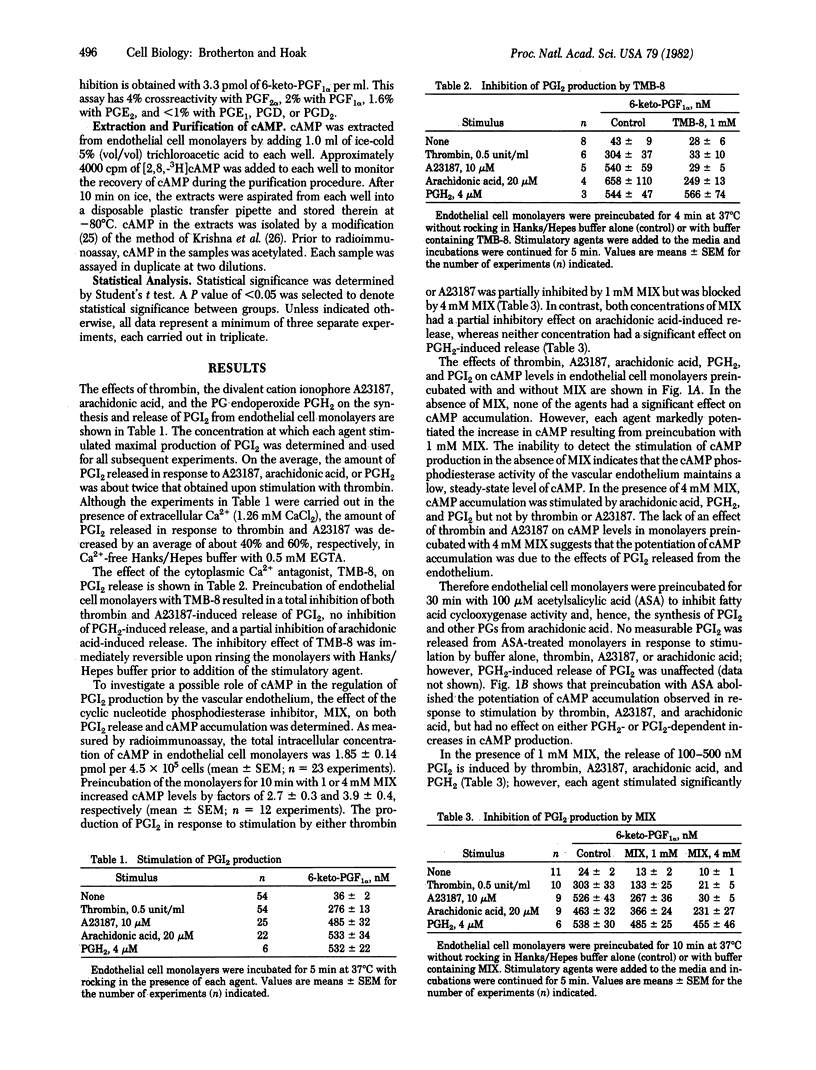
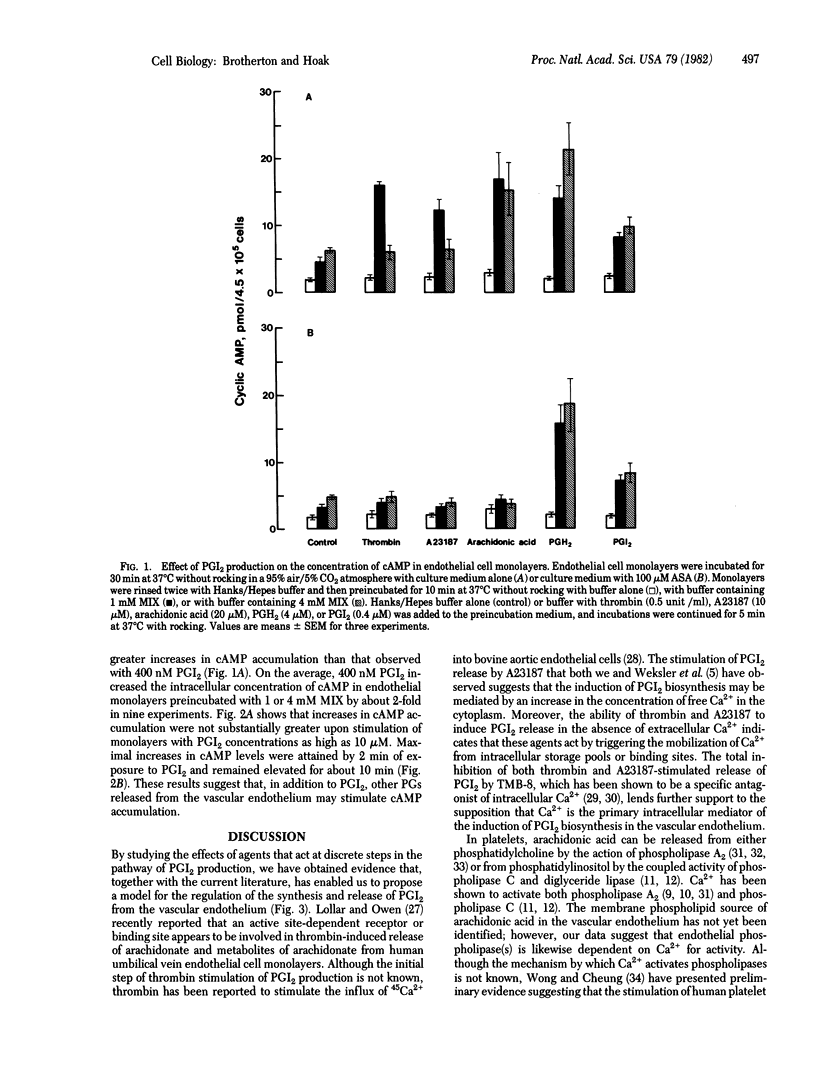
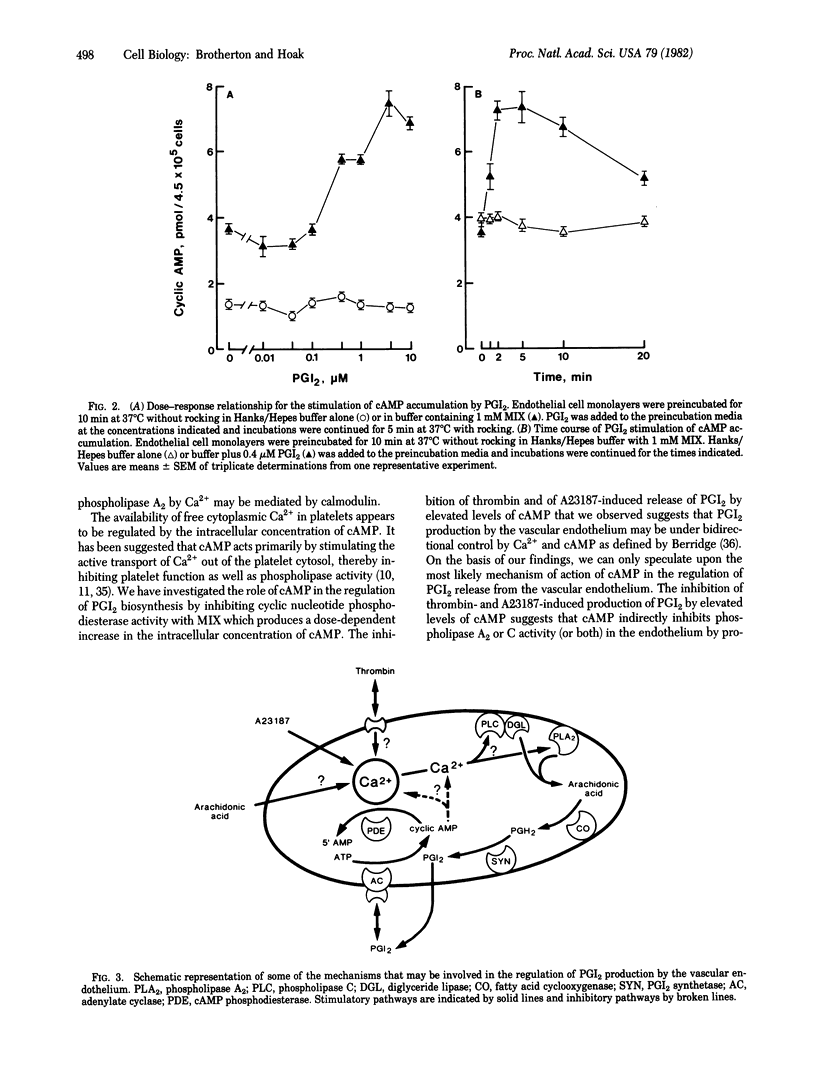
Incubation of primary monolayer cultures of human umbilical vein endothelial cells with buffer, thrombin (0.5 unit/ml), ionophore A23187 (10 microM), arachidonic acid (20 microM), prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) (4 microM) resulted in prostacyclin (PGI2) production in nanomolar quantities to the extent of 36 +/- 2, 276 +/- 13, 485 +/- 32, 533 +/- 22, and 532 +/- 22, respectively, as measured by radioimmunoassay of 6-keto-PGF alpha. Preincubation of the endothelium with 1 mM 8-(N,N-diethylamino)-octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate, an antagonist of cytoplasmic Ca2+, or with 4 mM 1-methyl-3-isobutylxanthine (MIX), an inhibitor of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity, blocked PGI2 release induced by thrombin or A23187, decreased arachidonic acid-induced release by approximately 50%, but had no effect on PGH2-induced release. Radioimmunoassay of cAMP in the endothelium showed that the basal level (1.85 +/- 0.14 pmol of cAMP per 4.5 x 10(5) cells) was increased by an average of 3.9-fold with 4 mM MIX. PGI2 (0.4 microM) had no significant effect on cAMP levels in the absence of MIX, but caused a 2-fold increase with 4 mM MIX. The findings suggest that: (i) the stimulation of PGI2 biosynthesis is mediated by Ca2+, (ii) increased cAMP inhibits PGI2 production, and (iii) cAMP phosphodiesterase activity modulates PGI2-induced increases in the intracellular concentration of cAMP.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger N. L., Becherer P. R., Majerus P. W. Characterization of prostacyclin synthesis in cultured human arterial smooth muscle cells, venous endothelial cells and skin fibroblasts. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):967–974. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Kennerly D. A., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Diglyceride lipase: a pathway for arachidonate release from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3238–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. The interaction of cyclic nucleotides and calcium in the control of cellular activity. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;6:1–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bills T. K., Smith J. B., Silver M. J. Selective release of archidonic acid from the phospholipids of human platelets in response to thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI108745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonassisi V., Venter J. C. Hormone and neurotransmitter receptors in an established vascular endothelial cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1612–1616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charo I. F., Feinman R. D., Detwiler T. C. Inhibition of platelet secretion by an antagonist of intracellular calcium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1462–1467. