Abstract
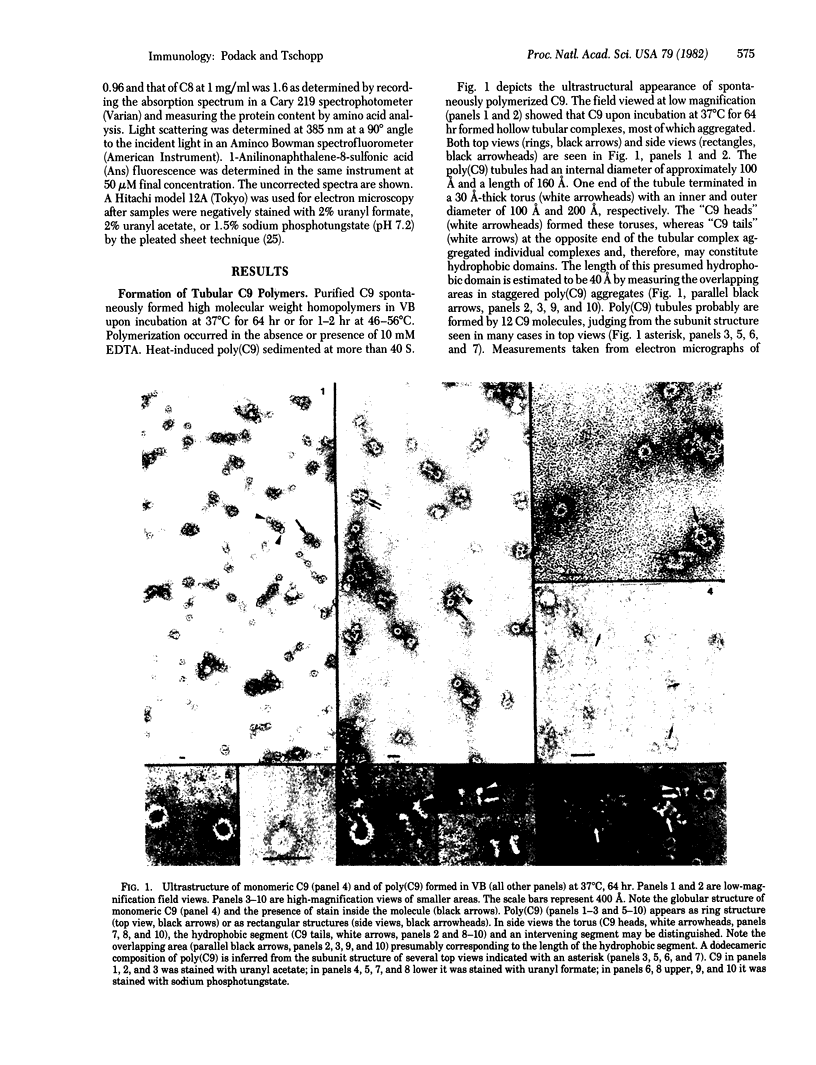
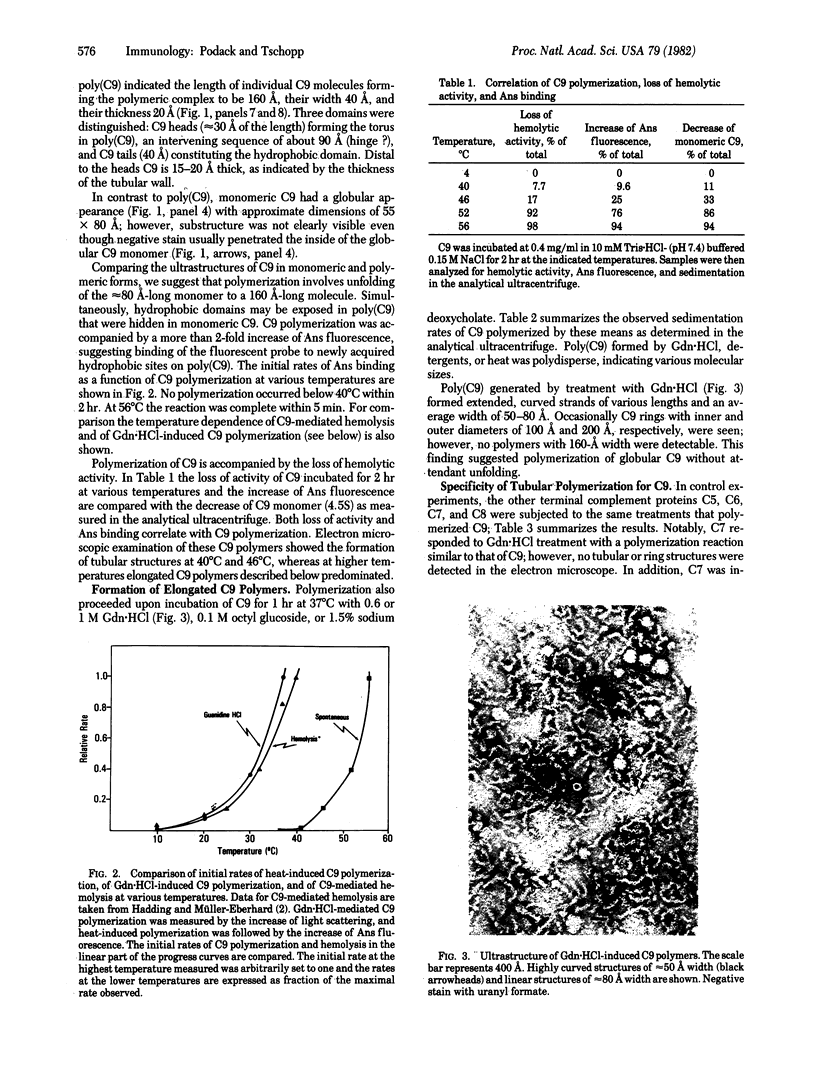
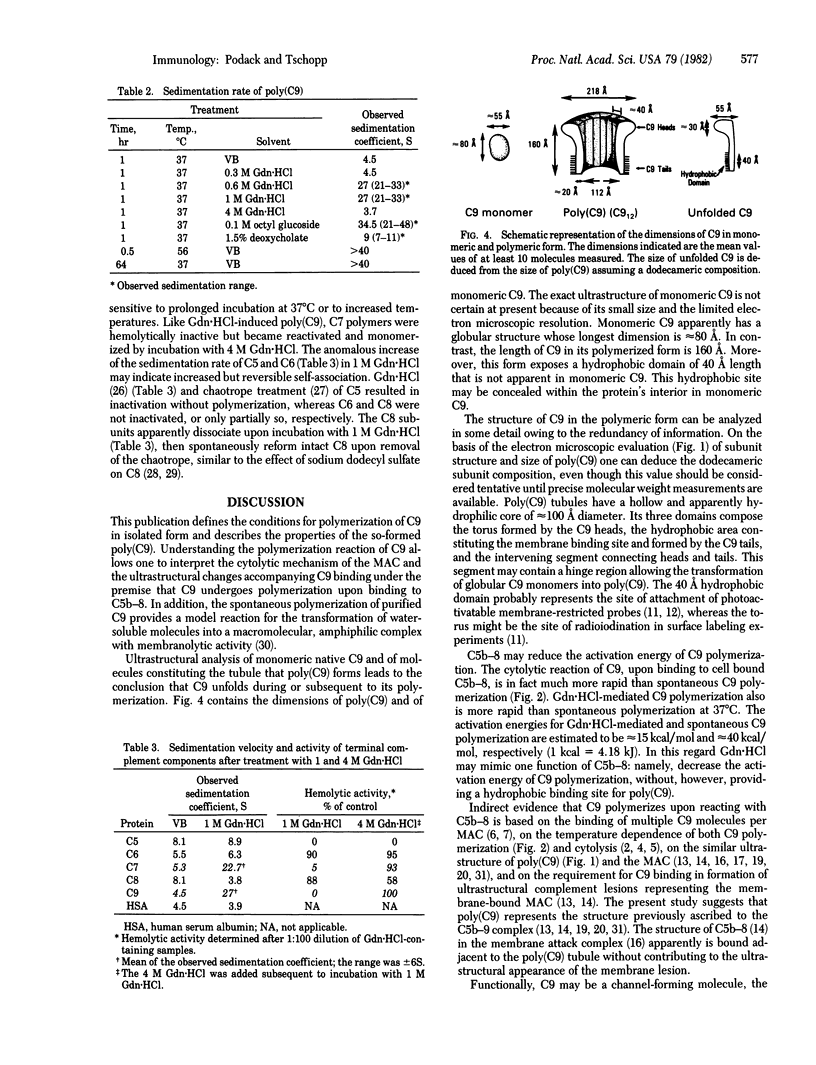
The ninth component of complement (C9) has a marked propensity to polymerize. C9 polymers [poly(C9)] formed spontaneously in Veronal-buffered saline upon incubation of purified C9 for 64 hr at 37 degrees C or within 2 hr at 46--56 degrees C. Poly(C9) formed at 37 degrees C was visualized by electron microscopy as a tubular structure with an internal diameter of 110 A and a length of 160 A. Its ultrastructure suggested a dodecameric composition and resembled that of the membrane attack complex of complement. The wider end of the tubular structure was formed by an approximately 30-A-thick torus with inner and outer diameters of 110 A and 220 A, respectively. Because the dimensions of C9 within poly(C9) were 160 x 55 A (maximal) and 20 A (minimal) and because monomeric C9 has dimensions of approximately 80 x 55 A, it is proposed that monomeric C9 unfolds during polymerization into tubules. Polymerization also occurred upon treatment of C9 for 1 hr at 37 degrees C with 0.6 M guanidine . HCl, 0.1 M octyl glucoside, or 1.5% sodium deoxycholate. Guanidine . HCl-induced C9 polymers consisted of elongated highly curved strands 55--80 A wide, suggesting that these polymers were formed by globular C9 that had not unfolded.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Evidence for a two-domain structure of the terminal membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5872–5876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Molecular weight of the membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement: characterization of the terminal complex as a C5b-9 monomer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1818–1822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The ninth component of human complement: purification and physicochemical characterization. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1291–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Podack E. R., Halverson C. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C5b-9 dimer: isolation from complement lysed cells and ultrastructural identification with complement-dependent membrane lesions. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):448–458. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Borsos T. Studies on the terminal stages of immune hemolysis. V. Evidence that not all complement-produced transmembrane channels are equal. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):71–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Gee A. P., Borsos T. Studies on the terminal stages of immune hemolysis. VI. Osmotic blockers of differing Stokes' radii detect complement-induced transmembrane channels of differing size. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dourmashkin R. R. The structural events associated with the attachment of complement components to cell membranes in reactive lysis. Immunology. 1978 Aug;35(2):205–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser A. F., Kolb W. P., Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular reorganization of lipid bilayers by complement: a possible mechanism for membranolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1410–1414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giavedoni E. B., Chow Y. M., Dalmasso A. P. The functional size of the primary complement lesion in resealed erythrocyte membrane ghosts. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadding U., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The ninth component of human complement: isolation, description and mode of action. Immunology. 1969 Jun;16(6):719–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer C. H., Wirtz G. H., Renfer L., Gresham H. D., Tack B. F. Large scale isolation of functionally active components of the human complement system. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3995–4006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu V. W., Esser A. F., Podack E. R., Wisnieski B. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement: photolabeling reveals insertion of terminal proteins into target membrane. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):380–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klob W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack mechanism of complement: the three polypeptide chain structure of the eigth component (C8). J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1131–1139. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Haxby J. A., Arroyave C. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Molecular analysis of the membrane attack mechanism of complement. J Exp Med. 1972 Mar 1;135(3):549–566. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Mode of action of human C9: adsorption of multiple C9 molecules to cell-bound C8. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):479–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M. Mechanism of cytolysis by complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2954–2958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels D. W., Abramovitz A. S., Hammer C. H., Mayer M. M. Increased ion permeability of planar lipid bilayer membranes after treatment with the C5b-9 cytolytic attack mechanism of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2852–2856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monahan J. B., Sodetz J. M. Binding of the eighth component of human complement to the soluble cytolytic complex is mediated by its beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10579–10582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Boyle M. D., Borsos T. Evidence for a temperature-dependent and temperature-independent pathway in the generation of complement-mediated transmembrane channels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):406–412. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Biesecker G., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The C5b-6 complex: reaction with C7, C8, C9. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):484–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Biesecker G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement: generation of high-affinity phospholipid binding sites by fusion of five hydrophilic plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):897–901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Esser A. F., Biesecker G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement: a structural analysis of its assembly. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):301–313. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Esser A. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Structural similarities between C6 and C7 of human complement. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1071–1077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement. Evidence for its dimeric structure based on hybrid formation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3145–3148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Stoffel W., Esser A. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Membrane attack complex of complement: distribution of subunits between the hydrocarbon phase of target membranes and water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4544–4548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Mayer M. M. Life-span and size of the trans-membrane channel formed by large doses of complement. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2281–2287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommel F. A., Mayer M. M. Studies of guinea pig complement component C9: reaction kinetics and evidence that lysis of EAC1-8 results from a single membrane lesion caused by one molecule of C9. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegan G. W., Smith C. A., Schumaker V. N. Changes in quaternary structure of IgG upon reduction of the interheavy-chain disulfide bond. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):907–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simone C. B., Henkart P. Permeability changes induced in erthrocyte ghost targets by antibody-dependent cytotoxic effector cells: evidence for membrane pores. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):954–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Lauf P. K. Analysis of solute diffusion across the C5b-9 membrane lesion of complement: evidence that individual C5b-9 complexes do not function as discrete, uniform pores. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2617–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Lauf P. K. Steady-state analysis of tracer exchange across the C5b-9 complement lesion in a biological membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5669–5673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steckel E. W., York R. G., Monahan J. B., Sodetz J. M. The eighth component of human complement. Purification and physicochemical characterization of its unusual subunit structure. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11997–12005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolfi R. L. Immune lytic transformation: a state of irreversible damage generated as a result of the reaction of the eighth component in the guinea pig complement system. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):46–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranum-Jensen J., Bhakdi S., Bhakdi-Lehnen B., Bjerrum O. J., Speth V. Complement lysis: the ultrastructure and orientation of the C5b-9 complex on target sheep erythrocyte membranes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(1):45–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Podack E. R. Membranolysis by the ninth component of human complement. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):1409–1414. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91981-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware C. F., Wetsel R. A., Kolb W. P. Physicochemical characterization of fluid phase (SC5b-9) and membrane derived (MC5b-9) attack complexes of human complement purified by immunoadsorbent affinity chromatography or selective detergent extraction. Mol Immunol. 1981 Jun;18(6):521–531. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel R. A., Jones M. A., Kolb W. P. Immunoadsorbent affinity purification of the fifth component (C5) of human complement and development of a highly sensitive hemolytic assay. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(3-4):319–335. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]