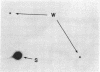
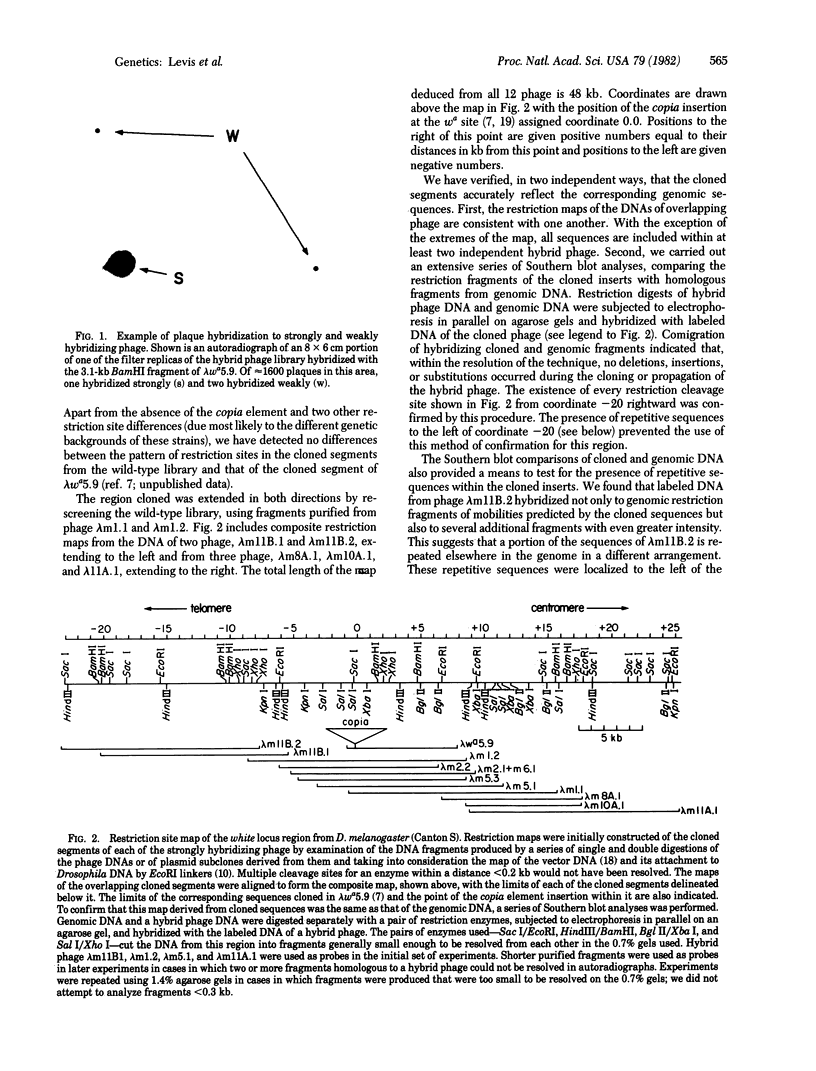
Abstract
The white locus of Drosophila melanogaster is a genetically well-characterized locus, mutations in which alter the degree of pattern of pigmentation of the eyes. Using a previously cloned DNA segment containing a portion of the white locus of a mutant allele, we have cloned and characterized the DNA of a 48-kilobase chromosomal region of the Canton S wild-type strain. We have mapped the positions, relative to restriction endonuclease cleavage sites, of several previously characterized chromosomal rearrangement breakpoints that bracket the while locus. These results define a segment of 14 kilobase that contains all of the white locus sequences necessary for the production of a wild-type eye color phenotype. By conventional criteria, no repetitive sequences are present within this 14-kilobase segment; however, we have identified an extremely weak DNA sequence homology between a portion of this segment and a chromosomal region in the vicinity of the zeste locus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M. A novel dominant mutant allele at the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster is mutable. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):519–525. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Judd B. H. A copy of the copia transposable element is very tightly linked to the Wa allele at the white locus of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90177-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Cloning of DNA sequences from the white locus of D. melanogaster by a novel and general method. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):693–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M. The Regulation of White Locus Expression: A Dominant Mutant Allele at the White Locus of DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1980 Jun;95(2):341–353. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.2.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsmuir P., Brorein W. J., Jr, Simon M. A., Rubin G. M. Insertion of the Drosophila transposable element copia generates a 5 base pair duplication. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):575–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90495-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J., Paro R. Isolation of a hybrid plasmid with homologous sequences to a transposing element of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):897–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. W., Judd B. H. Allelic pairing and gene regulation: A model for the zeste-white interaction in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1368–1372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Farrell J., Jr, Beckendorf S. K. Molecular limits on the size of a genetic locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7367–7371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T. H. SEX LIMITED INHERITANCE IN DROSOPHILA. Science. 1910 Jul 22;32(812):120–122. doi: 10.1126/science.32.812.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S., Brorein W. J., Jr, Dunsmuir P., Rubin G. M. Transposition of elements of the 412, copia and 297 dispersed repeated gene families in Drosophila. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):415–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmuson B., Montell I., Rasmuson A., Svahlin H., Westerberg B. M. Genetic instability in Drosophila melanogaster: evidence for regulation, excision and transposition at the white locus. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;177(4):567–570. doi: 10.1007/BF00272664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachat F. H., Hogness D. S. Repetitive sequences in isolated Thomas circles from Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:371–381. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorsa V., Green M. M., Beermann W. Cytogenetic fine structure and chromosomal localization of the white gene in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 12;245(141):34–37. doi: 10.1038/newbio245034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Drosophila genome organization: conserved and dynamic aspects. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:219–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausbaugh L. D., Kiefer B. I. Genetic modulation of RNA metabolism in Drosophila. III. Requirement for an rDNA-deficient X chromosome in YbbSuVar-3-mediated increases in RNA synthesis. Genetics. 1979 Oct;93(2):411–422. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Daniels D. L., Schroeder J. L., Williams B. G., Denniston-Thompson K., Moore D. D., Blattner F. R. Restriction maps for twenty-one Charon vector phages. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):401–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.401-410.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]