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czervionke R. L., Hoak J. C., Fry G. L. Effect of aspirin on thrombin-induced adherence of platelets to cultured cells from the blood vessel wall. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):847–856. doi: 10.1172/JCI109197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czervionke R. L., Smith J. B., Fry G. L., Hoak J. C., Haycraft D. L. Inhibition of prostacyclin by treatment of endothelium with aspirin. Correlation with platelet adherence. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):1089–1092. doi: 10.1172/JCI109379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czervionke R. L., Smith J. B., Hoak J. C., Fry G. L., Haycraft D. L. Use of a radioimmunoassay to study thrombin-induced release of PGI2 from cultured endothelium. Thromb Res. 1979;14(4-5):781–786. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amore P., Shepro D. Stimulation of growth and calcium influx in cultured, bovine, aortic endothelial cells by platelets and vasoactive substances. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Aug;92(2):177–183. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040920206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen A., Cohen P. Patterns of fatty acid release from endogenous substrates by human platelet homogenates and membranes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9342–9347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein M. B., Becker E. L., Fraser C. Thrombin, collagen and A23187 stimulated endogenous platelet arachidonate metabolism: differential inhibition by PGE1, local anesthetics and a serine-protease inhibitor. Prostaglandins. 1977;14(6):1075–1093. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman R. R., Bunting S., Miller O. V. Modulation of human platelet adenylate cyclase by prostacyclin (PGX). Prostaglandins. 1977 Mar;13(3):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman R. R., Sun F. F., Miller O. V., Johnson R. A. Prostaglandins H1 and H2. Convenient biochemical synthesis and isolation. Further biological and spectroscopic characterization. Prostaglandins. 1977 Jun;13(6):1043–1053. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M., Davies T., Lynham J. A., McClenaghan M. D. Regulation of blood platelet function by cyclic nucleotides. