Abstract
Experiments were undertaken to augment the information on the lowest radiation dose rates feasible for scoring transmitted induced mutations detected by the specific-locus method in the mouse. This is the type of information most suitable for estimating genetic hazards of radiation in man. The results also aid in resolving conflicting possibilities about the relationship between mutation frequency and radiation dose rate at low dose rates. There was no statistically significant difference between mutation frequencies obtained in spermatogonia with 300 R (1 R = 2.6 x 10(-4) coulombs/kg) of gamma radiation at two different dose rates, 0.005 and 0.0007 R/min, or between either of these frequencies and data obtained earlier at dose rates of 0.8 R/min and below. This supports the view in an earlier publication by one of us (W.L.R.) that, at approximately 0.8 R/min and below, mutation frequency is independent of dose rate. Because this independence is now shown to extend over the more than 1000-fold range from 0.8 to 0.0007 R/min, it seems likely that it would hold at still lower dose rates, perhaps even to the much lower dose rates encountered in most human exposures.
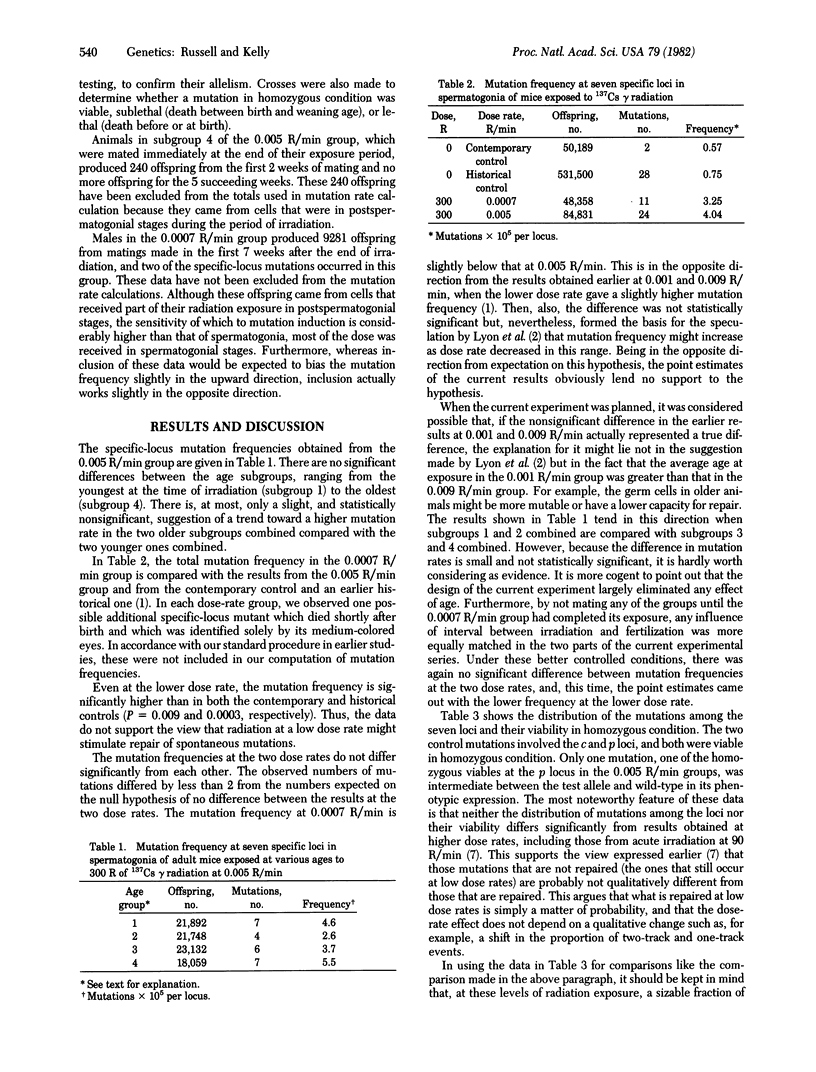
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Lyon M. F., Papworth D. G., Phillips R. J. Dose-rate and mutation frequency after irradiation of mouse spermatogonia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):101–104. doi: 10.1038/newbio238101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe H. B. "Benefit" and "harm" from exposure of vertebrate sperm to low doses of ionizing radiation. Health Phys. 1973 Aug;25(2):105–107. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197308000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL W. L. X-ray-induced mutations in mice. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:327–336. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. L., Kelly E. M. Mutation frequencies in male mice and the estimation of genetic hazards of radiation in men. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):542–544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



