Abstract
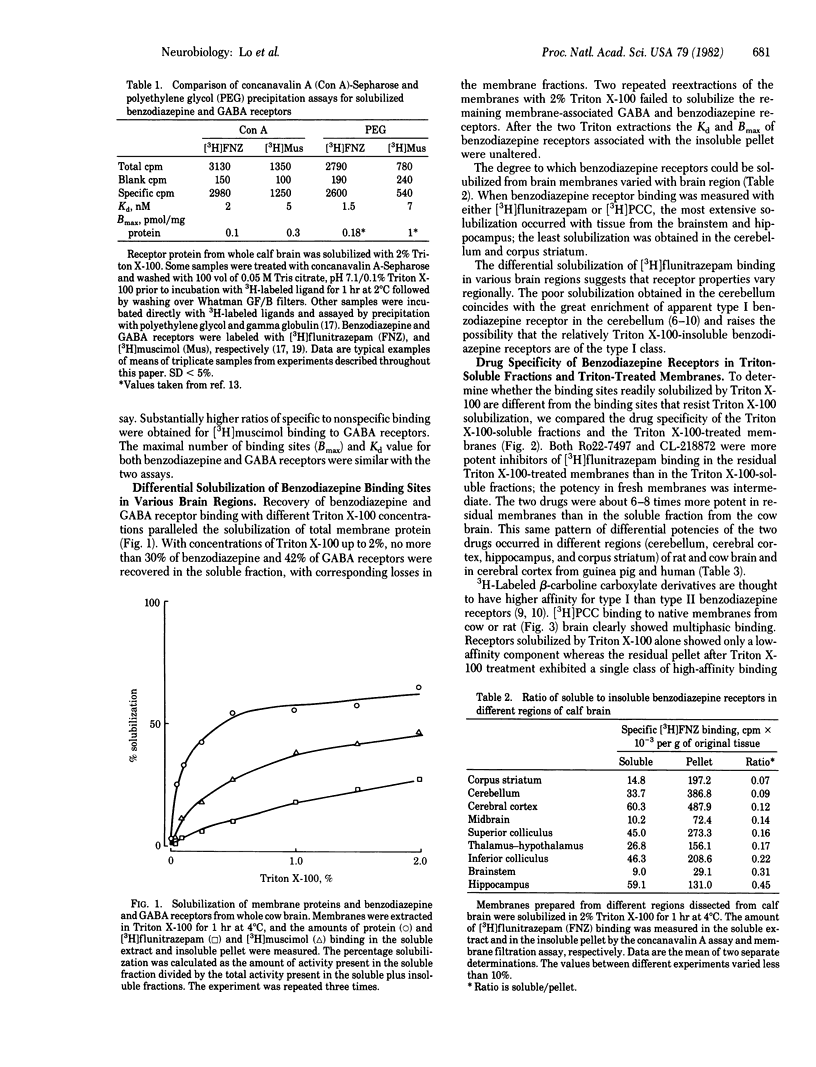
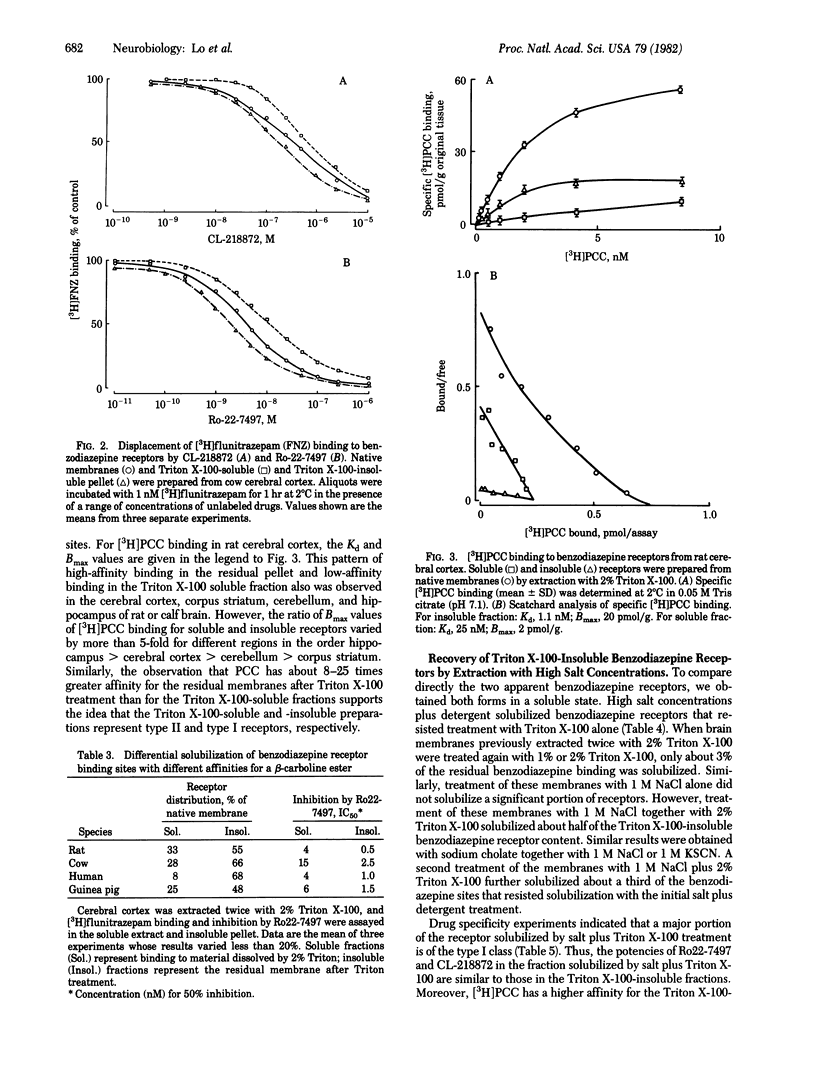
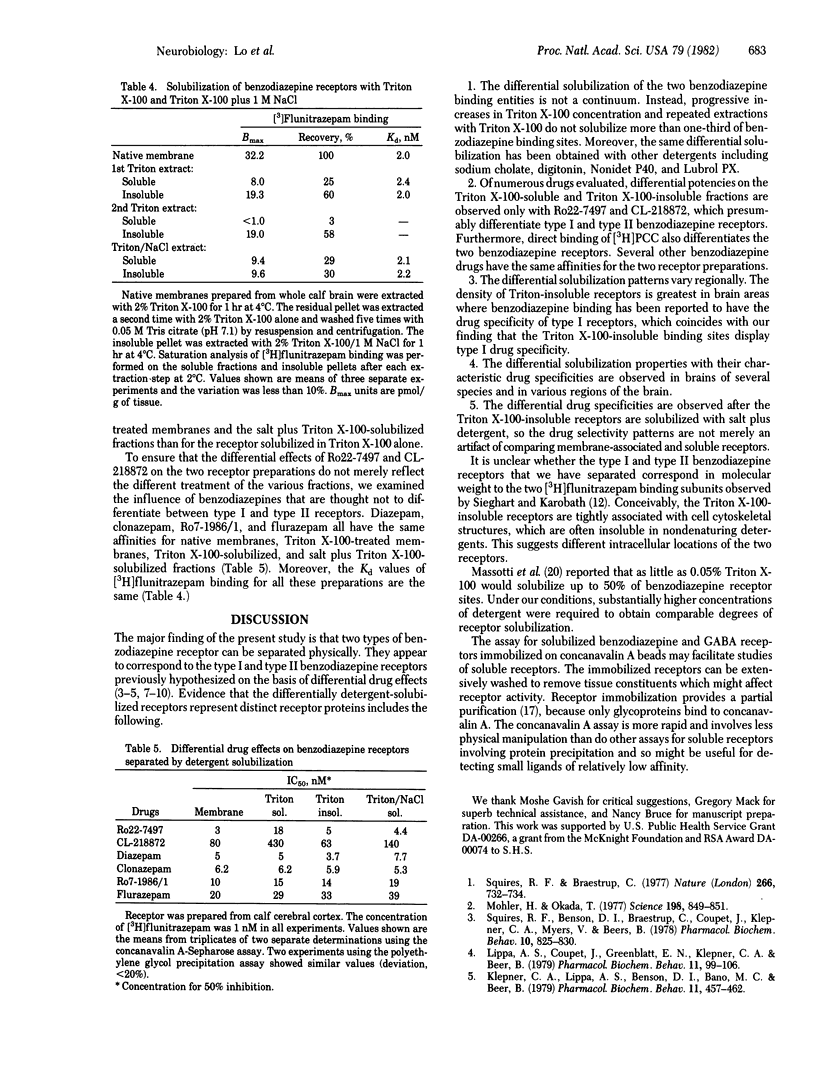
Two distinct benzodiazepine receptors are solubilized differentially by various detergents. The receptor sites that resist solubilization, designated type I, are most highly concentrated in the cerebellum and corpus striatum whereas the more readily solubilized receptors, type II, are most enriched in the hippocampus. The type I receptors display higher affinity for beta-carboline esters and a triazolopyridazine whereas several benzodiazepines do not differentiate the two receptors. The type I receptors can be solubilized with 2% Triton X-100/1 M NaCl; they retain the same drug specificity as in the particulate state.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano T., Ogasawara N. Solubilization of the benzodiazepine receptor from rat brain. Life Sci. 1980 Feb 25;26(8):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90236-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayub Khan Yousufi M., Thomas J. W., Tallman J. F. Solubilization of benzodiazepine binding site from rat cortex. Life Sci. 1979 Jul 30;25(5):463–469. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90580-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Nielsen M., Olsen C. E. Urinary and brain beta-carboline-3-carboxylates as potent inhibitors of brain benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2288–2292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Nielsen M. [3H]Propyl beta-carboline-3-carboxylate as a selective radioligand for the BZ1 benzodiazepine receptor subclass. J Neurochem. 1981 Aug;37(2):333–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlert F. J., Roeske W. R., Yamamura H. I. Multiple benzodiazepine receptors and their regulation by gamma-aminobutyric acid. Life Sci. 1981 Jul 20;29(3):235–248. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish M., Chang R. S., Snyder S. H. Solubilization of histamine H-1, GABA and benzodiazepine receptors. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 27;25(9):783–789. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish M., Snyder S. H. Soluble benzodiazepine receptors: GABAergic regulation. Life Sci. 1980 Feb 25;26(8):579–582. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90231-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish M., Snyder S. H. gamma-Aminobutyric acid and benzodiazepine receptors: copurification and characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1939–1942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Toffano G., Costa E. An endogenous protein modulates the affinity of GABA and benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):553–555. doi: 10.1038/275553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klepner C. A., Lippa A. S., Benson D. I., Sano M. C., Beer B. Resolution of two biochemically and pharmacologically distinct benzodiazepine receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1979 Oct;11(4):457–462. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(79)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang B., Barnard E. A., Chang L. R., Dolly J. O. Putative benzodiazepine receptor: a protein solubilised from brain. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 1;104(1):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippa A. S., Coupet J., Greenblatt E. N., Klepner C. A., Beer B. A synthetic non-benzodiazepine ligand for benzodiazepine receptors: a probe for investigating neuronal substrates of anxiety. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1979 Jul;11(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(79)90304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massotti M., Guidotti A., Costa E. Characterization of benzodiazepine and gamma-aminobutyric recognition sites and their endogenous modulators. J Neurosci. 1981 Apr;1(4):409–418. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-04-00409.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nexł E., Hock R. A., Hollenberg M. D. Lectin-agarose immobilization, a new method for detecting soluble membrane receptors. Application to studies with epidermal growth factor-urogastrone and transcobalamin-II. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8740–8743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M., Braestrup C. Ethyl beta-carboline-3-carboxylate shows differential benzodiazepine receptor interaction. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):606–607. doi: 10.1038/286606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W., Karobath M. Molecular heterogeneity of benzodiazepine receptors. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):285–287. doi: 10.1038/286285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Benson D. I., Braestrup C., Coupet J., Klepner C. A., Myers V., Beer B. Some properties of brain specific benzodiazepine receptors: new evidence for multiple receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1979 May;10(5):825–830. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(79)90341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Brastrup C. Benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):732–734. doi: 10.1038/266732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Niehoff D., Kuhar M. J., Beer B., Lippa A. S. Multiple benzodiazepine receptor localization by light microscopic radiohistochemistry. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Feb;216(2):425–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