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978;9:533–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Rosson G. M. Effects of adenosine on levels of adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate in human blood platelets in relation to adenosine incorporation and platelet aggregation. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;11(5):528–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins N. K., Gorman R. R. Regulation of endothelial cell cyclic nucleotide metabolism by prostacyclin. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):540–546. doi: 10.1172/JCI110064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp H. R., Oelz O., Roberts L. J., Sweetman B. J., Oates J. A., Reed P. W. Ionophores stimulate prostaglandin and thromboxane biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4251–4255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Weiss B., Brodie B. B. A simple, sensitive method for the assay of adenyl cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Oct;163(2):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käser-Glanzmann R., Jakäbovä M., George J. N., Lüscher E. F. Stimulation of calcium uptake in platelet membrane vesicles by adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate and protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 2;466(3):429–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90336-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands W. E., Samuelsson B. Phospholipid precursors of prostaglandins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 22;164(2):426–429. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Owen W. G. Evidence that the effects of thrombin on arachidonate metabolism in cultured human endothelial cells are not mediated by a high affinity receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 10;255(17):8031–8034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagodi M. H., Chiou C. Y. Pharmacological evaluation of a new Ca2+ antagonist, 8-(N,N-diethylamino)-octyl-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoate hydrochloride (TMB-8): studies in smooth muscles. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Jun;27(1):25–33. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmsten C., Granström E., Samuelsson B. Cyclic AMP inhibits synthesis of prostaglandin endoperoxide (PGG2) in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Weksler B. B., Jaffe E. A., Broekman M. J. Synthesis of prostacyclin from platelet-derived endoperoxides by cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):979–986. doi: 10.1172/JCI109967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Gryglewski R., Bunting S., Vane J. R. An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet aggregation. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):663–665. doi: 10.1038/263663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs E. A., Vane J. R. Human arterial and venous tissues generate prostacyclin (prostaglandin x), a potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation. Lancet. 1977 Jan 1;1(8001):18–20. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91655-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett W. C., Jesse R. L., Cohen P. Initiation of phospholipase A2 activity in human platelets by the calcium ion ionophore A23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 18;486(1):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Goldyne M., Granström E., Hamberg M., Hammarström S., Malmsten C. Prostaglandins and thromboxanes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:997–1029. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.005025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer A. I., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Handin R. I. Endothelial cell adenylate cyclase: activation by catecholamines and prostaglandin I2+. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 31;96(4):1640–1647. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91362-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoene N. W., Iacono J. M. The influence of phospholipase A2 on prostaglandin production in platelets. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Res. 1976;2:763–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Ogletree M. L., Lefer A. M., Nicolaou J. C. Antibodies which antagonise the effects of prostacyclin. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):64–65. doi: 10.1038/274064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateson J. E., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Effects of prostacyclin (PGX) on cyclic AMP concentrations in human platelets. Prostaglandins. 1977 Mar;13(3):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Ley C. W., Jaffe E. A. Stimulation of endothelial cell prostacyclin production by thrombin, trypsin, and the ionophore A 23187. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):923–930. doi: 10.1172/JCI109220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler B. B., Marcus A. J., Jaffe E. A. Synthesis of prostaglandin I2 (prostacyclin) by cultured human and bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3922–3926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. Y., Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin stimulates human platelet phospholipase A2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 27;90(2):473–480. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



